D-Glucose monohydrate
Synonym(s):D- (+)-Glucose monohydrate;Dextrose monohydrate
- CAS NO.:5996-10-1
- Empirical Formula: C6H14O7
- Molecular Weight: 198.17
- MDL number: MFCD00150744
- EINECS: 611-920-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 16:10:59
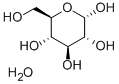
What is D-Glucose monohydrate?
Absorption
Polysaccharides can be broken down into smaller units by pancreatic and intestinal glycosidases or intestinal flora. Sodium-dependent glucose transporter SGLT1 and GLUT2 (SLC2A2) play predominant roles in intestinal transport of glucose into the circulation. SGLT1 is located in the apical membrane of the intestinal wall while GLUT2 is located in the basolateral membrane, but it was proposed that GLUT2 can be recruited into the apical membrane after a high luminal glucose bolus allowing bulk absorption of glucose by facilitated diffusion . Oral preparation of glucose reaches the peak concentration within 40 minutes and the intravenous infusions display 100% bioavailability.
Toxicity
Oral LD50 value in rats is 25800mg/kg. The administration of glucose infusions can cause fluid and/or solute overloading resulting in dilution of the serum electrolyte concentrations, over-hydration, congested states, or pulmonary oedema. Hypersensitivity reactions may also occur including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions from oral tablets and intravenous infusions.
Chemical properties
D-Glucose monohydrate is white or almost white, crystalline powder.
Chemical properties
Dextrose occurs as odorless, sweet-tasting, colorless crystals or as a white crystalline or granular powder. The JP XV describes dextrose as dextrose anhydrous; the PhEur 6.3 specifies dextrose as either dextrose anhydrous or dextrose monohydrate; and the USP 32 specifies dextrose as dextrose monohydrate.
The Uses of D-Glucose monohydrate
Replenisher (fluid and nutrient).
Indications
Glucose pharmaceutical formulations (oral tablets, injections) are indicated for caloric supply and carbohydrate supplementation in case of nutrient deprivation. It is also used in metabolic disorders such as hypoglycemia.
Background
Glucose is a simple sugar (monosaccharide) generated during phosynthesis involving water, carbon and sunlight in plants. It is produced in humans via hepatic gluconeogenesis and breakdown of polymeric glucose forms (glycogenolysis). It circulates in human circulation as blood glucose and acts as an essential energy source for many organisms through aerobic or anaerobic respiration and fermentation. It is primarily stored as starch in plants and glycogen in animals to be used in various metabolic processes in the cellular level. Its aldohexose stereoisomer, dextrose or D-glucose, is the most commonly occurring isomer of glucose in nature. L-glucose is a synthesized enantiomer that is used as a low-calorie sweetener and laxative. The unspecified form of glucose is commonly supplied as an injection for nutritional supplementation or metabolic disorders where glucose levels are improperly regulated. Glucose is listed on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
Production Methods
Dextrose, a monosaccharide sugar, occurs widely in plants and is manufactured on a large scale by the acid or enzymatic hydrolysis of starch, usually maize (corn) starch. Below 50°C a-D-dextrose monohydrate is the stable crystalline form produced; above 50°C the anhydrous form is obtained; and at still higher temperatures b-D-dextrose is formed, which has a melting point of 148–155°C.
Definition
A monosaccharide occurring widely in nature as D-glucose. It occurs as glucose units in sucrose, starch, and cellulose. It is important to metabolism because it participates in energy-storage and energy-release systems.
brand name
Cartose (Sterling Winthrop) Dextrose.
Agricultural Uses
Glucose is a monosaccharide sugar found in honey and fruits. It is the primary product of plant photosynthesis, which is optically active and dextrorotatory.
Glucose and its derivatives are critically important in the energy metabolism of living organisms. It is transported around the animal body through blood, and by lymph and cerebrospinal fluid, to cells where the energy is released during glycolysis.
Fructose, the stereoisomer of glucose, occurs in green plants, fruits and honey. It is sweeter than sucrose.
Yeasts readily ferment glucose to produce ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. It is also metabolized by bacteria into acetic and butyric acids, lactic acid, butyl alcohol, acetone, hydrogen, carbon dioxide and many other compounds.
