Choline salicylate
- CAS NO.:2016-36-6
- Empirical Formula: C12H19NO4
- Molecular Weight: 241.28
- MDL number: MFCD00242760
- EINECS: 217-948-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:35
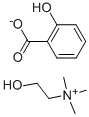
What is Choline salicylate?
Absorption
Onset: 1-2 hr after ingestion
In the oral form, choline salicylate is absorbed across the buccal mucosa. There is a need for caution not to exceed the stated dose and monitor for any signs of suggested salicylism, especially when this drug is used for infants .
In one study, it was found that this drug was more rapidly absorbed than ASA (absorption t1/2 = 0.1 vs 0.36 h) .
Toxicity
LD50, oral in mouse: 2690mg/kg .
Ld50, subcutaneous in mouse: 1gm/kg .
Interferes with thyroid function test .
Gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, fatigue, hypersensitivity reactions, skin eruptions, hemolytic anemia, weakness, dyspnoea; local irritation (rectally); Reye's syndrome.
Potentially Fatal: Paroxysmal bronchospasm; hepatotoxicity; renal impairment/failure; thrombocytopenia, iron-deficiency anemia, occult bleeding, leukopenia; mild chronic salicylate intoxication .
Salicylate poisoning is normally associated with plasma concentrations >350 mg/L (2.5 mmol/L). Most adult deaths due to salicylate poisoning occur in patients whose serum concentrations of salicylate are over 700 mg/L (5.1 mmol/L). Single doses of less than 100 mg/kg are very unlikely to lead to serious poisoning. Patients should be provided with supportive therapy or treatment for salicylate poisoning as necessary. This may include treatment like activated charcoal, urinary alkalinization and, in severe cases, hemodialysis .
Description
Choline salicylate is absorbed more rapidly than aspirin and produces higher salicylate plasma levels. It is available as a mint-flavored liquid.
Originator
Arthropan ,Purdue , US,1959
The Uses of Choline salicylate
Choline Salicylate displays protective effects in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. It has the potential to relieve pain associated with mouth ulcers.
Background
Choline salicylate is an anti-inflammatory pain reliever agent that is related to aspirin. It is used to decrease swelling and to treat mild-moderate pain. It is used to treat arthritis in both children and adults. This medicine can also be used for fever .
Choline Salicylate is the choline salt of salicylic acid, used as an analgesic, antipyretic and antirheumatic. It relieves mild to moderate pain and reduce fever and inflammation or swelling. Choline salicylate is effective in the treatment of gout, rheumatic fever, rheumatoid arthritis and muscle injuries .
This drug is also a main ingredient in teething gels to relieve pains associated with tooth growth in the infant population . The UK government has regulated its use, due to toxicity in those under 16 years of age. Topical oral salicylate gels are no longer indicated for people younger than 16 years for pain associated with infant teething, orthodontic devices, cold sores, or mouth ulcers .
Indications
The oral gel is indicated for the relief of pain and discomfort of common mouth ulcers, cold sores, denture sore spots, infant teething and mouth ulcers, and sore spots due to orthodontic devices in children .
Definition
ChEBI: Choline salicylate is a hydroxybenzoic acid. It is functionally related to a salicylic acid.
Manufacturing Process
A method of preparation is to react an acid salt of choline (such as choline chloride or choline bromide) with an alkaline salt of salicylic acid (such as sodium salicylate, potassium salicylate, or magnesium salicylate) in an alcoholic media.
brand name
Arthropan (Purdue Frederick).
Therapeutic Function
Analgesic; Antipyretic
Pharmacokinetics
This is an anti-inflammatory and antipyretic medication , .
If is often used in oral gel form for the relief of pain, discomfort, and inflammation caused by common mouth ulcers, cold sores, denture and sore spots, as well as mouth ulcers, and sore spots because of orthodontic devices .
Clinical Use
Choline salicylate has a lower incidence of GI side effects compared with aspirin, and it has been shown to be particularly useful in treating juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, in which aspirin was ineffective.
Metabolism
The metabolism of salicylic acid is by glycine and phenolic or acyl glucuronate conjugation with small amounts of the drug undergoing hydroxylation.
Properties of Choline salicylate
| Melting point: | 49.5-50.0° |
| Boiling point: | 384.06°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1442 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4596 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 183 °C |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Colourless to Light Brown Oil to Waxy |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethanaminium, 2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-, salt with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid (1:1) (2016-36-6) |
Safety information for Choline salicylate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Choline salicylate
Abamectin manufacturer
Shreenath Chemicals
Ralington Pharma
S S Pharmachem
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2016-36-6 Choline Salicylate Soln . 48-52 % / 80 % & 97 % w / 98%View Details
2016-36-6 Choline Salicylate Soln . 48-52 % / 80 % & 97 % w / 98%View Details
2016-36-6 -
 Choline salicylate 2016-36-6 98%View Details
Choline salicylate 2016-36-6 98%View Details
2016-36-6 -
 2016-36-6 Choline salicylate 98%View Details
2016-36-6 Choline salicylate 98%View Details
2016-36-6 -
 2016-36-6 98%View Details
2016-36-6 98%View Details
2016-36-6 -
 CHOLINE SALICYLATE CAS 2016-36-6View Details
CHOLINE SALICYLATE CAS 2016-36-6View Details
2016-36-6 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4