Castor oil
Synonym(s):Ricini oleum virginale
- CAS NO.:8001-79-4
- Empirical Formula: C57H104O9
- Molecular Weight: 933.43026
- MDL number: MFCD00130746
- EINECS: 232-293-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:51
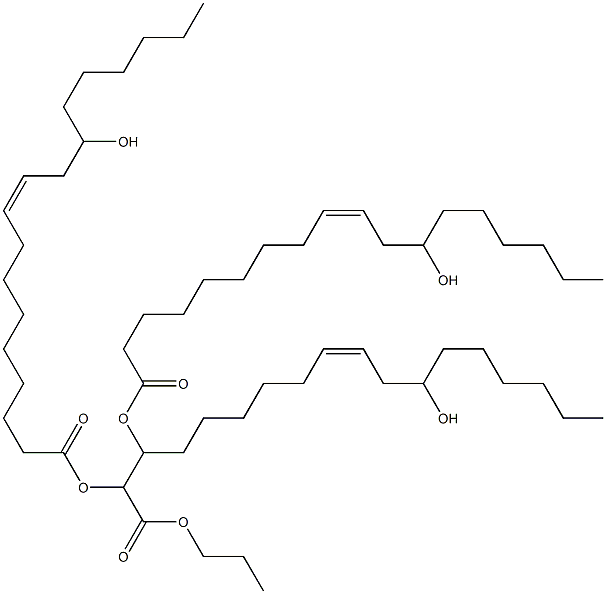
What is Castor oil?
Chemical properties
Castor oil is a clear, almost colorless or pale yellow-colored viscous oil. It has a slight odor and a taste that is initially bland but afterwards slightly acrid. It is soluble in alcohol, and is miscible with absolute alcohol, glacial acetic acid, chloroform and ether.
commercial grade pale grade special grade
refractive index (20°C) 1,482 - 1,483 1,482 - 1,483 1,482 - 1,483
specific gravity (15°C) 0,982 - 0,933 0,982 - 0,933 0,982 - 0,933
viscosity (25°C) Poise 1,6 - 2,8 1,6 - 2,8 1,6 - 2,8
viscosity Gardner scale G – I G – I G – I
colour max. 8 max. 6 max. 5
acid value mg KOH/g max.6 max. 4
iodine value (Wijs) g I2/100g min. 130 min. 130 min. 130
hydroxyl value mg KOH/g max. 25 max. 20
Occurrence
Castor is a perennial found in India and Africa.
The Uses of Castor oil
Castor oil has a wide range of uses in medicine, industry, and pharmaceuticals. Topical castor oil helps heal wounds and reduce inflammation and infection. Castor oil ointments can help heal ulcers. Topical applications can help relieve joint pain, muscle aches, headaches, and backaches. In beauty products, castor oil helps moisturize the skin and nourish the hair. Additionally, castor oil is used as a release agent and anti-sticking agent in hard candy production. It is also used as an industrial lubricant and as a component of biodiesel.
Production Methods
Castor oil is the fixed oil obtained by cold-expression of the seeds of Ricinus communis Linne (Fam. Euphorbiaceae). No other substances are added to the oil.
Definition
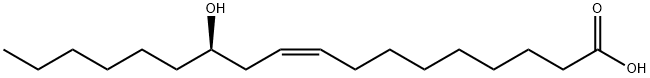
castor oil: A pale-coloured oil extractedfrom the castor-oil plant. Itcontains a mixture of glyceridesof fatty acids, the predominantacid being ricinoleic acid,C17H32(OH)COOH. It is used as adrying oil in paints and varnishesand medically as a laxative.
Indications
Castor oil is a bland oil that is hydrolyzed in the gut to yield ricinoleic acid, the active purging agent. This hydrolysis requires bile, a fact that is sometimes overlooked when castor oil is given as a laxative before radiography in biliary obstruction.The ricinoleic acid acts on the ileum and colon to induce an increased fluid secretion and colonic contraction.
Essential oil composition
The oil is a mixture of triglycerides of which 75 to 90% is ricinoleic acid.* This mixture is hydrolyzed to release ricinoleic acid, which exerts a cathartic effect. The cake remaining after the extraction of the oil is the castor pomace. The phytotoxins ricin and ricinine are found in the seed cake and oil. Ricin is a glycoproptein containing neutral A chain and acidic B chain connected by disulfur bonds.
