DL-Ephedrine hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:134-71-4
- Empirical Formula: C10H16ClNO
- Molecular Weight: 201.69
- MDL number: MFCD00012626
- EINECS: 205-153-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
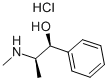
What is DL-Ephedrine hydrochloride ?
Description
Ephedrine is an alkaloid, which is from dry grass stems of ephedra plants such as ephedra, zhong ephedra, or ephedra. Ephedra is an herb recorded in “Chinese Pharmacopoeia,” which can be used for sweating and cold, adjustment of lung function, asthma, and swelling. Ephedrine can treat cold, chest tightness, bronchial asthma, and so on. Ephedra was used as a drug in China for more than 2000 years, which was recorded in history books of materia medica. Ephedra is also known as Longsa recorded in the book Shen Nong’s Herbal Classic of Materia Medica, Bixiang recorded in the book Another record by famous record, and Gougu recorded in the book Guang Ya. Ephedra was firstly recorded in the book Shen Nong’s Classic of Materia Medica.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Physical properties
Appearance: a white needle-like crystal or crystalline powder, odorless, and tastes bitter. Solubility: soluble in water and can be dissolved in ethanol but insoluble in chloroform or ether. Melting point: 217–220 °C.
History
In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), ephedrine and pseudoephedrine are main active ingredients in “herbal ephedra” . Organic chemist, Changi Changyi (1844– 1929), from Japan first isolated ephedrine from the herb “Shuanghui Ephedra” in 1885 . Ephedrine was successfully synthesized by chemist Ernst Sp?th from Austria (1886–1946) in 1920 . Kehui Chen (1898–1988) and its co-colleague Carl F. Schmidt extracted ephedrine from ephedra in 1923 and then clarified the pharmacological effects of ephedrine, which attracted the attention from Europe and the United States. Ephedrine was approved in clinical practice by the FDA of the United States. Structure of ephedrine was analyzed by Changi Changyi in 1926.
The Uses of DL-Ephedrine hydrochloride
α- and β-Adrenergic agonist. Bronchodilator.
The Uses of DL-Ephedrine hydrochloride
bronchodilator, cardiac stimulant
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmacology
Ephedrine has a similar effect with adrenaline. Ephedrine can bind α, β receptors and activate the receptor as adrenaline. Ephedrine makes the adrenergic nerve endings release medium and indirectly play the role of adrenaline. Ephedrine is stable and its effect is weaker than adrenaline, and the central excitatory effect is more obvious. Ephedrine can relax bronchial smooth muscle but less durable than adrenaline. Ephedrine can also relieve bronchial spasm, excite the heart, enhance myocardial contractility, and speed up the heart rate. However, its role in increasing the heart rate may be weakened by the vagus nerve excitement caused by increased blood pressure . Ephedrine accelerates heart rate and increases cardiac contractility by stimulating the beta receptor. Ephedrine stimulates the alpha receptor and contracts the arterial effect, but the contraction of the rabbit aorta is dominated by direct action. In recent years, ephedra has been found to have a role inhibiting the formation of acute blood clotting, promote fat synthesis in fat, and scavenge oxygenfree radicals.
Clinical Use
In clinical practice, ephedrine hydrochloride was used for the treatment of bronchial asthma, hypotension, central excitation , and toxicity by morphine and barbiturate. Ephedrine hydrochloride was also used to eliminate nasal mucosal congestion. Drug tolerance can occur quickly when ephedrine hydrochloride was used often in a short time. Ephedrine hydrochloride can also be used for hypotension and chronic hypotension caused by subarachnoid anesthesia or epidural anesthesia .
Side Effects
The side effects of ephedrine hydrochloride are anxiety, insomnia, palpitations, sweating, and other symptoms by central excitement caused by the long-term use of large doses which can be cured by hypnotic sedative drugs. Acute drug tolerance can be induced by repeated use in short time.
Safety Profile
Poison by subcutaneous, intravenous, andintraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects: cardac changes, nausea or vomiting, sweating. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of HCl and NOx. See also EPHEDRINE.
Properties of DL-Ephedrine hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 216-220 °C(lit.) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | H2O: soluble5%, clear, colorless |
| Water Solubility | 250g/L at 20℃ |
| Merck | 13,3639 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 134-71-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Racephedrine hydrochloride (134-71-4) |
Safety information for DL-Ephedrine hydrochloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for DL-Ephedrine hydrochloride
DL-Ephedrine hydrochloride manufacturer
New Products
3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Iodophenylacetic acid Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine Pivalic anhydride,98% Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride, 98% Glyoxylic acid solution, 50% in water tert-Butyl glycinate,97% 4-Ethoxybenzoic acid, 99% Sodium 1-octanesulfonate monohydrate 7-Ethyl Tryptophol 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) 5-Cyanophthalide 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 3-Methoxybenzonitrile Dibenzoyl Peroxide 4-Methoxybenzonitrile Titanium Dioxide Chloral PentachlorobenzonitrileRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
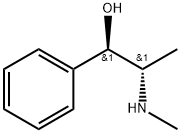

You may like
-
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 -
 Avibactam INT 1View Details
Avibactam INT 1View Details
1416134-48-9 -
 AvibactamView Details
AvibactamView Details
1416134-49-0 -
 Avibactam sodium seriesView Details
Avibactam sodium seriesView Details
1192651-49-2 -
 Avibactam seriesView Details
Avibactam seriesView Details
1192651-80-1 -
 Avibactam Sodium SaltView Details
Avibactam Sodium SaltView Details
1192491-61-4 -
 Avibactam intermediateView Details
Avibactam intermediateView Details
1171080-45-7 -
 Relibatan intermediateView Details
Relibatan intermediateView Details
1416134-63-8
