D-Phenothrin
- CAS NO.:26046-85-5
- Empirical Formula: C23H26O3
- Molecular Weight: 350.45
- MDL number: MFCD01735786
- EINECS: 247-431-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
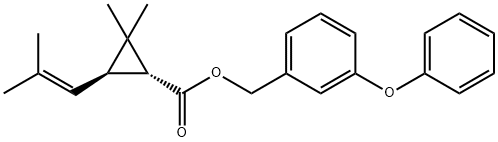
What is D-Phenothrin?
The Uses of D-Phenothrin
Phenothrin is used for the control of insects for public health. It is also used to protect stored grain.
Definition
ChEBI: (1R)-trans-phenothrin is a phenothrin. It is functionally related to a (+)-trans-chrysanthemic acid.
Metabolic pathway
Phenothrin is the name given to the 1RS-cis-trans isomer mixture (racemic). The product now used is d-phenothrin which is 95% 1R and 75% trans. It has no field use because the chrysanthemate moiety is very sensitive to photodegradation. Nevertheless, information on its photochemistry and its fate in soils and plants has been published. Several studies in rodents have been reported; this is a reflection of its use in public health. Phenothrin is degraded mainly by photo-oxidation and by hydrolysis and oxidation in plants and animals.
Degradation
Phenothrin is stable under normal storage conditions but it is labile to
base, being hydrolysed to trans-2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)-
cyclopropanecarboxylic acid (11, trans-chrysanthemic acid) and 3-phenoxybenzyl
alcohol (13,3PBAlc) (Scheme 2). It is sensitive to light and, for
example, as a thin film at midday in the summer at 55 ° N, it was degraded
with a DT50 of 2.5-3.0 hours (Samsonov and Makarov, 1996).
When (lR)-trans-[14C-carboxyl]phenotwhraisn irradiated in degassed
benzene solution, the only product was the cis-isomer. However, in oxygenated
benzene solution, degradation was about 10-fold faster and many
products were detected (Ruzo et al., 1982). A similar array of products was
seen on exposure of thin films to sunlight. Major products (Scheme 1)
were formed by oxidation at the isobutylene substituent giving the
epoxide (2), the alcohol (3), the aldehyde (4) and the carboxylic acid (5).
Caronaldehyde (6) and the caronic acid derivative (7) were formed by
cleavage of ozonolysis products and the hydroperoxide (8) was formed by
ene reactions at the 1’-position. Ester cleavage to 3PBAlc, 3PBAl and 3PBA
(not shown in Scheme 1) was relatively minor.
Properties of D-Phenothrin
| Boiling point: | 437.0±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.120±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 1.9×10-5Pa (21.4 °C) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| Water Solubility | <0.01 mg l-1 (25 °C) |
| form | Oil |
| color | Colourless to Dark Yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 26046-85-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | d-Phenothrin (26046-85-5) |
Safety information for D-Phenothrin
Computed Descriptors for D-Phenothrin
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 -
 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 -
 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
5968-21-8 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
