Captan
- CAS NO.:133-06-2
- Empirical Formula: C9H8Cl3NO2S
- Molecular Weight: 300.59
- MDL number: MFCD00041811
- EINECS: 205-087-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
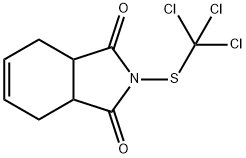
What is Captan?
Description
Captane is a pesticide belonging to the thiophtalimide group, mainly affecting agricultural workers. As a sensitizer and photosensitizer, it can induce contact urticaria. Its is used as a fungicide and a bacteriostatic agent in cosmetics and toiletries, particularily in shampoos. Cases of contact dermatitis were reoprted in painters, polishers and varnishers.
Chemical properties
Captan, when pure, is a colorless crystalline solid. The technical grade is a cream to yellow powder with a strong odor. It is commonly dissolved in a “carrier” which may be combustible.
The Uses of Captan
Captan is used to control a wide range of fungal diseases on many crops.
The Uses of Captan
Fungicide, often added to pesticide mixtures used to control diseases among fruits, vegetables.
The Uses of Captan
Fungicide; bacteriostat in soap.
The Uses of Captan
Fungicide used to control diseases on many fruit, ornamental and vegetable crops. Bacteriostat in soaps.
Definition
ChEBI: A dicarboximide that is 3a,4,7,7a-tetrahydrophthalimide in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen is replaced by a trichloromethyl group. A non-systemic fungicide introduced in the 1950s, it is widely used for the control of fungal diseases in fruits, vegetables, and ornamental crops.
General Description
Captan is a white solid dissolved in a liquid carrier. Captan is a water emulsifiable liquid. Captan can cause illness by inhalation, skin absorption and/or ingestion. The primary hazard of Captan is that Captan poses a threat to the environment. In case of release immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Since Captan is a liquid Captan can easily penetrate the soil to contaminate groundwater. Captan is used as a fungicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Slowly hydrolyzed in aqueous neutral and acidic media. Rapidly hydrolyzed in alkaline media. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Captan decomposes at or near the melting point. Captan is incompatible with strong alkaline and oxidizing materials, sulfur and (sulfur + moisture).
Hazard
A questionable carcinogen. A skin irritant. Avoid inhalation of dust or spray mist. Avoid con- tamination of feed and foodstuffs.
Health Hazard
Vapor irritates eyes. Ingestion causes depression, lachrymation, labored respiration, diarrhea.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating and toxic gases are produced in a fire; they may include sulfur dioxide, hydrogen chloride, phosgene, and oxides of nitrogen.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide: Most uses of captan on food crops in the United States have been canceled since 1989. It is still used in apple production, almonds and strawberries. It is often applied to packing and shipping boxes for fruits and vegetables. Captan is rapidly degraded in natural soil by chemical as well as biologic means (estimated half-life, days to weeks). It is also used as a preservative for awnings, draperies and leather, as a root dip and seed treatment. It is also added to paints, wallpaper paste, plastic and leather goods. There are over 320 federally registered pesticide products that contain captan.
Trade name
AACAPTAN®; AGROSOL S®[C]; AGROX® 2-WAY and 3-WAY[C]; AMERCIDE®; APRON®[C]; BEISTERGARD®; BANGTON®; BEAN SEED PROTECTANT®; CAPTANCAPTENEET® 26,538; CAPTAF®; CAPTAF®; CAPTAN® 50 W; CAPTAN SC®; CAPTEX®; CRIPTAN®; ESSO® FUNGICIDE 406; FLIT® 406; FUNGUS BAN® TYPE II; FUNGICIDE 406®; GLYODEX® 37-22; GRANOX PFM®; GUSTAFSON CAPTAN 30-DD; HEXACAP®; ISOTOX SEED TREATER® “D” and “F”; KAPTAN®; MALIPUR®; MERPAN®; MICRO-CHECK® 12; MIOSTAT®; NERACID®; ORTHOCIDE®; OSOCIDE®; POTATO SEED PIECE PROTECTANT®; SR 406®; STAUFFER CAPTAN®; TRIMEGOL®; VANICIDE®; VANICIDE® P-75; VANICIDE® 89; VANICIDE® 89RE; VANGARD® K; VANGUARD® K; VONDCAPTAN®
Contact allergens
A pesticide, belonging to the thiophthalimide group, mainly affects agricultural workers. Being sensitizer and photosensitizer, it can induce contact urticaria. It is used as a fungicide and a bacteriostatic agent in cosmetics and toiletries, particularly in shampoos. Cases of contact dermatitis were reported in painters, polishers, and varnishers
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic to humans by ingestion. Moderately toxic experimentally by ingestion and inhalation routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic and neoplastigenic data. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-, SOx, and NOx.
Potential Exposure
Captan is a thiophthalimide compound used as an agricultural fungicide for field crops and storage of produce and also as a preservative in cosmetics; an overthe-counter-drug.
First aid
f this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek med?ical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If556 Captanthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Environmental Fate
Biological. In water, captan reacted with the fungicide L-cysteine forming a compound
with an absorption maximum of 272 μm which was identified as 2-thiazolidinethione-4-
carboxylic acid. In addition, tetrahydrophthalimide also formed (Lukens and Sisler, 1958).
