Copper
Synonym(s):Copper;
- CAS NO.:7440-50-8
- Empirical Formula: Cu
- Molecular Weight: 63.55
- MDL number: MFCD00239961
- EINECS: 231-159-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 08:02:36

What is Copper?
Absorption
Copper absorption varies inversely with intake. Absorption range is 12-65%.
Toxicity
Copper toxicity is belevied to be due to fenton-type redox reactions occuring with high copper concentrations which produce damaging reactive oxygen species .
Description
Copper has long been used by humans for a variety of reasons. The name copper derives from the Latin for the metal, cuprum, which is named for the Roman source, the island of Cyprus. Copper has been used in a variety of alloys; of particular importance among copper alloys is bronze, which comprised most of the tools and weapons of the age that bears its name. Brass, a copper–zinc alloy, is also highly used, for example, in brass musical instruments. Copper has also long been used as a building material, and owing to the metal’s malleability, as well as high thermal and electric conductivity, continues to find new uses. Copper and its compounds are naturally present in the earth’s crust. Natural discharges to air and water may be significant. Therefore, it is important to consider the background levels that are commonly found and distinguish these from high levels that may be found as a result of anthropogenic activity. Copper is emitted into the air naturally from windblown dust, volcanoes, and anthropogenic sources, the largest of which are being primary copper smelters and ore processing facilities. It is associated with particulate matter. The mean concentration of copper in the atmosphere is 5–200 ng m-3.
Chemical properties
Reddish brown metal; the space lattice of Cu belongs to the cubic system, and its face-centered cubic lattice has a lattice constant of a=0.360775 nm (18°C).; density 8.92 g/cm3; Mohs hardness 2.5 to 3.0; Brinnel hardness 43 (annealed); electrical resistivity 1.71 microhm-cm at 25°C; Poisson's ratio 0.33; melts at 1,083°C; vaporizes at 2,567°C; insoluble in water; dissolves in nitric acid and hot sulfuric acid; slightly soluble in hydrochloric acid; also soluble in ammonium hydroxide, ammonium carbonate and potassium cyanide solutions.
Chemical properties
Copper is a reddish-brown metal which occurs free or in ores, such as malachite, cuprite, and chalcopyrite.
Copper is a group IB transition element on the periodic table and exists in four oxidation states: Cu0 Cu1+ (cuprous ion), Cu1+ (cupric ion), and Cu3+. In a natural state, copper is likely to be found in a variety of solid salts and compounds, but it can be found in the elemental form as well. Copper compounds generally are blue or green. The common green color of copper on exposure to air is a basic carbonate compound.

Copper is insoluble in water but readily dissolves in hot sulfuric and nitric acids. The vapor pressure is negligible at low temperatures, but in an industrial setting, in which very high temperatures are used to smelt copper ore, some potentially harmful copper fumes may be emitted. Although it not combustible in bulk, powdered copper may ignite. Fires and explosions may result from contact with oxidizing agents, strong mineral acids, alkali metals, and halogens (NIOSH, 2010).
Physical properties
Native copper has a distinctive reddish/brown color. Its first oxidation state (+1) formscompounds with copper ions named “cuprous,” also referred to as “copper(I),” and these ionsare easily oxidized with elements in group 16 (e.g., oxygen and sulfur) and elements in group17 (the halogens).Copper’s second oxidation state (+2) forms cupric compounds, also referred to as copper(II),which are more stable than copper(I) compounds. For example, copper in both oxidationstates can combine with fluorine: for copper(I) or cuprous fluoride, Cu+ + F- → CuF; and forcopper(II) or cupric fluoride, Cu2+ + 2F → CuF2.Copper’s melting point is 1,083°C, its boiling point is 2,567°C, and its density is 8.94g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are 32 known isotopes of copper, ranging from Cu-52 to Cu-80. Only twoof these 32 isotopes of copper are stable, and together they make up the amount ofnatural copper found in the Earth’s crust in the following proportions: Cu-63 = 69.17%and Cu-65 = 30.83%. All the other isotopes of copper are radioactive and are artificiallyproduced with half-lives ranging from a few nanoseconds to about 61 hours.
