Maltose
Synonym(s):4-O-α-D -Glucopyranosyl-D -glucose
- CAS NO.:69-79-4
- Empirical Formula: C12H22O11
- Molecular Weight: 342.3
- MDL number: MFCD00135877
- EINECS: 200-716-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
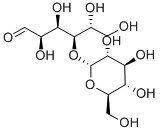
What is Maltose?
Chemical properties
colourless crystals or white powder
Chemical properties
Maltose occurs as white crystals or as a crystalline powder. It is odorless and has a sweet taste approximately 30% that of sucrose.
Originator
Maltos-10 ,Otsuka ,Japan ,1974
Occurrence
Maltose also is formed by yeast during breadmaking.
The Uses of Maltose
Maltose is a sweetener formed by the enzymatic action of yeast on starch. it consists of two dextrose molecules. maltose dissolves and crystallizes slowly in aqueous solutions, and is less sweet and more stable than sucrose. it is used in combination with dextrose in bread and in instant foods, and is also used in pancake syrups.
The Uses of Maltose
Nutrient, sweetener, culture media, stabilizer for polysulfides, brewing.
The Uses of Maltose
Maltose is used as a nutrient, sweetener, and culture medium.
What are the applications of Application
Maltose solution is a carbohydrate substrate used to characterize, identify, and differentiate various enzymes
Definition
The most common reducing disaccharide, composed of two molecules of glucose. Found in starch and glycogen.
Production Methods
Maltose monohydrate is prepared by the enzymatic degradation of starch.
Definition
A sugar found in germinating cereal seeds. It is a disaccharide composed of two glucose units. Maltose is an important intermediate in the enzyme hydrolysis of starch. It is further hydrolyzed to glucose.
Manufacturing Process
The process of manufacturing a maltose product from a suitably purified starch source includes preparing an aqueous starchy suspension, adjusting the acidity thereof to from 4.6 to 6.0 pH, liquefying the suspension by heating in the presence of a diastatic agent, diastatically saccharifying the liquefied mixture, filtering, and concentrating the liquid to a syrup.
Therapeutic Function
Sugar supplement
Pharmaceutical Applications
Maltose is a disaccharide carbohydrate widely used in foods and
pharmaceuticals. In parenteral products, maltose may be used as a
source of sugar, particularly for diabetic patients.
Crystalline maltose is used as a direct-compression tablet
excipient in chewable and nonchewable tablets.
Safety Profile
Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
Maltose is used in oral and parenteral pharmaceutical formulations
and is generally regarded as an essentially nontoxic and nonirritant
material. However, there has been a single report of a liver
transplantation patient with renal failure who developed hyponatremia
following intravenous infusion of normal immunoglobulin
in 10% maltose. The effect, which recurred on each of four
successive infusions, resembled that of hyperglycemia and was
thought to be due to accumulation of maltose and other osmotically
active metabolites in the extracellular fluid.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 26.8 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, SC): 38.6 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, IV): 25.2 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IP): 30.6 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 15.3 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 34.8 g/kg
Storage
Maltose should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Maltose may react with oxidizing agents. A Maillard-type reaction may occur between maltose and compounds with a primary amine group, e.g. glycine, to form brown-colored products.
Regulatory Status
In the USA, maltose is considered as a food by the FDA and is therefore not subject to food additive and GRAS regulations. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral solutions). Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. Included in parenteral products available in a number of countries worldwide.
Properties of Maltose
| Melting point: | 110 °C |
| Boiling point: | 397.76°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.5400 |
| refractive index | n |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Very soluble in water; very slightly soluble in cold ethanol (95%); practically insoluble in ether. |
| pka | 12.39±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| PH | 4.0-6.5 (25℃) |
| Water Solubility | 310.3g/L(20 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.08 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.07 |
| Merck | 13,5736 |
| BRN | 93798 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 69-79-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | D-Glucose, 4-o-«alpha»-D-glucopyranosyl-(69-79-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Glucose, 4-O-.alpha.-D-glucopyranosyl- (69-79-4) |
Safety information for Maltose
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Maltose
Maltose manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 69-79-4 D-(+)-Maltose 99%View Details
69-79-4 D-(+)-Maltose 99%View Details
69-79-4 -
 D-(+)-Maltose 98%View Details
D-(+)-Maltose 98%View Details
69-79-4 -
 Maltose Monohydrate CAS 69-79-4View Details
Maltose Monohydrate CAS 69-79-4View Details
69-79-4 -
 Maltose CASView Details
Maltose CASView Details -
 Maltose 95.00% CAS 69-79-4View Details
Maltose 95.00% CAS 69-79-4View Details
69-79-4 -
 Maltose solution CAS 69-79-4View Details
Maltose solution CAS 69-79-4View Details
69-79-4 -
 MALTOSE (69-79-4 ), For IndustrialView Details
MALTOSE (69-79-4 ), For IndustrialView Details
69-79-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
