diphenylpyraline
- CAS NO.:147-20-6
- Empirical Formula: C19H23NO
- Molecular Weight: 281.39202
- MDL number: MFCD00242657
- EINECS: 2056867
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-28 16:00:23
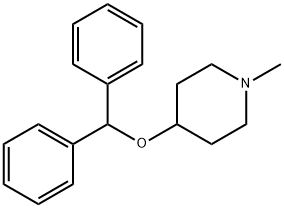
What is diphenylpyraline?
Absorption
Well absorbed after oral administration.
Originator
Diafen,Riker,US,1955
The Uses of diphenylpyraline
Diphenylpyraline is an H1 receptor antagonist (an antihistamine), and is commonly prescribed to treat allergic and vasomotor rhinitis. There is also some research being conducted on diphenylpyraline derivatives to determine their antimycobacterial and antifungal activity.
Indications
For use in the treatment of allergic rhinitis, hay fever, and allergic skin disorders.
Background
Diphenylpyraline is an antihistamine. Antihistamines used in the treatment of allergy act by competing with histamine for H 1-receptor sites on effector cells. Antihistamines prevent, but do not reverse, responses mediated by histamine alone. Antihistamines antagonize, in varying degrees, most of the pharmacological effects of histamine, including urticaria and pruritus.
Definition
ChEBI: Diphenylpyraline is a member of the class of piperidines that is the benzhydryl ether derivative of 1-methyl-4-hydroxypiperidine. A sedating antihistamine, it is used as the hydrochloride for the symptomatic relief of allergic conditions including rhinitis and hay fever, and in pruritic skin disorders. It is also used as the teoclate salt (piprinhydrinate) as an ingredient in compound preparations for the symptomatic relief of coughs and the common cold. It has a role as a H1-receptor antagonist and a cholinergic antagonist. It is a member of piperidines and a tertiary amine.
Preparation
Diphenylpyraline synthesis via coupling of 4-hydroxy-1-methylpiperidine with benzhydrylbromide.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 46 grams of 1-methyl-4-piperidinol (0.4 mol), 49.4 grams of
benzhydryl
omide (0.2 mol) and 100 ml of xylene was refluxed for
approximately 24 hours. The reaction mixture separated into two phases with
the upper phase containing the desired ether compound dissolved in xylene.
The lower phase consisted of the hydro
omide salt of the excess 1-methyl-4-
piperidinol. The upper phase was separated from the lower phase and the
desired benzhydryl ether recovered in the crude state by distilling off the
xylene under reduced pressure.
The crude benzhydryl ether was a clear reddish oil. It was dissolved in 75 ml
of 20% hydrochloric acid and the aqueous acid solution then washed three
times with 50 ml portions each of ethyl ether. The aqueous acid solution was
then decolorized with activated carbon and thereafter slowly admixed with 75
ml of 28% aqueous ammonia. The benzhydryl ether separated as an oily
material and was removed from the aqueous mixture by extraction with three
50 ml portions of ethyl ether.
On evaporation of the ethyl ether from the ethyl ether solution, the
benzhydryl ether was recovered as a pale yellow oil. The benzhydryl ether was
dissolved in 60 ml of isopropanol and the isopropanol solution acidified to a
pH of 3 with dry hydrogen chloride-methanol solution. The acidic propanol
solution was then diluted with ethyl ether until a faint turbidity was observed.
In a short time, the crystalline hydrochloride salt of the benzhydryl ether
separated from the propanol solution. The crystallized salt was recrystallized
once from 75 ml of isopropanol with the aid of ethyl ether in order to further
purify the material. A yield of the pure hydrochloride salt of 1-methylpiperidyl-
4-benzhydryl ether of 24.5 grams was obtained. This was 39% of the
theoretical yield. The pure material had a melting point of 206°C.
Therapeutic Function
Antihistaminic
Pharmacokinetics
Diphenylpyraline is an antihistamine that prevents, but does not reverse, responses mediated by histamine alone. Diphenylpyraline antagonizes most of the pharmacological effects of histamine, including urticaria and pruritus. Also, diphenylpyraline may exhibit anticholinergic actions (as do most of the antihistamines) and may thus provide a drying effect on the nasal mucosa.
Metabolism
Hepatic
Mode of action
Antihistamines such as diphenylpyraline used in the treatment of allergy act by competing with histamine for H1-receptor sites on effector cells. This reduces the effects of histamine, leading to a temporary reduction of allergy symptoms.
References
[1] H PUHAKKA E V T Rantanen. Diphenylpyraline (Lergobine) in the treatment of patients suffering from allergic and vasomotor rhinitis.[J]. Journal of International Medical Research, 1977, 5 1: 37-41. DOI:10.1177/030006057700500106.
[2] P. RAMAPPA K. G S. Synthesis and Characterization of Copper(II) Complexes with Diphenylpyraline Hydrochloride[J]. Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic and Metal-organic Chemistry, 1998, 21 1: 263-274. DOI:10.1080/00945719809351902.
[3] ROBERT WEIS Werner S Andreas J Kungl. Synthesis of new analogues of diphenylpyraline[J]. Tetrahedron, 2003, 59 9: Pages 1403-1411. DOI:10.1016/S0040-4020(03)00072-3.
Properties of diphenylpyraline
| Boiling point: | 424.06°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0423 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMF: 30 mg/ml,DMSO: 30 mg/ml,Ethanol: 30 mg/ml,Ethanol:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:1): 0.5 mg/ml |
| form | A crystalline solid |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for diphenylpyraline
Computed Descriptors for diphenylpyraline
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