Soil. The half-lives of captan in soil ranged from 3.5 days (pH 6.4, moisture content
17.5%) to >50 days (pH 6.2, moisture content 1.6%) (Burchfield, 1959). The half-lives of
captan in a sandy loam, clay loam and an organic amended soil under non-sterile conditions
were 10–354, 3.4–587 and 7.0–213 days, respectively, while under sterile conditions the
half-lives were 9.4–373, 2.8–303 and 4.3–191 days, respectively (Schoen and Winterlin,
1987).
Chemical/Physical. Captan undergoes hydrolysis under neutral or alkaline conditions
yielding 4-cyclohexene-1,2-dicarboximide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen chloride and sulfur
(Wolfe et al., 1976a). The estimated hydrolysis half-life of captan in a phosphate buffer
solution at pH 7.07 and 28–29°C is 2.96 hours. Between the pH range 2 to 6, the estimated
hydrolysis half-life is 10.70 hours (Wolfe et al., 1976a). Worthing and Hance (1991)reported hydrolysis half-lives of 8.3–32.4 hours and <2 minutes at pH values 7 and 10,
respectively.
Decomposes at or near the melting point (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Metabolic pathway
Captan contains an unstable trichloromethylthio (sulfenyl) moiety that
has been shown to undergo rapid hydrolytic and metabolic degradation
to tetrahydrophthalimide (2).
Studies of the decomposition of [35S]captanw ith conidia of Neurospora
crassa (Richmond and Somers, 1968) showed that the trichloromethythio
moiety can be transferred to the sulfur atoms of thiols such as cysteine
and glutathione (Richmond and Somers, 1966). Thus, in the presence of
thiols such as glutathione, captan is cleaved at the N-S bond to form
thiophosgene (3) and other gaseous products such as hydrogen sulfide,
hydrogen chloride and carbonyl sulfide (see Scheme 2). Thiophosgene is
rapidly hydrolysed by water. The trichlormethythio group and thiophosgene
are believed to be intermediates in the formation of thiazolidine-2-
thione-4-carboxylic acid (4) which is an addition product with cysteine. A
thiazolidine derivative of glutathione is also formed (5). Biotransformation
of captan in mammals generates primarily thiophosgene (3) and
tetrahydrophthalimide (2). Tetrahydrophthalimide (2) and various of its
hydroxylated derivatives are excreted in the urine. The thiophosgeneglutathione
adduct (5) subsequently degrades and is eventually excreted
in the urine as 2-thiazolidinethione-4-carboxylic acid (4).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with captanyou should be trained on its proper handling and storage.Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilatedarea away from water, heat, and incompatible materials.Metal containers involving the transfer of this chemicalshould be grounded and bonded. Where possible, automatically pump liquid from drums or other storage containers toprocess containers. Drums must be equipped with selfclosing valves, pressure vacuum bungs, and flame arresters.Use only nonsparking tools and equipment, especially whenopening and closing containers of this chemical. Sources ofignition, such as smoking and open flames, are prohibitedwhere this chemical is used, handled, or stored in a mannerthat could create a potential fire or explosion hazard. A regulated, marked area should be established where this chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHAStandard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN2773 Phthalimide derivative pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Toxicity evaluation
The half-life of captan is 1–10 days in a soil environment, and hours to days in water depending on acidities and temperatures. Captan is not mobile in soil but can significantly evaporate from the soil surface. It is quickly degraded in neutral water.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with tetraethyl pyrophosphate, parathion. Keep away from strong alkaline materials(e.g., hydrated lime) as captan may become unstable. May react with water releasing hydrogen chloride gas. Corrosive to metals in the presence of moisture.
Waste Disposal
Captan decomposes fairly readily in alkaline media (pH >8). It is hydrolytically stable at neutral or acid pH but decomposes when heated alone at its freezing/melting point. Alkaline hydrolysis is recommended
Properties of Captan
| Melting point: | 178°C |
| Boiling point: | 314.2°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.74 |
| vapor pressure | 1.0 x 10-5 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6360 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 2 °C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform: Slightly Soluble,Methanol: Slightly Soluble |
| pka | -2.68±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Amorphous Powder |
| Water Solubility | 3.3 mg l-1 (25 °C) |
| color | White, beige |
| Merck | 14,1772 |
| BRN | 234872 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 mg/m3. |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 133-06-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Captan(133-06-2) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 30, Sup 7) 1987 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Captan (133-06-2) |
Safety information for Captan
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H351:Carcinogenicity H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Captan
Captan manufacturer
India Pesticides Limited
Super Crop Safe Limited
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(Hydroxymethyl)benzoate N-Boc-2-chloroethylamine 1-Bromo-2-methoxy-3-nitrobenzene N-Methyl-3-cyclopenten-1-amine 2-Bromo-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde 1H-indazole-5-carboxamideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 133-06-2 Captan 99%View Details
133-06-2 Captan 99%View Details
133-06-2 -
 133-06-2 99%View Details
133-06-2 99%View Details
133-06-2 -
 133-06-2 Captan 98%View Details
133-06-2 Captan 98%View Details
133-06-2 -
 Captan 98% (GC) CAS 133-06-2View Details
Captan 98% (GC) CAS 133-06-2View Details
133-06-2 -
 Captan CAS 133-06-2View Details
Captan CAS 133-06-2View Details
133-06-2 -
 Captan CAS 133-06-2View Details
Captan CAS 133-06-2View Details
133-06-2 -
 Captan CAS 133-06-2View Details
Captan CAS 133-06-2View Details
133-06-2 -
 2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8