Camphor
Synonym(s):2-Bornanone;2-Camphanone;(±)-Camphor;(1S)-1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-one;D -Camphor
- CAS NO.:76-22-2
- Empirical Formula: C10H16O
- Molecular Weight: 152.23
- MDL number: MFCD00074738
- EINECS: 200-945-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
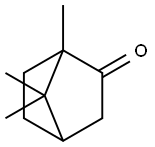
What is Camphor?
Description
Camphor, A white crystalline cyclicketone with a characteristic penetrating odor. It was formerly obtainedfrom the wood of the Formosancamphor tree, but can now besynthesized. The compound has acharacteristic odour associated withits use in mothballs. Used to make moth proofings, pharmaceuticals, and flavorings.
Chemical properties
Camphor is colourless solid with a characteristic odour that is obtained from the wood and bark of the camphor tree and is soluble in water and alcohol. It has two optically active forms (dextro and levo) and an optically inactive mixture (racemic) of these two forms. Camphor is used in pharmaceuticals,in disinfectants, in explosives,and to harden nitrocellulose plastics. It is produced by fractional distillation and crystallization of camphor oil or, synthetically, by dehydrogenation of isoborneol over a copper catalyst.
The Uses of Camphor
Camphor (Cinnamomum camphora) is credited with anesthetic, antiinflammatory, antiseptic, astringent, cooling, and refreshing properties, and thought to be slightly stimulating to blood circulation and function. Camphor is effective for oily and acne skin treatment, and has a scent similar to eucalyptus. In high concentrations, it can be an irritant and numb the peripheral sensory nerves. dl-Camphor is used as a plasticizer for celluloseesters and ethers; in the manufacture ofplastics and cymene; in cosmetics, lacquers,medicine, explosives, and pyrotechnics; andas a moth repellent.
Indications
Camphor is a ketone which, when applied in 1% to 3% concentration, has mild antipruritic effects through its anesthetic and counterirritant properties. Counterirritants are substances that, by inducing other sensations such as coolness or warmth, ‘‘crowd out’’ the perception of pain or itch. Camphor is used in various OTC topical analgesic products in concentrations as high as 9%.
Health Hazard
Vapors of camphor can irritate the eyes, nose,and throat. In humans, such irritation may be felt at >3 ppm concentration. Prolongedexposure can cause headache, dizziness, andloss of sense of smell. Ingestion can causeheadache, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea,and at high dosages can lead to convulsion,dyspnea, and coma. High dosages can beharmful to gastrointestinal tracts, kidney,and brain.
LD50 value, intraperitoneal (mice): 3000mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Flammable/combustible material. May be ignited by friction, heat, sparks or flames. Some may burn rapidly with flare burning effect. Powders, dusts, shavings, borings, turnings or cuttings may explode or burn with explosive violence. Substance may be transported in a molten form at a temperature that may be above its flash point. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished.
Toxicology
Camphor is a very toxic compound which can prove fatal for infants and children on ingestion even in very small doses. Camphor products are toxic and especially dangerous to young children. Mouthing or eating camphor can cause seizures. Applying balms or ointments in large amounts and adding it to the water of a room humidifier may also cause children to seize. The onset of symptoms may occur very quickly - as early as 5 to 20 minutes.
Potential Exposure
Camphor, a natural product, is used as a plasticizer for cellulose esters and ethers; it is used in lacquers and varnishes; and in explosives and pyrotechnics formulations. It is used as a moth repellent and as a medicinal.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
Camphor was not teratogenic to rats or rabbits when administered orally during the fetal period of organogenesis at doses up to 1000mg/kg body weight (bw)/day or 681mg/kg bw/day, respectively.9 Signs of maternal toxicity included clonic convulsions, reduced motility, and reduced body weight gain in rats and reduced food consumption and body weight gain in rabbits.
Source
Major component in pine oil (quoted, Verschueren, 1983). Also present in a variety of rosemary shoots (330–3,290 ppm) (Soriano-Cano et al., 1993), anise-scented basil leaves (1,785 ppm) (Brophy et al., 1993), Iberian savory leaves (2,660 ppm) (Arrebola et al., 1994), African blue basil shoots (7,000 ppm), Greek sage (160–5,040 ppm), Montane Mountain mint (3,395–3,880 ppm), yarrow leaves (45–1,780 ppm), and coriander (100–1,300 ppm) (Duke, 1992).
storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store ina flammable materials storage area. Prior to working withcamphor you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Before entering confined space where this chemicalmay be present, check to make sure that an explosive concentration does not exist. Camphor must be stored to avoidcontact with oxidizers, such as permanganates, nitrates, peroxides, chlorates, and perchlorates, and especially chromicanhydride since violent reactions occur. Store in tightlyclosed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away fromheat, sparks, or flame. Sources of ignition, such as smokingand open flames are prohibited where camphor is used, handled, or stored in a manner that could create a potential fireor explosion hazard.
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Violent, possibly explosive, reaction with strong oxidizers, especially chromic anhydride, potassium permanganate. May accumulate static electrical charges, and may cause ignition of its vapors.
Properties of Camphor
| Melting point: | 175-177 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 204 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.992 |
| vapor density | 5.2 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 4 mm Hg ( 70 °C) |
| FEMA | 4513 | dl-CAMPHOR |
| refractive index | 1.5462 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 148 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Soluble in acetone, ethanol, diethylether, chloroform and acetic acid. |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| color | White or Colorless |
| Odor | at 10.00 % in dipropylene glycol. camphoreous |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +0.15 to -0.15°, c = 10% in ethanol |
| explosive limit | 0.6-4.5%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 0.12 g/100 mL (25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,1732 |
| JECFA Number | 2199 |
| BRN | 1907611 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (x 10-5 atm?m3/mol):
3.00 at 20 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 12 mg/m3 (2 ppm), STEL 18
mg/m3 (3 ppm) (ACGIH); IDLH 200 mg/m3
(NIOSH).
. |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, metallic salts, combustible materials, organics. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 76-22-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Camphor(76-22-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Camphor (76-22-2) |
Safety information for Camphor
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H371:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Camphor
| InChIKey | DSSYKIVIOFKYAU-MHPPCMCBSA-N |
Camphor manufacturer
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 DL-Camphor CAS 76-22-2View Details
DL-Camphor CAS 76-22-2View Details
76-22-2 -
 (±)-Camphor CAS 76-22-2View Details
(±)-Camphor CAS 76-22-2View Details
76-22-2 -
 Camphor pure CAS 76-22-2View Details
Camphor pure CAS 76-22-2View Details
76-22-2 -
 Dl-camphor 95% CAS 76-22-2View Details
Dl-camphor 95% CAS 76-22-2View Details
76-22-2 -
 Camphor, micro analytical reagent CAS 76-22-2View Details
Camphor, micro analytical reagent CAS 76-22-2View Details
76-22-2 -
 Camphor CAS 76-22-2View Details
Camphor CAS 76-22-2View Details
76-22-2 -
 CAMPHOR powder (purified) CAS 76-22-2View Details
CAMPHOR powder (purified) CAS 76-22-2View Details
76-22-2 -
 Camphor (dl) CAS 76-22-2View Details
Camphor (dl) CAS 76-22-2View Details
76-22-2
