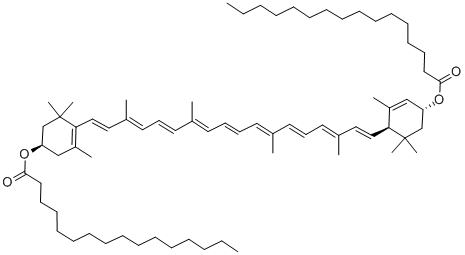
Carotene
Synonym(s):(+)-α-Carotene
- CAS NO.:7488-99-5
- Empirical Formula: C40H56
- Molecular Weight: 536.89
- MDL number: MFCD00136012
- EINECS: 200-838-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-10 14:44:25
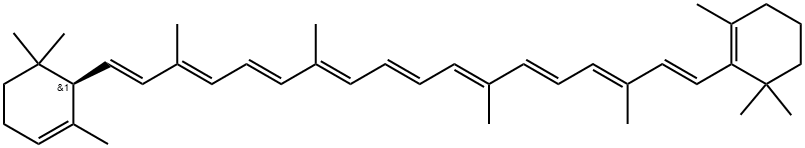
What is Carotene?
Description
α-Carotene is a precursor of vitamin A that has been found in various fruits and vegetables. It inhibits proliferation of GOTO human neuroblastoma cells more potently than β-carotene and halts the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase concomitantly with a reduction in the mRNA expression of the protooncogene N-Myc. It is also more potent than β-carotene in mouse models of skin and lung carcinogenesis and decreases the number of hepatomas in mice with spontaneous liver carcinogenesis when administered in drinking water at a concentration of 0.05%. α-Carotene levels are increased in patients with coronary heart disease and are inversely correlated with the risk of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer.
The Uses of Carotene
carotene is used to provide a red-orange color in cosmetic formulations. It is the primary yellow coloring component of butter, carrots, and egg yolk. Carotene is found in plants as well as in many animal tissues.
The Uses of Carotene
Carotene is a colorant and provitamin, being a hydrocarbon which is one of two subgroups of the carotenoids (yellow, orange, or red pig- ments). the other subgroup is xanthophylls. functions as a colorant with beta-apo-8-carotenal being a red-orange carotenoid and betabeing a yellow carotenoid. it is also a vitamin a precursor that is converted by the body to vitamin a. it is used in ice cream, cheese, and other dairy products.
The Uses of Carotene
(6''R)-β,ε-Carotene is a trans isomer of carotenoid pigment found in plants. It is a terpenoid hydrocarbon.
What are the applications of Application
α-Carotene is a control for HPLC
Definition
ChEBI: (6'R)-beta,epsilon-carotene is an alpha-carotene. It is an enantiomer of a (6'S)-beta,epsilon-carotene.
General Description
α-Carotene is a carotenoid, which shows anticarcinogenic activity.
Biochem/physiol Actions
One of the primary isomers of carotene, enantiomerically pure form of metabolite in carotenoid biosynthesis, biosynthesis of plant secondary metabolites, biosynthesis of terpenoids and steroids and the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites.
Purification Methods
Purify α-carotene by chromatography on columns of calcium hydroxide, alumina or magnesia. Crystallise it from CS2/MeOH, toluene/MeOH, diethyl ether/pet ether, or acetone/pet ether. Store it in the dark, under N2 or Ar at -20o. It gives a blue colour with max at 542nm when mixed with SbCl3 in CHCl3. [Karrer & Walker Helv Chim Acta 16 641 1933, Eugster et al. Helv Chim Acta 52 1729 1969, Eugster & Karrer Helv Chim Acta 38 610 1955, Strain J Biol Chem 105 523 1934, Beilstein 5 III 2457, 5 IV 2620.]
Properties of Carotene
| Melting point: | 187.50° (evacuated tube) |
| Boiling point: | 644.94°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 18643 +385° (c = 0.08 in benzene) |
| Density | 0.9380 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5630 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| color | Orange to Very Dark Orange |
| Odor | Slight characteristic |
| λmax | λ: 445-449 nm Amax |
| BRN | 3227603 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive, Temperature Sensitive |
Safety information for Carotene
Computed Descriptors for Carotene
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 α-Carotene CAS 7488-99-5View Details
α-Carotene CAS 7488-99-5View Details
7488-99-5 -
 α-Carotene CAS 7488-99-5View Details
α-Carotene CAS 7488-99-5View Details
7488-99-5 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