General Description
Pale-yellow or almost colorless transparent viscous liquid with a faint mild odor and nauseating taste. Density 0.95 g / cm3. A mixture of glycerides, chiefly ricinolein (the glyceride of ricinoleic acid) .
Reactivity Profile
Castor oil can develop heat spontaneously in the air. [Hawley]. Reacts with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Heat is also generated by interaction with caustic solutions. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing with alkali metals and hydrides.
Health Hazard
If ingested causes severe diarrhea.
Fire Hazard
Castor oil is combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Castor oil is a versatile substance with applications in cosmetics, food products, and pharmaceutical formulations:
1. In Pharmaceutical Formulations: It is commonly used in topical creams and ointments at concentrations ranging from 5% to 12.5%. Additionally, castor oil finds use in oral tablet and capsule formulations, ophthalmic emulsions, and serves as a solvent for intramuscular injections.
2. Therapeutic Use: Historically, castor oil was administered orally for its laxative effects. However, this method of use is now considered obsolete.
3. Cosmetics and Food Products: Beyond its pharmaceutical applications, castor oil is also widely utilized in the cosmetics industry and food products, although the specific uses in these industries are not detailed in the provided content.
Safety Profile
An allergen. A human skin and eye irritant. Combustible when exposed to heat. Spontaneous heating may occur. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical, fog, mist. See also CASTOR BEAN.
Safety
Castor oil is used in cosmetics and foods and orally, parenterally,
and topically in pharmaceutical formulations. It is generally
regarded as a relatively nontoxic and nonirritant material when
used as an excipient.
Castor oil has been used therapeutically as a laxative and oral
administration of large quantities may cause nausea, vomiting,
colic, and severe purgation. It should not be given when intestinal
obstruction is present.
Although widely used in topical preparations, including
ophthalmic formulations, castor oil has been associated with
some reports of allergic contact dermatitis, mainly to cosmetics
such as lipsticks.
Storage
Castor oil is stable and does not turn rancid unless subjected to
excessive heat. On heating at 3008℃ for several hours, castor oil
polymerizes and becomes soluble in mineral oil. When cooled to
08℃, it becomes more viscous.
Castor oil should be stored at a temperature not exceeding 258℃
in well-filled airtight containers protected from light.
Incompatibilities
Castor oil is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM injections; ophthalmic emulsions; oral capsules and tablets; topical creams, emulsions, ointments, and solutions). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Castor oil
| Melting point: | -10 °C |
| Boiling point: | 313 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.955 g/mL at 25 °C |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2263 | CASTOR OIL (RICINUS COMMUNIS L.) |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Room Temperature, under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Miscible with chloroform, diethyl ether, ethanol, glacial
acetic acid, and methanol; freely soluble in ethanol (95%) and
petroleum ether; practically insoluble in water; practically
insoluble in mineral oil unless mixed with another vegetable
oil. |
| form | Viscous Hygroscopic Liquid |
| Specific Gravity | 0.961 |
| color | Clear almost colorless or slightly yellow |
| Odor | Slight characteristic odor |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +5°, c = 5 in ethanol |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 20 ºC |
| FreezingPoint | -10℃ |
| Merck | 14,1898 |
| Dielectric constant | 4.8(14℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. May be light sensitive. |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Castor oil(8001-79-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Castor oil (8001-79-4) |
Safety information for Castor oil
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Castor oil
Castor oil manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran







You may like
-
 Castor Oil 99%View Details
Castor Oil 99%View Details -
 CASTOR OIL 99%View Details
CASTOR OIL 99%View Details -
 Dehydrated Castor Oil 99%View Details
Dehydrated Castor Oil 99%View Details -
 Castor oil 8001-79-4 98%View Details
Castor oil 8001-79-4 98%View Details
8001-79-4 -
 Castor oil CAS 8001-79-4View Details
Castor oil CAS 8001-79-4View Details
8001-79-4 -
 Castor oil, equivalent to of DAB, refined CAS 8001-79-4View Details
Castor oil, equivalent to of DAB, refined CAS 8001-79-4View Details
8001-79-4 -
 Castor oil, equivalent to USP CAS 8001-79-4View Details
Castor oil, equivalent to USP CAS 8001-79-4View Details
8001-79-4 -
 Castor oil CAS 8001-79-4View Details
Castor oil CAS 8001-79-4View Details
8001-79-4
