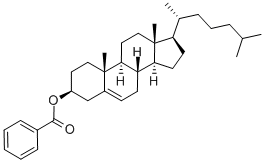
Cholesterol
Synonym(s):Cholesterol;Cholesterol from wool fat;Cholesterol, Highly Purified - CAS 57-88-5 - Calbiochem;Cholesterolum;Synthetic cholesterol
- CAS NO.:57-88-5
- Empirical Formula: C27H46O
- Molecular Weight: 386.66
- MDL number: MFCD00003646
- EINECS: 200-353-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
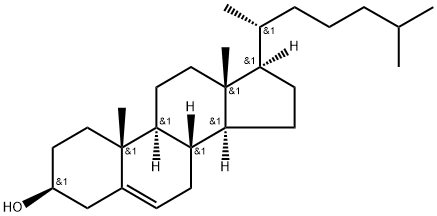
What is Cholesterol?
Description
Cholesterol is a soft waxy substance that is a steroidal alcohol or sterol. It is the most abundant
steroid in the human body and is a component of every cell. Cholesterol is essential to life
and most animals and many plants contain this compound. Cholesterol biosynthesis occurs
primarily in the liver, but it may be produced in other organs. A number of other substances
are synthesized from cholesterol including vitamin D, steroid hormones (including the sex
hormones), and bile salts. Cholesterol resides mainly in cell membranes.
Humans produce about 1 gram of cholesterol daily in the liver. Dietary cholesterol is consumed
through food. High cholesterol foods are associated with saturated fats and trans-fatty
acids (commonly called trans fats). Dietary cholesterol comes from animal products (plants
contain minute amounts of cholesterol) such as meats and dairy products.
Description
Cholesterol strengthens cell walls, helps the body digest fat, and serves as a building block for hormones. The human liver makes its own cholesterol, and animal-derived foods are a dietary source. In the liver, cholesterol molecules bind to protein molecules to form lipoproteins that can travel through the bloodstream.
Chemical properties
White to faintly yellow cryst. powder
Chemical properties
Cholesterol occurs as white or faintly yellow, almost odorless, pearly leaflets, needles, powder, or granules. On prolonged exposure to light and air, cholesterol acquires a yellow to tan color.
History
Cholesterol was discovered in 1769 by Poulletier dela Salle (1719–1787), who isolated the compound from bile and gallstones. It was rediscovered by Michel Eugène Chevreul (1786–1889) in 1815 and named cholesterine. The name comes from the Greek words khole meaning bile and steros meaning solid or stiff . The “ine” ending was later changed to “ol” to designate it as an alcohol.
The Uses of Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a major component of all biological membranes; ~25% of total brain lipid is Cholesterol. Cholesterol is the principal sterol of the higher animals. Cholesterol was found in all body tis sues, especial in the brain, spinal cord, and in animal fats or oils. Cholesterol is the main constituent of gallstones.
The Uses of Cholesterol
Cholesterol is commonly associated with cardiovascular disease and its routine measurement is used to measure its potential health risk. High blood serum cholesterol levels are often correlated with excessive plaque deposits in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries. Although high total blood cholesterol levels are associated with heart disease, it is important to distinguish between types of cholesterol when interpreting cholesterol levels. Cholesterol has been labeled as good and bad depending on its physiological role. Forms of cholesterol depend on the lipoproteins that are associated with it. Lowdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL cholesterol) is often referred to as bad cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) is identified as good cholesterol. An understanding of the difference between LDL and HDL cholesterol requires an understanding of substances associated with cholesterol in the body. Cholesterol is a lipid so it has very low solubility in water and blood. For the cholesterol synthesized in the liver to be delivered by the bloodstream to the rest of the body, the liver manufactures lipoproteins that can be viewed as carriers for cholesterol (and triglycerides).
The Uses of Cholesterol
analeptic, antibacterial
The Uses of Cholesterol
Cholesterol be used as pharmaceutical intermediates and be used as synthetic materials of liquid crystal polymers.
The Uses of Cholesterol
cholesterol is a moisturizer and emollient that acts as a powerful emulsifier in water-in-oil systems. Cholesterol is a fat-like substance found in plant and animal cells. It is also present in the secretion of the sebaceous glands and, therefore, is a component of the fat on the skin’s surface. It is considered a noncomedogenic raw material. It may sometimes be obtained from sheep’s wool wax.
What are the applications of Application
Cholesterol is a structural component of cell membranes
Background
The principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils.
Definition
ChEBI: A cholestanoid consisting of cholestane having a double bond at the 5,6-position as well as a 3beta-hydroxy group.
Production Methods
The commercial material is normally obtained from the spinal cord
of cattle by extraction with petroleum ethers, but it may also be
obtained from wool fat. Purification is normally accomplished by
repeated bromination. Cholesterol may also be produced by entirely
synthetic means.
Cholesterol produced from animal organs will always contain
cholestanol and other saturated sterols.
