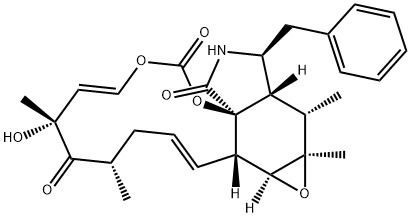
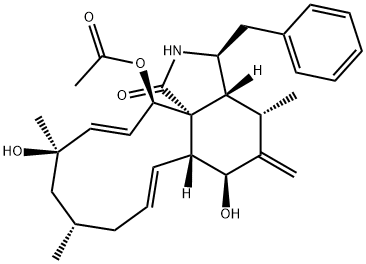
CYTOCHALASIN B
Synonym(s):Cytochalasin B, Helminthosporium dematioideum - CAS 14930-96-2 - Calbiochem;Phomin
- CAS NO.:14930-96-2
- Empirical Formula: C29H37NO5
- Molecular Weight: 479.61
- MDL number: MFCD00077704
- EINECS: 239-000-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 15:44:27

What is CYTOCHALASIN B?
Description
Cytochalasin B (14930-96-2) is a cell permeable fungal toxin which binds to the barbed end of actin, inhibiting its polymerization.1 Inhibits cell division, migration and glucose transport.2 Causes cell cycle arrest at G2/M and induces apoptosis in HCT-116 colorectal carcinoma cells.3? Cytochalasin B-induced membrane vesicles (CIMVs) retain cell surface receptors of the parent cells and retain fusion specificity with target cells.4 CIMVs are a promising new vector system for drug and biomolecule delivery due to their natural origin and participation in intercellular communication.5
Description
Cytochalasin B is a mycotoxin that penetrates cell walls and inhibits several cellular processes. In 1967, W. B. Turner isolated it from the fungus?Helminthosporium dematioideum. ?That same year, D. C. Aldridge and co-workers reported its structure. Since then, researchers discovered that its inhibition activity ranges from glucose transport to network formation by actin filaments. Because of its many cytological properties, cytochalasin B is frequently used in cell research.
I. Sokolov and colleagues at Tufts University (Medford, MA) and four other institutions report the latest cytochalasin B findings. In 2006, Sokolov’s group showed that it can?restore elasticity to mouse skin cells. Then, earlier this year, they found that it also?shrinks skin cells of older mice, making the skin smoother. Despite it toxicity, it showed no adverse effects on skin or elsewhere in the body.
Sokolov and his team plan to test cytochalasin B creams on human skin in the near future.
Chemical properties
white to off-white powder
The Uses of CYTOCHALASIN B
Cytochalasin B is one of the most extensively studied members of a family of potent mycotoxins produced by several species of fungi. All members of the class exhibit profound effects on cytoskeletal proteins, giving rise to pronounced morphogenic activity in animals and plants. Like most cytochalsins, cytochalasin B exhibits potent inhibition of actin filament function leading to cell death by apoptosis, and displays a broad range of resultant cellular actions. Despite the common mode of action, there is evidence that individual members of this class display diverse selectivity. However, lack of comparative co-metabolite analysis has restricted a more complete understanding of their individual selectivity.
The Uses of CYTOCHALASIN B
A cell-permeable fungal toxin used in actin polymerization studies and cytological
The Uses of CYTOCHALASIN B
As tools in cytological research and in characterization of polymerization properties of actin, q.v.
What are the applications of Application
Cytochalasin B is a cell-permeable fungal toxin used in actin polymerization studies and cytological research.
Definition
ChEBI: An organic heterotricyclic compound, that is a mycotoxin which is cell permeable an an inhibitor of cytoplasmic division by blocking the formation of contractile microfilaments.
General Description
Cytochalasin B is a cell-permeable fungal toxin / mycotoxin that binds to the ′barbed′ end of actin / actin filaments. This binding leads to:
- Disruption of actin filaments and of interaction of actin filaments in solution
- Inhibition of actin polymerization
- Inhibition of subunit association and dissociation
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cell permeable fungal toxin that disrupts contractile microfilaments by inhibiting actin polymerization. This, in turn, induces DNA fragmentation, inhibits cell division, and disrupts many cell processes. Inhibits glucose transport.
Storage
Store at -20°C
Purification Methods
Purify it by MeOH extraction, reverse phase C18 silica gel batch extraction by selective elution with 1:1 v/v hexane/tetrahydrofuran, crystallisation, subjected to TLC and recrystallisation [Lipski et al. Anal Biochem 161 332 1987]. It is soluble in EtOH (3.6%), Me2CO (1%), Me2SO (37%) and Me2NCHO (49%) at 24o, and can be crystallised from the first two solvents. It interferes with cellular movement [Korm Physiol Reviews 62 672 1982].
References
Threadoropoulos et al. (1994), Cytochalasin B may shorten actin filaments by a mechanism independent of barbed end capping; Biochem. Pharmacol., 47 1875 Whitesell et al. (2005), Compartmentalization of transport and phosphorylation of glucose in a hepatoma cell line; Biochem. J., 386 245 Buldak et al. (2014), Changes in subcellular localization of visfatin in human colorectal HCT-116 carcinoma cell line after cytochalasin B treatment; Eur. J. Histochem., 58 2408 Gomzikova et al. (2018), Evaluation of cytochalasin B-Induced Membrane Vesicles Fusion specificity with Target Cells; Biomed. Res. Int., 2018 7053623 Gomzikova et al. (2017), Cytochalasin B-induced membrane vesicles convey angiogenic activity of parental cells; Oncotarget, 8 70496
Properties of CYTOCHALASIN B
| Melting point: | 218-223 °C |
| Boiling point: | 577.96°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1490 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6290 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 85℃ |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | ethanol: 20 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 13.60±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Merck | 13,2819 |
| BRN | 1096207 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cytochalasin B (14930-96-2) |
Safety information for CYTOCHALASIN B
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H361:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for CYTOCHALASIN B
| InChIKey | UXVDBQLLXVKPRS-UZBFCAAUSA-N |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Cytochalasin B CAS 14930-96-2View Details
Cytochalasin B CAS 14930-96-2View Details
14930-96-2 -
 Cytochalasin B, from drechslera dematioidea CAS 14930-96-2View Details
Cytochalasin B, from drechslera dematioidea CAS 14930-96-2View Details
14930-96-2 -
 Cytochalasin B, Helminthosporium dematioideum CAS 14930-96-2View Details
Cytochalasin B, Helminthosporium dematioideum CAS 14930-96-2View Details
14930-96-2 -
 Cytochalasin B from Drechslera dematioidea CAS 14930-96-2View Details
Cytochalasin B from Drechslera dematioidea CAS 14930-96-2View Details
14930-96-2 -
 Cytochalasin B from Drechslera dematioidea CAS 14930-96-2View Details
Cytochalasin B from Drechslera dematioidea CAS 14930-96-2View Details
14930-96-2 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