Origin of Name
Copper’s name comes from the Latin word cuprum or cyprium, which is related to the name “Cyprus,” the island where it was found by the ancient Romans.
Occurrence
Copper is the 26th most abundant element on Earth, but it is rare to find pure metallicdeposits. It is found in many different types of mineral ores, many of which are close to thesurface and easy to extract. It is found in two types of ores: (1) sulfide ores, such as covellite,chalcopyrite, bornite, chalcocite, and enargite; and (2) oxidized ores, such as tenorite, malachite, azurite, cuprite, chrysocolla, and brochanite.It is found in most countries of the world, but only a few high-grade deposits are costeffective to mine. Examples of some of its ores are cuprite (CuO2), tenorite (CuO), malachite[CuCO3 ? Cu(OH)2], chalcocite (Cu2S), covellite (CuS), bornite (Cu6FeS4), and chalcopyrite,also known as copper pyrite.Copper ores are found worldwide, in Russia, Chile, Canada, Zambia, and Zaire and, in theUnited States, in Arizona, Michigan, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Tennessee, and Utah.High-grade ores of 99% pure metal were found in the United States (and other countries), butmany of these native ore deposits have been mined over the past hundred years and are nowexhausted. Even so, many low-grade ores with concentrations of 10% to 80% pure copper stillexist and await a technology that will make them more profitable for exploitation.
History
The discovery of copper dates from prehistoric times. It is said to have been mined for more than 5000 years. It is one of man’s most important metals. Copper is reddish colored, takes on a bright metallic luster, and is malleable, ductile, and a good conductor of heat and electricity (second only to silver in electrical conductivity). The electrical industry is one of the greatest users of copper. Copper occasionally occurs native, and is found in many minerals such as cuprite, malachite, azurite, chalcopyrite, and bornite. Large copper ore deposits are found in the U.S., Chile, Zambia, Zaire, Peru, and Canada. The most important copper ores are the sulfides, oxides, and carbonates. From these, copper is obtained by smelting, leaching, and by electrolysis. Its alloys, brass and bronze, long used, are still very important; all American coins are now copper alloys; monel and gun metals also contain copper. The most important compounds are the oxide and the sulfate, blue vitriol; the latter has wide use as an agricultural poison and as an algicide in water purification. Copper compounds such as Fehling’s solution are widely used in analytical chemistry in tests for sugar. High-purity copper (99.999 + %) is readily available commercially. The price of commercial copper has fluctuated widely. The price of copper in December 2001 was about $1.50/kg. Natural copper contains two isotopes. Twenty-six other radioactive isotopes and isomers are known.
Characteristics
Copper, a versatile metal relatively easy to find, has made it useful for humans for manycenturies. It is malleable, ductile, and easily formed into many shapes such as ingots, pipes,wire, rods, tubing, sheets, powder, shot, and coins. Although copper is resistant to weak acids,it will dissolve in strong or hot acids. It resists atmospheric corrosion better than does iron.One reason is that it forms a bluish-green film (called patina) over its surface when exposed tomoist air or seawater. This coating of copper carbonate and copper sulfate provides a protective layer for the underlying metal that makes it ideal for use on boats, roofs, pipes, and coins.The surfaces of some copper church steeples and the Statue of Liberty have now oxidized toform a pleasing patina.One of copper’s most useful characteristics is that it is an excellent conductor of electricityand heat.
The Uses of Copper
Copper is a metal that occurs naturally throughout the environment, in rocks, soil, water, and air. Copper is an essential element in plants and animals (including humans), which means it is necessary for us to live. Therefore, plants and animals must absorb some copper from eating, drinking, and breathing.
