(S)-(+)-Ketoprofen
Synonym(s):(S)-(+)-3-Benzoyl-α-methylbenzeneacetic acid;(S)-2-(3-Benzoylphenyl)propionic acid
- CAS NO.:22161-81-5
- Empirical Formula: C16H14O3
- Molecular Weight: 254.28
- MDL number: MFCD00673316
- EINECS: 606-944-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-27 17:31:30
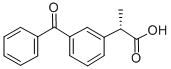
What is (S)-(+)-Ketoprofen?
Absorption
After oral ingestion, the Dexketoprofen onset of action is within 30 minutes. The plasma half-life of Dexketoprofen is about 4-6 hours. The Cmax is about 30 minutes
Toxicity
Nausea and/or vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea, digestive problems (dyspepsia) are the most common symptoms of toxicity. More toxicity symptoms include dizziness, sleepiness, disturbed sleep, nervousness, headache, palpitations, flushing, stomach problems, constipation, dry mouth, flatulence, skin rash, tiredness, pain, feeling feverish and shivering, and malaise.
Severe toxicity can lead to thrombocytopenia and anemia with bleeding episodes. Dexketoprofen is associated with a small increased risk of myocardial infarction .
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of (S)-(+)-Ketoprofen
Anti-inflammatory; analgesic
The Uses of (S)-(+)-Ketoprofen
COX inhibitor
Indications
For short-term treatment of mild to moderate pain, including dysmenorrhoea, musculoskeletal pain and toothache .
Background
Dexketoprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It is available in the various countries in Europe, Asia and Latin America. It has analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory properties .
What are the applications of Application
(S)-(+)-Ketoprofen is a Cox inhibitor
What are the applications of Application
(S)-Ketoprofen is an inhibitor of TXB2 generation and of Cox
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that is (S)-hydratropic acid substituted at position 3 on the phenyl ring by a benzoyl group. A cyclooxygenase inhibitor, it is used to relieve short-term pain, such as muscular pain, dental pain and dysmenorrhoea.
Biological Activity
(s)-ketoprofen, a dual cox1/2 inhibitor, can be used as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug to treat arthritis-related inflammatory pains. ketoprofen is photolabile and undergoes degradation when irradiated by sunlight to induce various skin diseases [1].
Pharmacokinetics
This drug is an isomer of ketoprofen. Dexketoprofen a propionic acid derivative with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties .
in vitro
the combination of uvb irradiation with ketoprofen dose-dependently induced the cytotoxicity and suppressed dna synthesis in hacat cells. uvb-irradiated kp inhibited the cell growth and induced g2/m cell cycle arrest by regulating the levels of cdc2, cyclin b1, chk1, tyr15-phosphorylated cdc2 and p21. the dapi staining results has revealed that kp accentuated the apoptotic response to uvb radiation in hacat cells [1].
in vivo
in a placebo-controlled, double-blind study in the rhesus monkeys macaca mulatta with periodontal disease, administeration of kp at 1% level in suitable topical vehicles to the gingiva once daily at a standard dose of 1.8 ml per monkey for 6 months effectively inhibited gcf-ltb4 and gcf-pge2 and positively altered alveolar bone activity [2]. ketoprofen at a dose of 3.63 mg/kg bwt (phenylbutazone equimolar dose) showed significant analgesic effects and reduced hoof pain and lameness to a greater extent [3]. treatment with ketoprofen (40 and 80 mg/kg diet) greatly reduced the incidence of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder by >70% from that seen in dietary mice [4].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists:
antagonism of hypotensive effect; increased risk of
nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemia
Analgesics: avoid concomitant use of 2 or more
NSAIDs, including aspirin (increased side effects);avoid with ketorolac (increased risk of side effects
and haemorrhage).
Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of convulsions
with quinolones
Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins and
phenindione enhanced; possibly increased risk of
bleeding with heparins, dabigatran and edoxaban -
avoid long term use with edoxaban
Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with
SSRIs and venlaflaxine.
Antidiabetic agents: effects of sulphonylureas enhanced.
Antiepileptics: possibly increased phenytoin
concentration.
Antivirals: increased risk of haematological toxicity
with zidovudine; concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: may potentiate nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: reduced excretion of methotrexate;
increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib.
Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity;
antagonism of diuretic effect, hyperkalaemia with
potassium-sparing diuretics.
Lithium: excretion decreased.
Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleeding
Probenecid: excretion reduced by probenecid.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity
Metabolism
Dexketoprofen is highly lipophilic, and is metabolized in the liver by glucuronidation . In one study, after oral administration of 25 mg of dexketoprofen to young healthy adults, Tmax was approximately 30 min for a Cmax of 3.7 ± 0.72 mg/l . Dexketoprofen trometamol is metabolized by the hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP2C8 and CYP2C9) .
Dexketoprofen trometamol has a number of metabolites, with hydroxyl derivatives making up the greatest volume . In humans, hydroxylation plays a minor role.
Dexketoprofen is primarily conjugated to an acyl-glucuronide
Metabolism
Dexketoprofen is the S-enantiomer of ketoprofen.The main elimination route for dexketoprofen is glucuronide conjugation in the liver followed by renal excretion.
References
[1]. liu s, mizu h, yamauchi h. molecular response to phototoxic stress of uvb-irradiated ketoprofen through arresting cell cycle in g2/m phase and inducing apoptosis[j]. biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2007, 364(3): 650-655.
[2]. li k l, vogel r, jeffcoat m k, et al. the effect of ketoprofen creams on periodontal disease in rhesus monkeys[j]. journal of periodontal research, 1996, 31(8): 525-532.
[3]. owens j g, kamerling s g, stanton s r, et al. effects of ketoprofen and phenylbutazone on chronic hoof pain and lameness in the horse[j]. equine veterinary journal, 1995, 27(4): 296-300.
[4]. hawk e t, kelloff g j, mccormick d l. differential activity of aspirin, ketoprofen and sulindac as cancer chemopreventive agents in the mouse urinary bladder[j]. carcinogenesis, 1996, 17(5): 1435-1438.
Properties of (S)-(+)-Ketoprofen
| Melting point: | 75-78 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 431.3±28.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.198±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥10.6 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥20.55 mg/mL in EtOH |
| form | White solid. |
| pka | 4.23±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| optical activity | [α]22/D +49°, c = 1 in methanol |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 22161-81-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for (S)-(+)-Ketoprofen
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for (S)-(+)-Ketoprofen
(S)-(+)-Ketoprofen manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(Hydroxymethyl)benzoate N-Boc-2-chloroethylamine 1-Bromo-2-methoxy-3-nitrobenzene N-Methyl-3-cyclopenten-1-amine 2-Bromo-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde 1H-indazole-5-carboxamideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 DEXKETOPROFEN 99%View Details
DEXKETOPROFEN 99%View Details -
 Dexketoprofen 99%View Details
Dexketoprofen 99%View Details
22161-81-5 -
 (S)-(+)-Ketoprofen CAS 22161-81-5View Details
(S)-(+)-Ketoprofen CAS 22161-81-5View Details
22161-81-5 -
 7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 -
 1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 -
 4-bromo-3,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride 1581266-79-6 98%View Details
4-bromo-3,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride 1581266-79-6 98%View Details
1581266-79-6 -
 2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 -
 N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
5434-30-0