D(+)-Carnitine
- CAS NO.:541-14-0
- Empirical Formula: C7H15NO3
- Molecular Weight: 161.2
- MDL number: MFCD00083279
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 15:12:12
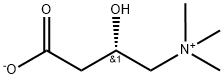
What is D(+)-Carnitine?
Chemical properties
white to light yellow crystal powde
The Uses of D(+)-Carnitine
Essential cofactor of fatty acid metabolism; required for the transport of fatty acids through the inner mitochondrial membrane. Synthetized primarily in the liver and kidney; highest concentrations found in heart and skeletal muscle. Dietary sources include red meat, dairy products, beans, avocado.
Definition
ChEBI: The (S)-enantiomer of carnitine.
Purification Methods
The S(L) isomer is levocarnitine, Vitamin B7. The R or S isomers crystallise from EtOH/Me2CO (hygroscopic). The R or S hydrochlorides crystallise from hot EtOH or EtOH/Et2O and have m 142o(dec). The RS-isomer crystallises from hot EtOH (hygroscopic). The RS hydrochloride crystallises in needles from hot EtOH and has m 196o(dec). [(±) Mazzetti & Lemmon J Org Chem 22 228 1957, Beilstein 4 H 513, 4 I 548, 4 II 937-8, 4 III 1632-5, 4 IV 3185.]
Properties of D(+)-Carnitine
| Melting point: | 197 °C |
| Boiling point: | 287.5°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D +30.9° |
| Density | 1.1587 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 13,1862 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for D(+)-Carnitine
Computed Descriptors for D(+)-Carnitine
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