The use of copper dates back to prehistoric times. The metal, its compounds, and alloys have numerous applications in every sphere of life–making it one of the most important metals. Practically all coinages in the world are made out of copper or its alloys. Its alloys, bronze and brass, date from ancient times. More modern alloys such as monel, gun metals, and berylliumcopper also have wide applications. The metal is an excellent conductor of electricity and heat and is used in electric wiring, switches and electrodes. Other applications are in plumbing, piping, roofing, cooking utensils, construction materials, and electroplated protective coatings. Its compounds, namely the oxides, sulfates, and chlorides, have numerous of commercial applications.
Copper is distributed widely in nature as sulfides, oxides, arsenides, arsenosulfides, and carbonates. It occurs in the minerals cuprite, chalcopyrite, azurite, chalcocite, malachite and bornite. Most copper minerals are sulfides or oxides. Native copper contains the metal in uncombined form.The principal copper minerals with their chemical compositions and percentage of copper are listed below:
The Uses of Copper
Copper is distributed widely in nature; it is the twenty-sixth most abundant element in the earth’s crust and is an essential element for many life forms. Copper is an abundant reddish, odorless metal that takes on a greenish-blue patina when exposed to the elements. It was the first metal worked by humans, and copper salts were among the first materials regularly used for therapeutic and cosmetic purposes.
Most animals require copper for certain biological processes. A deficiency of copper, as well as an excess, can have adverse health effects. The daily intake of copper in the United States ranges from 2 to 5 mg, almost all of which is excreted in the feces. Shellfish, seeds, nuts, and grains are rich sources of dietary copper. Minute amounts of cupric ion are absorbed and stored, mainly in the liver, blood, and brain. Copper is an essential cofactor in several enzyme systems (Shaligram and Campbell, 2012). Cuproenzymes catalyze important biochemical reactions, including iron absorption and hemebiosynthesis (Colotti et al., 2013).Copper deficiency may lead to anemia and neutropenia, and eventually to bone lesions resembling scurvy and to pathological fractures without hemorrhage (Kumar et al., 2005; Halfdanarson et al., 2008). Copper is also found in some intrauterine devices for the prevention of pregnancy (IPCS, 1998; Szymanski et al., 2012).
The Uses of Copper
Copper, being easy to mine and refine, has become a very versatile metal over the course ofcivilization. Early in human history, it was discovered that soft copper could be made harderand stronger when alloyed with other metals. Copper was and still is important to technologyand the development of civilizations. Over the past several thousand years, brass has foundmultiple uses, such as in coins, cooking utensils, and many types of instruments and hardwarethat are resistant to corrosion. Even today, brass is used to make musical instruments andbathroom, kitchen, and marine hardware. The U.S. one-cent penny was originally made ofcopper, but today the penny is made of zinc with a coating of copper. Copper is also an alloymetal used as a substitute for some of the silver in several other U.S. coins.Some common uses are in electrical wiring and components of electronic equipment,roofing, and pipes and plumbing and in the manufacturing of alloys such as brass, bronze,Monel metal, electroplating, jewelry, cooking utensils, insecticides, marine paints, cosmetics,and wood preservatives.Copper is second only to silver as an excellent conductor of electricity. This factor and itsavailability made it essential for the expansion of modern technologies. It was, and still is, adesired metal for wires to carry electricity, but the rapid expansion of modern communicationswould require more copper than could be made economically available. The solution has beento use optical fiberglass transmission cables as a substitute for copper wire. In addition, andeven more important, is the recent explosive growth of wireless transmission as a substitute forcopper wire in the communication industries.
Background
Copper is a transition metal and a trace element in the body. It is important to the function of many enzymes including cytochrome c oxidase, monoamine oxidase and superoxide dismutase . Copper is commonly used in contraceptive intrauterine devices (IUD) .
Indications
For use in the supplementation of total parenteral nutrition and in contraception with intrauterine devices .
Definition
Metallic element of atomic number 29, group IB of the periodic table, aw 63.546, valences 1, 2; two stable isotopes.
Production Methods
Copper can be found free in nature (although not as commonly
today). A naturally forming “patina” forms on copper
in the environment (e.g., Statue of Liberty in NewYork City).
