D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate
Synonym(s):DL -α-Tocopherol acetate;all-rac-α-Tocopheryl acetate;Vitamin E acetate
- CAS NO.:58-95-7
- Empirical Formula: C31H52O3
- Molecular Weight: 472.74
- MDL number: MFCD00072052
- EINECS: 200-405-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-22 14:18:24
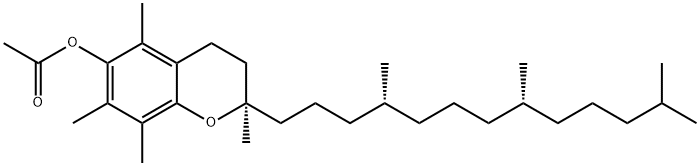
What is D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate?
Absorption
In addition to any following information, owing to d-alpha-Tocopherol acetate's closely related chemical nature with alpha-Tocopherol acetate, please also refer to the drug information page for alpha-Tocopherol acetate for further data.
50 to 80% absorbed from gastrointestinal tract.
Toxicity
In addition to any following information, owing to d-alpha-Tocopherol acetate's closely related chemical nature with alpha-Tocopherol acetate, please also refer to the drug information page for alpha-Tocopherol acetate for further data.
Chemical properties
off-white crystalline solid
The Uses of D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate
Used in prevention and treatment of vitamin E deficiencies.
The Uses of D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate
α-Tocopherol acetate is the most bioactive of the naturally occurring forms of Vitamin E. Richest sources are green vegetables, grains, and oils, particularly palm, safflower and sunflower oils.
The Uses of D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate
(+)-α-Tocopherol acetate has been used:
- as a component of growth medium for retinal cell lines
- as an external standard in high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to study its composition in leafy vegetables
- in the preparation of trans-resveratrol-encapsulated lipid nanocarriers (R-nano)
Background
Alpha-tocopherol is the primary form of vitamin E that is preferentially used by the human body to meet appropriate dietary requirements. In particular, the RRR-alpha-tocopherol (or sometimes called the d-alpha-tocopherol stereoisomer) stereoisomer is considered the natural formation of alpha-tocopherol and generally exhibits the greatest bioavailability out of all of the alpha-tocopherol stereoisomers. Moreover, RRR-alpha-tocopherol acetate is a relatively stabilized form of vitamin E that is most commonly used as a food additive when needed .
Alpha-tocopherol acetate is subsequently most commonly indicated for dietary supplementation in individuals who may demonstrate a genuine deficiency in vitamin E. Vitamin E itself is naturally found in various foods, added to others, or used in commercially available products as a dietary supplement. The recommended dietary allowances (RDAs) for vitamin E alpha-tocopherol are: males = 4 mg (6 IU) females = 4 mg (6 IU) in ages 0-6 months, males = 5 mg (7.5 IU) females = 5 mg (7.5 IU) in ages 7-12 months, males = 6 mg (9 IU) females = 6 mg (9 IU) in ages 1-3 years, males = 7 mg (10.4 IU) females = 7 mg (10.4 IU) in ages 4-8 years, males = 11 mg (16.4 IU) females = 11 mg (16.4 IU) in ages 9-13 years, males = 15 mg (22.4 IU) females = 15 mg (22.4 IU) pregnancy = 15 mg (22.4 IU) lactation = 19 mg (28.4 IU) in ages 14+ years . Most individuals obtain adequate vitamin E intake from their diets; genuine vitamin E deficiency is considered to be rare.
Nevertheless, vitamin E is known to be a fat-soluble antioxidant that has the capability to neutralize endogenous free radicals. This biologic action of vitamin E consequently continues to generate ongoing interest and study in whether or not its antioxidant abilities may be used to help assist in preventing or treating a number of different conditions like cardiovascular disease, ocular conditions, diabetes, cancer and more. At the moment however, there exists a lack of formal data and evidence to support any such additional indications for vitamin E use.
Indications
In addition to any following information, owing to d-alpha-Tocopherol acetate's closely related chemical nature with alpha-Tocopherol acetate, please also refer to the drug information page for alpha-Tocopherol acetate for further data.
Vitamin E, known for its antioxidant activities, is protective against cardiovascular disease and some forms of cancer and has also demonstrated immune-enhancing effects. It may be of limited benefit in some with asthma and rheumatoid arthritis. It may be helpful in some neurological diseases including Alzheimer's, some eye disorders including cataracts, and diabetes and premenstrual syndrome. It may also help protect skin from ultraviolet irradiation although claims that it reverses skin aging, enhances male fertility and exercise performance are poorly supported. It may help relieve some muscle cramps.