Definition
cholesterol: A sterol occurringwidely in animal tissues and also insome higher plants and algae. It canexist as a free sterol or esterified witha long-chain fatty acid. Cholesterol isabsorbed through the intestine ormanufactured in the liver. It servesprincipally as a constituent of bloodplasma lipoproteins and of thelipid–protein complexes that formcell membranes. It is also importantas a precursor of various steroids, especiallythe bile acids, sex hormones,and adrenocorticoid hormones. Thederivative 7-dehydrocholesterol isconverted to vitamin D3 by the actionof sunlight on skin. Increased levelsof dietary and blood cholesterol havebeen associated with atherosclerosis,a condition in which lipids accumulateon the inner walls of arteries andeventually obstruct blood flow.
General Description
Cholesterol is a minor sterol present in plants. It is majorly associated with the plant membranes and is a constituent of leaf surface lipids.
Hazard
Questionable carcinogen.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Cholesterol is used in cosmetics and topical pharmaceutical
formulations at concentrations of 0.3–5.0% w/w as an emulsifying
agent. It imparts water-absorbing power to an ointment and has
emollient activity.
Cholesterol also has a physiological role. It is the major sterol of
the higher animals, and it is found in all body tissues, especially in
the brain and spinal cord. It is also the main constituent of
gallstones.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cholesterol is a lipid that makes up about 20-25% of the structural components of the cell membranes. It determines the fluidity and permeability of the membrane, making it permeable to water but not to ions and protons. Cholesterol also regulates the functions of the transporters and signaling proteins present on the plasma membrane. The major sites of cholesterol synthesis are small intestine and liver.
Safety Profile
Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Mutation data reported. Used in pharmaceutical and dermal preparations as an emulsifying agent. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
Cholesterol is generally regarded as an essentially nontoxic and
nonirritant material at the levels employed as an excipient. It has,
however, exhibited experimental teratogenic and reproductive
effects, and mutation data have been reported.
Cholesterol is often derived from animal sources and this must
be done in accordance with the regulations for human consumption.
The risk of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)
contamination has caused some concern over the use of animalderived
cholesterol in pharmaceutical products. However, synthetic
methods of cholesterol manufacture have been developed.
Metabolism
Not Available
storage
Cholesterol is stable and should be stored in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Purification Methods
Crystallise cholesterol from ethyl acetate, EtOH or isopropyl ether/MeOH. [Hiromitsu & Kevan J Am Chem Soc 109 4501 1987.] For extensive details of purification through the dibromide, see Fieser [J Am Chem Soc 75 5421 1953] and Schwenk and Werthessen [Arch Biochem Biophys 40 334 1952], and by repeated crystallisation from acetic acid; see Fieser [J Am Chem Soc 75 4395 1953]. Like many sterols, cholesterol gives colour reactions with conc H2SO4: When cholesterol is dissolved in a small volume of CHCl3 and mixed with conc H2SO4, the colour of the organic layer becomes crimson, then changes to purple and on further standing in air it turns to blue, then green and finally yellow. The H2SO4 layer develops a green fluorescence. [Beilstein 6 III 2607, 6 IV 4000.]
Incompatibilities
Cholesterol is precipitated by digitonin.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections;
ophthalmic, topical, and vaginal preparations).
Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included
in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Cholesterol
| Melting point: | 148-150 °C |
| Boiling point: | 360 °C |
| alpha | -36 º (c=2, dioxane) |
| Density | 1.06 |
| refractive index | 1.5250 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 250 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: 0.002 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 15.03±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Specific Gravity | 1.067 |
| Odor | wh. or faintly yel. pearly granules or crystals, almost odorless |
| Water Solubility | negligible |
| Merck | 14,2201 |
| BRN | 1915888 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.9(Ambient) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 57-88-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cholesterol(57-88-5) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 31, Sup 7) 1987 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cholesterol (57-88-5) |
Safety information for Cholesterol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H351:Carcinogenicity H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Cholesterol
| InChIKey | HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N |
Cholesterol manufacturer
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



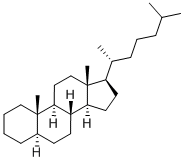

You may like
-
 Cholesterol supplierView Details
Cholesterol supplierView Details
57-88-5 -
 Cholesterol ex. Sheep Wool (Lanolin) extrapure AR CAS 57-88-5View Details
Cholesterol ex. Sheep Wool (Lanolin) extrapure AR CAS 57-88-5View Details
57-88-5 -
 Cholesterol ex. Sheep Wool (Lanolin) Reference Standard Grade for molecular biology CAS 57-88-5View Details
Cholesterol ex. Sheep Wool (Lanolin) Reference Standard Grade for molecular biology CAS 57-88-5View Details
57-88-5 -
 Cholesterol CAS 57-88-5View Details
Cholesterol CAS 57-88-5View Details
57-88-5 -
 Cholesterol, 97% CAS 57-88-5View Details
Cholesterol, 97% CAS 57-88-5View Details
57-88-5 -
 Cholesterol (stabilized with α-Tocopherol) CAS 57-88-5View Details
Cholesterol (stabilized with α-Tocopherol) CAS 57-88-5View Details
57-88-5 -
 Cholesterol (ER) CAS 57-88-5View Details
Cholesterol (ER) CAS 57-88-5View Details
57-88-5 -
 Cholesterol, GR 99%+ CAS 57-88-5View Details
Cholesterol, GR 99%+ CAS 57-88-5View Details
57-88-5