The “patina” is commonly copper carbonate (from reaction
with water and carbon dioxide). This thin copper carbonate
layer covers exposed pure copper and prevents further oxidation.
The name copper is derived from the Latin word
cuprum, which, in turn, is derived from an earlier word,
cyprium or “Cyprium metal.” The Romans obtained much of
their copper from Cyprus, as the name implies.
Copper is found at a concentration of 50 ppm in the earth’s
crust, and its concentration in seawater is 0.001–0.02 ppm.
Although copper can also be obtained in an almost pure state
in nature, about 85% of the copper mined today is derived
from low-grade ores containing 2% or less of the metal. The
major ore is chalcopyrite (CuFeS2). Ores are removed by
open-pit mining as well as underground mining.
General Description
Reddish lustrous malleable odorless metallic solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Solid pieces are very slowly oxidized by air to give a green basic carbonate. Solid pieces become covered by a black oxide when heated in air. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Copper combines violently with chlorine trifluoride in the presence of carbon [Mellor 2, Supp. 1, 1956]. Is oxidized by sodium peroxide with incandescence [Mellor 2:490-93, 1946-1947]. Forms an unstable acetylide when acetylene is passed over samples that have been heated enough to form an oxide coating. Reacts more rapidly in powdered or granular form. Subject to explosive reaction then mixed in finely divided form with finely divided bromates chlorates and iodates of barium, calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, or zinc; these reactions are initiated by heat, percussion, and occasionally light friction [Mellor 2:310, 1946-1947]. A solution of sodium azide in Copper pipe with lead joints formed Copper azide and lead azide, both of these compounds can detonate [Klotz, 1973].
Hazard
Copper dust and powder, as well as a few of its compounds, are flammable, or even explosivewhen ignited in contained areas. Many of copper’s compounds are extremely toxic andpoisonous either with skin contact or when inhaled or ingested and should be handled by professionals in controlled environments. Even so, both plants and animals, including humans,require traces of copper for the proper metabolism of their foods.
Health Hazard
Occupational workers exposed to copper fumes, dust and mists in work areas develop symptoms of poisoning. These include irritation to the mucous membrane, nasal, and pharyngeal irritation; nasal perforation, eye irritation, metallic or sweet taste, dermatitis; prolonged periods of exposure to high concentrations cause anemia, adverse effects to the lung, liver, and kidney. The exposed worker also suffers from metal fume fever; chills, muscle aches, nausea, fever, dry throat, coughing, weakness, lassitude, irritation of the eyes and the upper respiratory tract, discolored skin and hair, and acute lung damage. Occupational workers exposed to copper dust suffer from gastrointestinal disturbances, headache, vertigo, drowsiness, and hepatomegaly. Vineyard workers chronically exposed to Bordeaux mixture (copper sulfate and lime) exhibit degenerative changes of the lungs and liver. Dermal exposure to copper may cause contact dermatitis in some individuals. Copper is required for collagen formation. Copper defi ciency is associated with atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular conditions. Any kind of imbalance of copper in the body causes health disorders that include, but are not limited to, arthritis, fatigue, adrenal burnout, insomnia, scoliosis, osteoporosis, heart disease, cancer, migraine headaches, seizures, gum disease, tooth decay, skin and hair problems, and uterine fi broids, endometriosis (in females). Copper defi ciency is associated with aneurysms, gout, anemia, and osteoporosis. Exposures to copper in the form of dusts and mists cause irritation to the eyes, respiratory system, mucous membrane, nasal, pharyngeal irritation cough, dyspnea (breathing diffi culty), and wheezing. Prolonged exposures are known to cause nasal perforation. Copper has caused anemia and damage to the lung, liver, and kidney in experimental laboratory animals. Reports have indicated that copper dusts and fumes are potential occupational carcinogens.
