Cyhexatin
- CAS NO.:13121-70-5
- Empirical Formula: C18H34OSn
- Molecular Weight: 385.17
- MDL number: MFCD00078642
- EINECS: 236-049-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
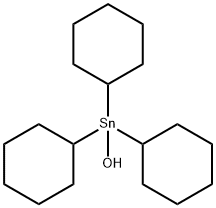
What is Cyhexatin?
Description
Cyhexatin is a colorless to white, nearly odorless, crystalline powder. Molecular weight=385.16;Boiling point=227℃(decomposes); Freezing/Meltingpoint=195-198℃. Practically insoluble in water
Chemical properties
Cyhexatin is a colorless to white, nearly odor- less, crystalline powder.
The Uses of Cyhexatin
Cyhexatin is a derivative of tricyclohexyltin and an effective acaricide used in the control of spider mites.
The Uses of Cyhexatin
Acaricide.
The Uses of Cyhexatin
Cyhexatin is used to control the motile stages of phytophagous mites on pome and stone fruit, vines, hops, cotton, vegetables and ornament ah.
Definition
ChEBI: Cyhexatin is an organotin acaricide.
General Description
Technical Cyhexatin is a nearly odorless white crystalline powder that has no true melting point but degrades to bis(tricyclohexyl)tin oxide at 121 to 131°C which decomposes at 228°C; a melting point of 195-198°C is also reported. Very insoluble in water (less than 1 mg/L at 25°C), but wettable by water. Soluble in some organic solvents (acetone 1.3 g/L; xylenes 3.6 g/L; carbon tetrachloride 28 g/L; dichloromethane 34 g/L). Used as an acaricide (an agent to kill plant-feeding mites) in almonds, walnuts, hops and some fruits.
Reactivity Profile
Cyhexatin is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Soluble in some organic solvents (acetone 1.3 g/L; xylenes 3.6 g/L; carbon tetrachloride 28 g/L; dichloromethane 34 g/L). Stable in aqueous suspensions in neutral and alkaline pH (above pH 6), but reacts exothermically as a base in the presence of strong acids to form salts. Converts to dicyclohexyltin oxide and further to cyclohexylstannoic acid upon exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. Experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also TIN COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Used as an agricultural chemical and pesticide. A potential danger to those involved in the manu- facture, formulation, and application of this acaricide (miticide).
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Speed in removing material from skinis of extreme importance. Shampoo hair promptly if contaminated. Seek medical attention immediately. If thischemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, beginrescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Metabolic pathway
There is little published information of the degradation and metabolism of cyhexatin. However, useful information on the fate of cyhexatin in a water/sediment system can be deduced from published data on azoc yclotin.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, dark,well-ventilated area away from oxidizers.
Shipping
UN2786 Organotin pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous material. UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1- Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Cyhexatin is stable to hydrolysis at temperatures up to 100 °C from slightly acid (pH 6) to alkaline conditions (PM).
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with strong oxidizers. May react exothermically as base in the Incompatible with strong oxidizers. May react exothermically as base in the Incompatible with strong oxidizers. Reacts exothermically as base in the presence of strong acids, forming salts. Keep away from ultraviolet radiation which may cause conver- sion to dicyclohexyltin oxide and further to cyclohexylstan- noic acid .
Properties of Cyhexatin
| Melting point: | 195-198°C |
| Boiling point: | 426.1±28.0 °C(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 3×10-7 Pa (20 °C) |
| Flash point: | >100 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated) |
| pka | 6.76±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | solid |
| Water Solubility | <1 mg l-1(25 °C) |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 4: no reaction with water under neutral conditions |
| Merck | 13,2789 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 13121-70-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cyhexatin (13121-70-5) |
Safety information for Cyhexatin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment |
Computed Descriptors for Cyhexatin
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Cyhexatin 98.00% CAS 13121-70-5View Details
Cyhexatin 98.00% CAS 13121-70-5View Details
13121-70-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8