D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate
Synonym(s):D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate;Maltose monohydrate;Maltobiose;D -(+)-Maltose monohydrate;D -Maltose monohydrate
- CAS NO.:6363-53-7
- Empirical Formula: C12H24O12
- Molecular Weight: 360.31
- MDL number: MFCD00149343
- EINECS: 613-294-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
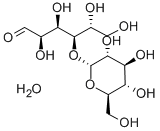
What is D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate?
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder
Chemical properties
Maltose occurs as white crystals or as a crystalline powder. It is odorless and has a sweet taste approximately 30% that of sucrose.
The Uses of D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate
D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate, is commonly found in foods and commonly utilized in brewing processes. It is also used in various culture media in the cell and tissue culture applications. D-(+)-Maltose Monohydrate is used as a substrate for α-glucosidase. It is also used as a substrate for the identification, differentiation and characterization of enzymes such as maltase(s); maltose α-D-glucosyltransferase(s); maltose-transporting ATPase(s); maltose O-acetyltransferase(s) and maltose epimerase(s) and phosphorylase(s). D-Maltose is used to study maltose-binding proteins and disaccharide transport systems.
The Uses of D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate
A disaccharide commonly found in foods and commonly utilized in brewing processes.
The Uses of D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate
D-Maltose, an α(1→4) linked disaccharide of D-glucose, is used as a substrate for the identification, differentiation and characterization of enzymes such as maltase(s); maltose α-D-glucosyltransferase(s); maltose-transporting ATPase(s); maltose O-acetyltransferase(s) and maltose epimerase(s) and phosphorylase(s). D-Maltose is used to study maltose-binding proteins and disaccharide transport systems.
What are the applications of Application
D-Maltose, Monohydrate is a disaccharide
Production Methods
Maltose monohydrate is prepared by the enzymatic degradation of starch.
General Description
Maltose monohydrate is commonly used as a tablet filler or excipient in pharmaceutical industry.
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Maltose is a disaccharide carbohydrate widely used in foods and
pharmaceuticals. In parenteral products, maltose may be used as a
source of sugar, particularly for diabetic patients.
Crystalline maltose is used as a direct-compression tablet
excipient in chewable and nonchewable tablets.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Maltose is a disaccharide containing two glucose molecules with an α(1→4) glycosidic linkage. Maltose can be derived from starch in food through the action of amylase. Maltose can be found in many food products, including beer, cereals, and pasta.
Safety
Maltose is used in oral and parenteral pharmaceutical formulations
and is generally regarded as an essentially nontoxic and nonirritant
material. However, there has been a single report of a liver
transplantation patient with renal failure who developed hyponatremia
following intravenous infusion of normal immunoglobulin
in 10% maltose. The effect, which recurred on each of four
successive infusions, resembled that of hyperglycemia and was
thought to be due to accumulation of maltose and other osmotically
active metabolites in the extracellular fluid.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 26.8 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, SC): 38.6 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, IV): 25.2 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IP): 30.6 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 15.3 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 34.8 g/kg
storage
Maltose should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place.
Purification Methods
Purify maltose by chromatography from aqueous solution on to a charcoal/Celite (1:1) column, wash it with water to remove glucose and other monosaccharides, then elute it with aqueous 75% EtOH. Crystallise it from water, aqueous EtOH or EtOH containing 1% nitric acid. Dry it as the monohydrate at room temperature under vacuum over H2SO4 or P2O5. Also purify it by dissolving it in MeOH, evaporating to a syrup which on standing for 12hours in contact with 1/10th its volume of H2O gives crystals of the monohydrate. Its iodine number is 55.5. The osazone has m 200o(dec) and [] D 20 +58o (c 1.4, H2O). [Howarth et al. J Chem Soc 793 1937, Beilstein 17 III/IV 3057, 17 V 189.]
Incompatibilities
Maltose may react with oxidizing agents. A Maillard-type reaction may occur between maltose and compounds with a primary amine group, e.g. glycine, to form brown-colored products.
Regulatory Status
In the USA, maltose is considered as a food by the FDA and is therefore not subject to food additive and GRAS regulations. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral solutions). Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. Included in parenteral products available in a number of countries worldwide.
Properties of D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate
| Melting point: | 119-121 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| alpha | 137 º (c=4, H2O, NH3) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | White |
| PH | 5.0-7.0 (25℃, 0.5M in H2O) |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +130±2°, 24 hr, c = 4% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | 1080 g/L (20 ºc) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.08 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.07 |
| Merck | 14,5714 |
| BRN | 5784659 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 6363-53-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | «beta»-Maltose monohydrate(6363-53-7) |
Safety information for D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate
D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
ASM Organics
New Products
1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine tert-Butyl carbazate 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 3-Pyridineacrylic acid Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% Tadalafil Clopidogrel bisulfate Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Cabergoline Fexofinadine HCl Etoricoxib 4-Amino Acetophenone 2-Chloro Acetophenone Amlodipine Base 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid Pyrrolidine Diiodo PentoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Maltose (NRC Grade) CAS 6363-53-7View Details
Maltose (NRC Grade) CAS 6363-53-7View Details
6363-53-7 -
 D-Maltose Monohydrate for tissue culture CAS 6363-53-7View Details
D-Maltose Monohydrate for tissue culture CAS 6363-53-7View Details
6363-53-7 -
 Maltose Monohydrate (SQ) CAS 6363-53-7View Details
Maltose Monohydrate (SQ) CAS 6363-53-7View Details
6363-53-7 -
 D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate CAS 6363-53-7View Details
D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate CAS 6363-53-7View Details
6363-53-7 -
 Maltose CAS 6363-53-7View Details
Maltose CAS 6363-53-7View Details
6363-53-7 -
 D-(+)-Maltose Monohydrate CAS 6363-53-7View Details
D-(+)-Maltose Monohydrate CAS 6363-53-7View Details
6363-53-7 -
 D-Maltose Monohydrate for bacteriology and biochemistry CAS 6363-53-7View Details
D-Maltose Monohydrate for bacteriology and biochemistry CAS 6363-53-7View Details
6363-53-7 -
 D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate 95% CAS 6363-53-7View Details
D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate 95% CAS 6363-53-7View Details
6363-53-7