Agricultural Uses
Copper (Cu) is a transition element, belonging to Group 11 (formerly Group IA) of the Periodic Table. It is an important non-ferrous metal and a micronutrient with two distinct functions - to serve as a plant nutrient by being an activator or by being a part of certain enzymes like tyrosinase, lactase, ascorbic acid oxidase, cytochrome oxidase, etc., and secondly to play a role in many electron transfer processes.
adsorbed
Copper is a component of several enzyme complexes that influence carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism in plants. Its other function is to neutralize harmful soil conditions. This is done by adding copper sulphate to the soil to maximize the crop yield. The addition of large quantities of copper in certain peat soils in Kerala (India) was found to precipitate or inactivate some toxins present in the soil and neutralize the harmful conditions. About 70% of copper in a plant is found in chlorophyll and plays an important metabolic function.
Plants absorb copper through leaves as cupric ions (Cu2+)i n the form of a complex, such as EDTA. In soils, copper is found mostly in the cupric (Cu2+) form, adsorbed by clay minerals as well as organic complexes to an extent of 2 to 100ppm. The content of soil organic matter, pH and other metallic ions such as iron, manganese or aluminum influence the availability of copper in the soil. The amount of exchangeable copper decreases as the pH increases. Enhancing the concentration of aluminum beyond 0.1 ppm in soil solutions is found to decrease copper uptake in wheat plants. The ratio of copper to other metallic ions in the rooting medium is more important for plant growth than the absolute concentration of copper.
The retention of copper in soil increases in proportion to the organic matter content. Depending on their stability, copper-humus complexes make copper available to plants. The copper content in soil ranges from 5 to 60mg per kg, although both lower and higher values are not uncommon. The average amount of copper in soils is about 9 to 10mg per kg. The most familiar copper mineral in soils, chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), has copper in the cuprous (Cu+) form. These minerals have very low solubility which increases with pH. The nature of the reactions of copper with various organic matter is still to be fully explored. Soils which are high in organic matter are more prone to copper deficiencies than those with a lesser organic matter content.
The symptoms of copper deficiency vary with crops and are similar to those of potassium deficiency. Copper has low soil mobility and is considered to be deficient when the copper level is below 4 ppm in dry matter. Copper deficiency causes the early aging of chlorophyll and a subsequent fall in crop yield. Lucerne, carrot, onion, barley, oats, wheat and orange are sensitive to copper deficiency. Copper deficiency is common in vegetables, small grains and fruits growing on sands, organic soils or over-limed acidic soils. In corn, the youngest leaves become yellow and stunted. As the deficiency becomes severe, the young leaves turn pale and the older ones die In many vegetable crops, the leaves lack turgor and assume a bluish-green hue. Stem melanosis is a disease occuring in certain beet varieties due to copper deficiency. Organic soils are often copper deficient, as are calcareous soils, the pH of which falls in the range of 8.0to 8.4. A foliar spray of a few kilograms of copper salt per hectare is enough to correct copper deficiency for many years. Copper deficiency increases the incidence of lodging, when simultaneous growth occurs as a response to nitrogen fertilization. Since pollen and ovaries are very sensitive to copper deficiency, flowering and fruiting may be adversely affected or even become absent.
Like most micronutrients, excess copper is toxic to plants. It reduces the iron activity and leads to iron deficiency.
Copper toxicity symptoms include a reduced shoot vigor, a poorly developed and discolored root system and leaf-chlorosis. The toxicity can be seen at places of iron ore deposits and copper smelting. In citrus and lettuce, high copper levels induce iron chlorosis. Copper also significantly inhibits the uptake of zinc, and vice versa.
The most common copper fertilizers include copper sulphate and copper ammonium phosphate. Copper sulphate solution is sprayed on plant leaves. Copper ammonium phosphate is added directly to the soil or sprayed on plants as a suspension in water. Copper salts, produced as frits or chelate, are suitable for soil application. Copper chelate are available for soil as well as for foliar application, in view of the slow release of copper to plants and prevention of copper ions getting converted into insoluble compounds in the soil.