What are the applications of Application
(+)-α-Tocopherol acetate is a lipid soluble anti-oxidant that protect cell membranes from oxidative damage in vitro
Definition
ChEBI: Alpha-Tocopherol acetate is a tocol.
General Description
Odorless off-white crystals. Darkens at 401° F.
Air & Water Reactions
D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to light and air. . Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
An ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate are not available. D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate is probably combustible.
Contact allergens
Tocopherol and tocopheryl acetate are used mainly as antioxidants. Tocopheryl acetate, an ester of tocopherol (vitamin E), can induce allergic contact dermatitis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
α-Tocopherol acetate or vitamin E-acetate has antioxidant properties and reduces lipid peroxidation. However, vitamin E acetate on pyrolysis leads to the generation of carcinogens like alkenes and benzenes.
Pharmacokinetics
In addition to any following information, owing to d-alpha-Tocopherol acetate's closely related chemical nature with alpha-Tocopherol acetate, please also refer to the drug information page for alpha-Tocopherol acetate for further data.
Vitamin E has antioxidant activity. It may also have anti-atherogenic, antithrombotic, anticoagulant, neuroprotective, antiviral, immunomodulatory, cell membrane-stabilizing and antiproliferative actions. Vitamin E is a collective term used to describe eight separate forms, the best-known form being alpha-tocopherol. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin and is an important antioxidant. It acts to protect cells against the effects of free radicals, which are potentially damaging by-products of the body's metabolism. Vitamin E is often used in skin creams and lotions because it is believed to play a role in encouraging skin healing and reducing scarring after injuries such as burns. There are three specific situations when a vitamin E deficiency is likely to occur. It is seen in persons who cannot absorb dietary fat, has been found in premature, very low birth weight infants (birth weights less than 1500 grams, or 3? pounds), and is seen in individuals with rare disorders of fat metabolism. A vitamin E deficiency is usually characterized by neurological problems due to poor nerve conduction. Symptoms may include infertility, neuromuscular impairment, menstrual problems, miscarriage and uterine degradation. Preliminary research has led to a widely held belief that vitamin E may help prevent or delay coronary heart disease. Antioxidants such as vitamin E help protect against the damaging effects of free radicals, which may contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer. It also protects other fat-soluble vitamins (A and B group vitamins) from destruction by oxygen. Low levels of vitamin E have been linked to increased incidence of breast and colon cancer.
Safety Profile
When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Metabolism
In addition to any following information, owing to d-alpha-Tocopherol acetate's closely related chemical nature with alpha-Tocopherol acetate, please also refer to the drug information page for alpha-Tocopherol acetate for further data.
Hepatic.
Properties of D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate
| Melting point: | ~25 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 224 °C0.3 mm Hg(lit.) |
| alpha | 3 º (c=2, in ethanol 25 ºC) |
| Density | 0.953 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetone, in anhydrous ethanol and in fatty oils, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | oil or semi-solid |
| color | yellow |
| Odor | cryst., odorless |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 17 ºC |
| Merck | 14,9495 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 58-95-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Vitamin e acetate(58-95-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-.alpha.-Tocopheryl acetate (58-95-7) |
Safety information for D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H413:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate
D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 231-710-0 Vitamine E Acetate 98%View Details
231-710-0 Vitamine E Acetate 98%View Details
231-710-0 -
 58-95-7 99%View Details
58-95-7 99%View Details
58-95-7 -
 D-Alpha-tocopheryl acetate 96% CAS 58-95-7View Details
D-Alpha-tocopheryl acetate 96% CAS 58-95-7View Details
58-95-7 -
 D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate 96.00% CAS 58-95-7View Details
D-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate 96.00% CAS 58-95-7View Details
58-95-7 -
 D-α-Tocopherol Acetate CAS 58-95-7View Details
D-α-Tocopherol Acetate CAS 58-95-7View Details
58-95-7 -
 (+)-α-Tocopherol acetate CAS 58-95-7View Details
(+)-α-Tocopherol acetate CAS 58-95-7View Details
58-95-7 -
 (+)-α-Tocopherol acetate CAS 58-95-7View Details
(+)-α-Tocopherol acetate CAS 58-95-7View Details
58-95-7 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
