Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride
Synonym(s):Chloroformic acid dimethyl amide;Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride
- CAS NO.:79-44-7
- Empirical Formula: C3H6ClNO
- Molecular Weight: 107.54
- MDL number: MFCD00000635
- EINECS: 201-208-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
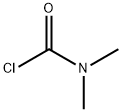
What is Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride ?
Description
DMCC is a liquid. Molecularweight= 107.55; Specific gravity (H2O:1) 5 1.2; Boilingpoint= 165℃; Freezing/Melting point = 2 33℃; Vaporpressure = 2.5 mmHg at 25℃; Flash point = 68.3℃.Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M RatingSystem): Health 3, Flammability 2, Reactivity 1 . Reactivewith water; decomposes.
Chemical properties
Clear colorless liquid
The Uses of Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride has been used primarily as a chemical intermediate in the production of dyes, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and rocket fuel (IARC 1999, HSDB 2009).
The Uses of Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride
As a chemical intermediate in the manufacture of carbamate drugs and pesticides
The Uses of Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride
Dimethylcarbamyl chloride is used to make dyes and pharmaceuticals.
Definition
ChEBI: Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is a halide. It is functionally related to a carbamic acid.
General Description
A colorless to yellow liquid with a pungent odor. Burns to skin, eyes and mucous membranes. A lachrymator. Used to make dyes and pharmaceuticals.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts with water or moisture in the air to form hydrochloric acid and dimethylcarbamic acid.
Reactivity Profile
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is water reactive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, alcohols, bases (including amines). May react vigorously or explosively if mixed with diisopropyl ether or other ethers in the presence of trace amounts of metal salts [J. Haz. Mat., 1981, 4, 291]. Gives toxic fumes of NOx and HCl when burned [USCG, 1999].
Health Hazard
Material is extremely destructive to the mucous membranes, upper respiratory tract, eyes, and skin. Symptoms of exposure include burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis, shortness of breath, headache, nausea, and vomiting.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic fumes of NO x and HCl
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, and tumorigenic data. Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by inhalation and ingestion. Human mutation data reported. Can cause skin and paplllary tumors by skin contact, and squamous cell carcinoma by inhalation. Will react with water or steam to produce toxic and corrosive fumes. A powerful lachrymator. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cland NOx. See also CHLORIDES.
Toxicology
The LD50 is 1170 mg/kg upon oral administration to rats and 350 mg/kg upon intraperitoneal administration to mice. The compound is irritating to the skin and eyes. All the test animals survived an 8-min inhalation test in an atmosphere saturated with vapors of the substance at 20℃. Longer exposure times led to death. No sensitization was observed in animal experiments.
Potential Exposure
AgriculturalChemical; Tumorigen, Mutagen. DMCC is used as a chemical intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, rocket fuel, and dye synthesis. Human exposure islimited to, but not restricted to, chemical workers, pesticideformulators, dye makers, and pharmaceutical workers.DMCC has been found at levels up to 6 ppm during the production of phthaloyl chlorides. It is possible that levels ofexposure might be higher in facilities in which the chemicalis used for further synthesis. When DMCC is used as a dyeintermediate, exposure can occur from the amount of residue in the product and its ability to migrate.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. If victim is conscious, administer water ormilk. Do not induce vomiting
Carcinogenicity
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Storage
(1) Color Code—White: Corrosive or ContactHazard; Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location.(2) Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store in asecure poison location. Prior to working with DMCC youshould be trained on its proper handling and storage. Storein tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated areaaway from strong oxidizers, strong acids, strong bases, andmoisture, since violent reactions can occur. Metal containers involving the transfer of this chemical should begrounded and bonded. Where possible, automatically pumpliquid from drums or other storage containers to processcontainers. Drums must be equipped with self-closingvalves, pressure vacuum bungs, and flame arresters. Useonly nonsparking tools and equipment, especially whenopening and closing containers of this chemical. Sources ofignition, such as smoking and open flames, are prohibitedwhere this chemical is used, handled, or stored in a mannerthat could create a potential fire or explosion hazard.Wherever this chemical is used, handled, manufactured, orstored, use explosion-proof electrical equipment and fittings. A regulated, marked area should be established wherethis chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance withOSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Shipping
This compound requires a shipping label of“CORROSIVE.” It falls in Hazard Class 8 and PackingGroup II.
Purification Methods
It must be distilled under high vacuum to avoid decomposition. [Beilstein 4 IV 224.]
Incompatibilities
Strong oxidizers; strong acids; strongbases. Reacts with water (rapidly hydrolyzes to carbondioxide, dimethylamine, dimethylcarbamic acid, and hydrochloric acid). Attacks metals in the presence of moisture.
Properties of Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride
| Melting point: | −33 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 167-168 °C775 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.168 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 155 °F |
| solubility | Chloroform (Soluble), DMSO (Sparingly) |
| pka | -1.85±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless to Yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.172 |
| Water Solubility | Decomposes |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| BRN | 878197 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.005 ppm (Skin) |
| Stability: | Moisture Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 79-44-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2A (Vol. 12, Sup 7, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Carbamic chloride, dimethyl-(79-44-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride (79-44-7) |
Safety information for Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Dimethylcarbamyl chloride CAS 79-44-7View Details
Dimethylcarbamyl chloride CAS 79-44-7View Details
79-44-7 -
 Dimethylcarbamoyl Chloride CAS 79-44-7View Details
Dimethylcarbamoyl Chloride CAS 79-44-7View Details
79-44-7 -
 Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride, 98% CAS 79-44-7View Details
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride, 98% CAS 79-44-7View Details
79-44-7 -
 Dimethylcarbamyl chloride CAS 79-44-7View Details
Dimethylcarbamyl chloride CAS 79-44-7View Details
79-44-7 -
 Dimethylcarbamyl chloride 95.00% CAS 79-44-7View Details
Dimethylcarbamyl chloride 95.00% CAS 79-44-7View Details
79-44-7 -
 Dimethylcarbamyl chloride >98% (GC) CAS 79-44-7View Details
Dimethylcarbamyl chloride >98% (GC) CAS 79-44-7View Details
79-44-7 -
 Dimethylcarbamyl chloride 98% CAS 79-44-7View Details
Dimethylcarbamyl chloride 98% CAS 79-44-7View Details
79-44-7 -
 Dimethylcarbamyl chloride CAS 79-44-7View Details
Dimethylcarbamyl chloride CAS 79-44-7View Details
79-44-7