Industrial uses
The most important characteristics of copperimmersion coatings are their high electricalconductivity, good lubrication properties, andunique appearance. In addition to steel, they canbe applied to brass and aluminum and to printedcircuit boards.
Because of their conductivity, copper immersioncoatings have proved particularly usefulfor printed circuits. They are not especiallynoted for their decorative appeal, but can beused in applications where a particular appearanceis required, e.g., inexpensive, decorativehardware such as casket parts. Because of theirgood lubrication properties they can also beused on steel wire in die-forming operations.
Pharmacokinetics
Copper is incorporated into many enzymes throughout the body as an essential part of their function . Copper ions are known to reduce fertility when released from copper-containing IUDs .
Safety Profile
Toxic by inhalation. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Human systemic effects by ingestion: nausea and vomiting. See also COPPER COMPOUNDS. Liquid copper explodes on contact with water. Potentially explosive reaction with acetylenic compounds, 3-bromopropyne, ethylene oxide, lead azide, and ammonium nitrate. Iptes on contact with chlorine, chlorine trifluoride, fluorine (above 121℃), and hydrazinium nitrate (above 70'). Reacts violently with C2H2, bromates, chlorates, iodates, (Cl2 + OF2), dimethyl sulfoxide + trichloroacetic acid, ethylene oxide, H202, hydrazine mononitrate, hydrazoic acid, H2S + air, Pb(N3)2, K2O2, NaN3, Na2O2, sulfuric acid. Incandescent reaction with potassium dioxide. Incompatible with 1 -bromo-2 propyne.
Potential Exposure
Exposure to fume may occur in copper and brass plants; and during the welding of copper alloys; Metallic copper is an excellent conductor of electricity and is widely used in the electrical industry in all gauges of wire for circuitry, coil, and armature windings; high conductivity tubes; commutator bars, etc. It is made into castings, sheets, rods, tubing, and wire and is used in water and gas piping; roofing materials; cooking utensils; chemical and pharmaceutical equipment and coinage. Copper forms many important alloys: Be-Cu alloy, brass, bronze; gunmetal, bell metal; German silver; aluminum bronze, silicon bronze; phosphor bronze; and manganese bronze. Copper compounds are used as insecticides, algicides, molluscicides, plant fungicides, mordants, pigments, catalysts; as a copper supplement for pastures; and in the manufacture of powdered bronze paint and percussion caps. They are also utilized in analytical reagents, in paints for ships’ bottoms; in electroplating; and in the solvent for cellulose in rayon manufacture.
First aid
If copper dust or powder gets into the eyes,remove any contact lenses at once and irrigate immediatelyfor at least 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lowerlids. Seek medical attention immediately. If copper dusts orpowder contacts the skin, remove contaminated clothingand wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medicalattention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled,remove from exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart action has stopped.Transfer promptly to a medical facility. When this chemicalhas been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Note to physician: In case of fume inhalation, treat pulmonary edema. Give prednisone or other corticosteroid orallyto reduce tissue response to fume. Positive-pressure ventilation may be necessary. Treat metal fume fever with bedrest, analgesics, and antipyretics. The symptoms of metalfume fever may be delayed for 4-12 h following exposure:it may last less than 36 h
Environmental Fate
Copper reduces glutathione, which is necessary for normal cell viability. The amino acid transferases are inhibited in the presence of excess copper; lipid peroxidation also occurs. Copper combines with thiol groups, which reduces the oxidation state II to I in copper and oxidizes the thiol groups to disulfides, especially in the cell membrane.
Metabolism
Not Available
Storage
Color Code—Red Stripe (copper powder)Flammability Hazard: Do not store in the same area as otherflammable materials. Prior to working with copper youshould be trained on its proper handling and storage. Storein tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated areaaway from acetylene gas, oxidizers, and other incompatiblematerials listed above. Use only nonsparking tools andequipment, especially when opening and closing containersof this chemical. Copper powder: sources of ignition, suchas smoking and open flames, are prohibited where copperpowder is used, handled, or stored in a manner that couldcreate a potential fire or explosion hazard. Store to avoidconditions which create fumes or fine dusts.