Plants and animals convert complex carbohydrates (like starch and glycogen) into glucose to meet their energy needs. Glucose is produced commercially by hydrolysing corn starch with dilute mineral acid. Commercial glucose is mostly used in the manufacture of confections and in the canning industry.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Dextrose is widely used in solutions to adjust tonicity and as a sweetening agent.Dextrose is also used as a wet granulation diluent and binder, primarily in chewable tablets.Although dextrose is comparable as a tablet diluent to lactose, tablets produced with dextrose monohydrate require more lubrication, are less friable, and have a tendency to harden. The mildly reducing properties of dextrose may be used when tableting to improve the stability of active materials that are sensitive to oxidation.
Dextrose is also used therapeutically and is the preferred source of carbohydrate in parenteral nutrition regimens.
Pharmacokinetics
Blood glucose is an obligatory energy source in humans involved in various cellular activities, and it also acts as a signalling molecule for diverse glucose-sensing molecules and proteins. Glucose undergoes oxidation into carbon dioxide, water and yields energy molecules in the process of glycolysis and subsequent citric cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Glucose is readily converted into fat in the body which can be used as a source of energy as required. Under a similar conversion into storage of energy, glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen. Glucose stores are mobilized in a regulated manner, depending on the tissues' metabolic demands. Oral glucose tablets or injections serve to increase the supply of glucose and oral glucose administration is more effective in stimulating insulin secretion because it stimulates the incretin hormones from the gut, which promotes insulin secretion.
Safety
D-Glucose monohydrate is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is metabolized to carbondioxide and water with therelease ofenergy.
Concentrated D-Glucose monohydrate solutions given by mouth may cause nausea and vomiting. D-Glucose monohydrate solutions of concentration greater than 5% w/v are hyperosmotic and are liable to cause local vein irritation following intravenous administration. Thrombophlebitis has been observed following the intravenous infusion of isoosmotic D-Glucose monohydrate solution with low pH, probably owing to the presence of degradation products formed by overheating during sterilization. The incidence of phlebitis may be reduced by adding sufficient sodium bicarbonate to raise the pH of the infusion above pH 7.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 9g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 25.8g/kg
Physiological effects
D-Glucose monohydrate is the monohydrate form of D-glucose, it restore blood glucose levels, provide calories, may aid in minimizing liver glycogen depletion and exerts a protein-sparing action.Dextrose Monohydratealso plays a role in the production of proteins and in lipid metabolism.
Metabolism
Glucose can undergo aerobic oxidation in conjunction to the synthesis of energy molecules. Glycolysis is the initial stage of glucose metabolism where one glucose molecule is degraded into 2 molecules of pyruvate via substrate-level phosphorylation. These products are transported to the mitochondria where they are further oxidized into oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Storage
D-Glucose monohydrate has good stability under dry storage conditions. Aqueous solutions may be sterilized by autoclaving. However, excessive heating can cause a reduction in pH and caramelization of solutions.
Thebulkmaterialshouldbestoredinawell-closedcontainerina cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Dextrose solutions are incompatible with a number of drugs such as cyanocobalamin, kanamycin sulfate, novobiocin sodium, and warfarin sodium. Erythromycin gluceptate isunstable indextrose solutions at a pH less than 5.05. Decomposition of B-complex vitamins may occur if they are warmed with dextrose.
In the aldehyde form, dextrose can react with amines, amides, amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Brown coloration and decomposition occur with strong alkalis.
Dextrose may cause browning of tablets containing amines (Maillard reaction).
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (capsules; inhalations; IM, IV, and SC injections; tablets, oral solutions, and syrups). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of D-Glucose monohydrate
| Melting point: | 83°C |
| Density | 1.54 |
| solubility | Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | Solid |
| color | Colorless crystals |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 5.9 |
| Water Solubility | 1 g/1.1 ml water @ 250C |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 5996-10-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for D-Glucose monohydrate
Computed Descriptors for D-Glucose monohydrate
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Dextrose Mono hydrate 99%View Details
Dextrose Mono hydrate 99%View Details -
 Dextrose monohydrate 99%View Details
Dextrose monohydrate 99%View Details -
 D-Glucose monohydrate 14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 98%View Details
D-Glucose monohydrate 14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 98%View Details
14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 -
 14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 D-Glucose monohydrate 98%View Details
14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 D-Glucose monohydrate 98%View Details
14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 -
 D-Glucose monohydrate 14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 99%View Details
D-Glucose monohydrate 14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 99%View Details
14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 -
 14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 98%View Details
14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 98%View Details
14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 -
 14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 98%View Details
14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 98%View Details
14431-43-7 / 77938-63-7 -
 DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE Extra Pure CASView Details
DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE Extra Pure CASView Details
