D-Pantethine
Synonym(s):Bis(N-pantothenylamidoethyl) disulfide;LBF factor;Pantethein oxidized form
- CAS NO.:16816-67-4
- Empirical Formula: C22H42N4O8S2
- Molecular Weight: 554.72
- MDL number: MFCD07357234
- EINECS: 240-842-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
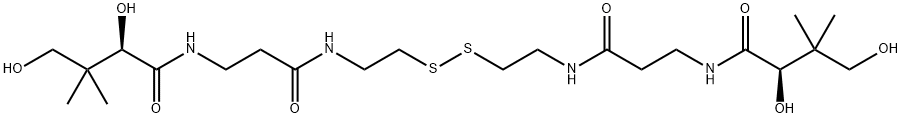
What is D-Pantethine?
Chemical properties
Colorless to pale yellow, clear, viscous liquid
Originator
Atarone,Vinas
The Uses of D-Pantethine
antilipemic
What are the applications of Application
D-Pantethine is a form of pantothenic acid or vitamin B5
Background
Pantethine is a naturally occurring compound synthesized in the body from pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) via addition of cysteamine. It consists of two molecules of pantetheine that form a dimer via disufide linkages, and acts as an intermediate in the production of Coenzyme A. Coenzyme A plays an essential role as a cofactor in the metabolism of lipids and carbohydrates including fatty acid oxidation, carbohydrate metabolism, pyruvate degradation, and amino acid catabolism . Pantethine is available as a dietary supplement for lowering blood cholesterol and triglycerides.
Definition
ChEBI: An organic disulfide that consists of two molecules of pantothenic acid linked by amide bonds to a cysteamine disulfide bridging group.
Manufacturing Process
To 11 g of hydrazine hydrate (85%) cooled in an ice bath are added 11.5 g of methyl d-pantothenate and the cold mixture is stirred vigorously. After the reaction takes place and the mixture is warmed to 30°C, it is allowed to stand at room temperature for two days, and then evaporated to dryness in vacuo at 50°C. The residue (14.7 g) of pantothenyl hydrazide is a clear glassy oil.
To 7.3 g of crude d-pantothenyl hydrazide dissolved in 21 ml of water and stirred in a beaker cooled on an ice bath is added sufficient. 6 N hydrochloric acid to shift the pH to 4. Then a solution of 1.7 g of sodium nitrite in 5 ml of water is added dropwise over a period of one hour, keeping the pH at 4 by additions of 6 N hydrochloric acid. After stirring for one-half hour, 2.8 g of bis(β-aminoethyl)disulfide dihydrochloride are added. The pH is then adjusted to 8.5 with 50% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and the solution allowed to stir for one and one-half hours. It is then acidified to pH 7.5 and concentrated in vacuo to clear colorless viscous oil. The pure product can be isolated from this oil by the next method. The crude bis(Npantothenylamidoethyl)disulfide so obtained is purified by dissolving the crude reaction product in 45 ml of anhydrous n-butanol and pouring the resulting solution through a chromatograph column containing 272 g of activated carbon. The column is washed with n-butanol and fractions are collected from time to time and the fractions containing solids assaying about 25 to 40% pure bis(N-pantothenylamidoethyl)disulfide against Lactobacillus: helveticus 80 poured onto a chromatograph column containing 136 g of an alkaline earth aluminum silicate known commercially as Super -filtrol. The column is washed thoroughly with anhydrous n-butanol and the washings and main solution discarded. N-Butanol saturated with water is poured through the column to elute the bis(N-pantothenylamidoethyl)disulfide and the resulting solution evaporated to dryness in vacuum at low temperature to obtain the desired product in pure form.
Instead of pouring the anhydrous n-butanol solution onto the alkaline earth aluminum silicate chromatograph column, one can simply repeat the treatment with a carbon chromatograph column to obtain the pure product. In some instances, the first carbon treatment produces fractions containing pure bis(N-pantothenylamidoethyl)disulfide and in those cases it is, of course, not necessary to treat the fraction with alkaline earth aluminum silicate nor again with activated carbon.
Therapeutic Function
Growth factor, Antihyperlipidemic
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intravenous route. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx and NOx.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of D-Pantethine
| Boiling point: | 987.2±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D27 +13.5° (c = 3.75 in water) |
| Density | 1.1949 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | syrup |
| pka | 12.71±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Crystals from MeOH/Me2CO |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for D-Pantethine
Computed Descriptors for D-Pantethine
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 D-Pantethine CAS 16816-67-4View Details
D-Pantethine CAS 16816-67-4View Details
16816-67-4 -
 D-Pantethine CAS 16816-67-4View Details
D-Pantethine CAS 16816-67-4View Details
16816-67-4 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8