Shipping
UN3089 Metal powders, flammable, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid. Copper, elemental is not specifically cited in DOT’s PerformanceOriented Packaging Standards.
Toxicity evaluation
The largest release of copper by far is to land, and the major
sources of release are mining and milling operations, agriculture,
solid waste, and sludge from publicly owned treatment
works. Sediment is an important sink and reservoir for copper. In relatively clean sediment, the copper concentration is <50 ppm; polluted sediment may contain several thousand ppm of copper.
Copper is released to water as a result of natural weathering of soil and discharges from industries and sewage treatment plants. Copper compounds may also be intentionally applied to water to kill algae. Of special concern is copper that gets into drinking water from the water distribution system.
The major species of soluble copper found in freshwater,
seawater, and a combination of the two over a range of pHs is
Cu2+, Cu(HCO3)+, and Cu(OH)2. At the pH values and
carbonate concentrations characteristic of natural waters, most
dissolved Cu(II) exists as carbonate complexes rather than as
free (hydrated) cupric ions.
The transport of copper is largely dependent on source
characteristics as well as particle size; however, it can bind to
many inorganic ligands. Some copper compounds are water
soluble, and this can increase transport distance, as well as
likelihood the metal will be taken up by organisms or adsorb to
organic residues.
Incompatibilities
Copper dust, fume, and mists form shock-sensitive compounds with acetylene gas, acetylenic compounds, azides, and ethylene oxides. Incompatible with acids, chemically active metals, such as potassium; sodium, magnesium, zinc, zirconium, strong bases. Violent reaction, possibly explosive, if finely divided material come in contact with strong oxidizers
Waste Disposal
Copper-containing wastes can be concentrated through the use of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or evaporators to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and sent to a reclaiming firm. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated through the use of caustics and the sludge deposited in a chemical waste landfill. Copper-containing soluble wastes can be concentrated through the use of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or evaporators to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and sent to a reclaiming firm. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated through the use of caustics and the sludge deposited in a chemical waste landfill
Properties of Copper
| Melting point: | 1083.4 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 2567 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 8.94 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| Flash point: | -23 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | slightly soluble in dilute acid solutions |
| form | wire |
| color | Rust-brownish |
| Specific Gravity | 8.92 |
| Resistivity | 1.673 μΩ-cm, 20°C |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Sensitive | air sensitive |
| Merck | 13,2545 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 1 mg(Cu)/m3 (dusts and mists)
(ACGIH and MSHA); 0.2 mg/m3 (fumes)
(ACGIH). |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, active halogen compounds, chlorine, fluorine, iodine, bromine, ammonia. May react explosively with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-50-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Copper(7440-50-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Copper (7440-50-8) |
Safety information for Copper
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. |
Computed Descriptors for Copper
| InChIKey | RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Copper manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Vineeth Precious Catalysts Pvt. Ltd.
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
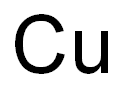


You may like
-
 Copper 99%View Details
Copper 99%View Details -
 Copper Powder 98%View Details
Copper Powder 98%View Details -
 Copper Powder 98%View Details
Copper Powder 98%View Details -
 Copper rod, 6.35mm (0.25 in.) dia. CAS 7440-50-8View Details
Copper rod, 6.35mm (0.25 in.) dia. CAS 7440-50-8View Details
7440-50-8 -
 Copper rod, 6.35mm (0.25 in.) dia. CAS 7440-50-8View Details
Copper rod, 6.35mm (0.25 in.) dia. CAS 7440-50-8View Details
7440-50-8 -
 Copper powder, 99% 99%View Details
Copper powder, 99% 99%View Details -
 Copper bronze, powder CASView Details
Copper bronze, powder CASView Details -
 Copper ICP standard CASView Details
Copper ICP standard CASView Details
