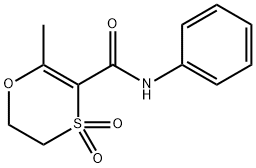
Carboxin
Synonym(s):Carbathiine
- CAS NO.:5234-68-4
- Empirical Formula: C12H13NO2S
- Molecular Weight: 235.3
- MDL number: MFCD00055403
- EINECS: 226-031-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
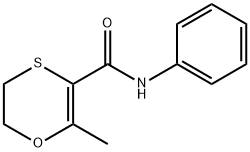
What is Carboxin?
Description
Carboxin is a white crystalline solid.Molecular weight=235.32; Freezing/Meltingpoint=91.5-95℃ (depending on crystal structure); Vaporpressure=1.78 x 10 2 7 mmHg. Practically insoluble inwater; solubility=25 mg/L; 0.15 g/L at 20℃.
Chemical properties
Carboxin is a white crystalline solid
The Uses of Carboxin
Carboxin is used as a seed treatment for cereals and as a seedling treatment on many cereals, beans, and vegetable crops and cotton. It is also used for the treatment of turf.
The Uses of Carboxin
Carboxine is an fungicide used for the control of fruit rot of custard apple.
The Uses of Carboxin
Systemic plant fungicide.
What are the applications of Application
Carboxine is An agricultural fungicide and seed treatment agent
Background
A systemic agricultural fungicide and seed treatment agent.
Definition
ChEBI: An anilide obtained by formal condensation of the amino group of aniline with the carboxy group of 2-methyl-5,6-dihydro-1,4-oxathiine-3-carboxylic acid. A fungicide for control of bunts and smuts normally that is normally used as a seed treatment.
General Description
Off-white crystals. Systemic fungicide and seed protectant.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide: Carboxin is a General Use Pesticide (GUP) and is used as a seed protectant. It is often used in combination with other fungicides such as thiram or captan. Carboxin is a systemic anilide fungicide. It is used as a seed treatment for control of smut, rot, and blight on barley, oats, rice, cotton, vegetables, corn and wheat. It is also used to control fairy rings on turf grass. Carboxin may be used to prevent the formation of these diseases or may be used to cure existing plant diseases. Also used as a wood preservative.
Trade name
CADAN®; CARBOXIN OXATHION PESTICIDE®; CASWELL No. 165 A®; D-735®; F-735®; FLO PRO V SEED PROTECTANT®[C]; KEMIKAR®; OXALIN®; PADAN®; SANVEX®; THIOBEL®; VEGETOX®; VITAFLO®; VITAVAX® 200FF; V 4X®
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by skin contact and possibly other routes. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the production, Formulation and application of this systemic fungicide, seed protectant and wood preservative
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Environmental Fate
Biological. The sulfoxidation of carboxin to carboxin sulfoxide by the fungus Ustilago
maydis was reported by Bollag and Liu (1990).
Soil. Carboxin oxidized in soil forming carboxin sulfoxide. The half-life in soil was
reported to be 24 hours (Worthing and Hance, 1991).
Plant. In plants (barley, cotton and wheat) and water, carboxin oxidizes to the corresponding sulfoxide (Worthing and Hance, 1991).
Metabolic pathway
Carboxin is a systemic fungicide which is very stable to hydrolysis but is readily oxidised at sulfur to a sulfoxide and a sulfone. The latter, oxycarboxin, is itself a commercial fungicide. Metabolism is mainly by oxidation at sulfur in soil, plants and animals but hydroxylation of the phenyl ring is also important in animals. Hydrolysis has been convincingly demonstrated only in plants (peanut).
Metabolism
Not Available
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store ina secure poison location. Prior to working with carboxin youshould be trained on its proper handling and storage. Storein tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area
Shipping
UN2588 Pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Carboxin is stable to hydrolysis (25 °C) at pH 5,7 and 9. Measurable rates
are seen only at higher pH and occur by nucleophilic attack by hydroxyl
ion at carbonyl. The half-life in 0.5 N NaOH is 107 days. Thus chemical
hydrolysis is not expected to be significant under environmental conditions
(El-Dib and Aly, 1976).
The compound is very labile to aqueous photolysis with a DT50 of
<3 hours (PM).
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Avoid heat and humidity. Thermal decomposition products may include cyanide gas and cyanide salts.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Properties of Carboxin
| Melting point: | 91.1-91.7°C |
| Boiling point: | 420.6±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.45 |
| vapor pressure | 2.5 x 10-5 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 14.31±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | Crystals |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 10.095 g/100 mL |
| Merck | 13,1837 |
| BRN | 983249 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Carboxin(5234-68-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carboxin (5234-68-4) |
Safety information for Carboxin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Carboxin
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![2-[(2-AMINOETHYL)THIO]ETHAN-1-OL](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/24304-84-5.gif)

You may like
-
 5234-68-4 Carboxin 98%View Details
5234-68-4 Carboxin 98%View Details
5234-68-4 -
 Carboxin CAS 5234-68-4View Details
Carboxin CAS 5234-68-4View Details
5234-68-4 -
 Carboxin 98% CAS 5234-68-4View Details
Carboxin 98% CAS 5234-68-4View Details
5234-68-4 -
 Carboxine, 98% CAS 5234-68-4View Details
Carboxine, 98% CAS 5234-68-4View Details
5234-68-4 -
 Carboxine CAS 5234-68-4View Details
Carboxine CAS 5234-68-4View Details
5234-68-4 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4