D-CAMPHOR
Synonym(s):(+)-Camphor;(1R)-1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-one;2-Bornanone;2-Camphanone
- CAS NO.:464-49-3
- Empirical Formula: C10H16O
- Molecular Weight: 152.23
- MDL number: MFCD00064149
- EINECS: 207-355-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-28 17:40:27
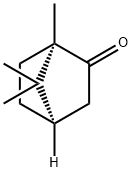
What is D-CAMPHOR?
Description
(1R)-(+)-Camphor is a terpene that has been found in C. sativa, C. indica, and C. sativa/C. indica hybrid strains as well as the essential oils from a variety of herbs including rosemary, lavender, and sage and has diverse biological activities. It inhibits norepinephrine secretion and cytosolic calcium and sodium increases induced by the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) agonist 1,1-dimethyl-4-phenylpiperazinium iodide (DMPP) in chromaffin cells (IC50s = 70, 88, and 19 μM, respectively). (1R)-(+)-Camphor (65-260 μM) induces proliferation of and increases expression of collagen IA, collagen IIIA, collagen IVA, and elastin in human primary dermal fibroblasts. In vivo, (1R)-(+)-camphor increases expression of collagen IA, collagen IIIA, collagen IVA, and elastin in skin in UV-exposed mice when administered at doses of 26 and 55 mM in drinking water post UV-exposure. It reduces cough frequency in citric acid-challenged guinea pigs. (1R)-(+)-Camphor is insecticidal, reducing digging activity and inducing mortality of fire ant workers. It has also been used as a building block in the synthesis of cannabinergic ligands.
Description
Camphor is a naturally occurring terpene found in trees in the laurel family (Lauraceae), notably camphor laurel, or Cinnamomum camphora, that is native to east and south Asia and now grows worldwide. It has been used in folk medicine for centuries.
Camphor can exist in two enantiomers: (+)- or (R)-camphor (shown), the predominant natural isomer, and (–)-or (S)-camphor1, which occurs in sand sage (Artemisia filifolia), a flowering plant native to the western United States. Synthetic camphor is usually a racemic mixture2 of the two enantiomers.
Camphor, with its familiar, penetrating odor, has a wide range of uses, including as a plasticizer for modified celluloses; in lacquers, varnishes, and plastics; as a moth repellent alternative to p-dichlorobenzene; and as a preservative in cosmetics and embalming fluids. In medicine, it is an ingredient in topical creams and ointments to treat itching, irritation, and joint pain; and it is used internally to prevent or relieve gas in the gastrointestinal tract.
1. CAS Reg. No. 464-48-2.
2. CAS Reg. No. 76-22-2.
Chemical properties
white crystals
Chemical properties
d-Camphor has a warm, minty, almost ethereal diffusive aroma. For other details of description, see Camphor Tree.
Occurrence
Frequently occurring in nature as the d- or l-form; the optically inactive form is seldom encountered. The d-form has been reported found in Cinnamomum camphora Ness. (Laurus camphora L.) from China, Japan and the East Indies; in Sassafras officinale, Lavandula spica and in other Labiatae. The l-form is reported found in the essential oils of Salvia grandiflora, Matricaria parthenium, Artemisia herba alba; the optically inactive form is found in Chrysanthemum japonicum sinense. Also reported found in orange peel oil, lemon peel oil, apricot, raspberry, anise, cinnamon root bark, ginger, pepper, coriander, calamus, sweet fennel and rosemary.
The Uses of D-CAMPHOR
D-Camphor may be used as reference material for the quantification of the analyte in Saraca asoca and coriander using chromatography techniques.
The Uses of D-CAMPHOR
(R)-(+)-Camphor is a terpenoid with a wide variety of use. (R)-(+)-Camphor has insecticidal activity and is also used as an antimicrobial agent. (R)-(+)-Camphor is used as a culinary flavouring agent in parts of asia.
The Uses of D-CAMPHOR
analgesic, antiinfective, antipruritic
The Uses of D-CAMPHOR
(1R)-(+)-Camphor is used as a chiral intermediate and auxiliary. It is also used as a skin antipruritic and as an anti-infective agent.
Background
Camphor is a bicyclic monoterpene ketone found widely in plants, especially Cinnamomum camphora. It is used topically as a skin antipruritic and as an anti-infective agent. When ingested, camphor has a rapid onset of toxic effects, and camphorated oil is the product most often responsible for its toxicity. The FDA ruled that camphorated oil could not be marketed in the United States and that no product could contain a concentration higher than 11%. It appears in the list of drug products withdrawn or removed from the market for safety or effectiveness. However, camphor can be found in several nonprescription medications at lower concentrations.
Definition
ChEBI: The (R)- enantiomer of camphor.
Aroma threshold values
Detection at 1 to 1.29 ppm
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 20 ppm: medicinal, camphoraceous, mentholic and woody.
General Description
Colorless or white crystals. Sublimes. Flash point 149°F. Burns readily with a bright, smoky flame. Penetrating aromatic odor. Pungent, aromatic taste followed by a sensation of cold.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
D-CAMPHOR is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents and chlorinated solvents.
Fire Hazard
D-CAMPHOR is combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Flammable
Synthesis
Natural camphor is obtained by distillation from the plants of Cinnamomum or Laurus camphora from China and Japan, together with the corresponding essential oils; the raw camphor contains several impurities. It is separated from the water and the essential oil by pressure or by centrifugation and subsequently purified by sublimation or crystallization. Synthetic camphor is prepared from pinene isolated by fractional distillation of turpentine oil; pinene is reacted to bornyl chloride with gaseous HCl under pressure and then to camphene. The distilled and purified camphene is then oxidized to camphor with Na+ or K+ bichromate in the presence of H2SO4.
Metabolism
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from EtOH, 50% EtOH/water, MeOH, or pet ether or from glacial acetic acid by addition of water. It can be sublimed (50o/14mm) and also fractionally crystallised from its own melt. It is steam volatile. It should be stored in tight containers as it is appreciably volatile at room temperature. The solubility is 0.1% (H2O), 100% (EtOH), 173% (Et2O) and 300%
Properties of D-CAMPHOR
| Melting point: | 178-182 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 204 °C |
| alpha | D25 +41 to +43° (c = 10 in U.S.P. alcohol) according to U.S.P. specif |
| Density | 0,99 g/cm3 |
| vapor density | 5.24 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 4 mm Hg ( 70 °C) |
| refractive index | 44.5 ° (C=20, EtOH) |
| FEMA | 2230 | D-CAMPHOR |
| Flash point: | 148 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, very soluble in alcohol and in light petroleum, freely soluble in fatty oils, very slightly soluble in glycerol. |
| appearance | white crystals |
| form | Crystals |
| color | White |
| Odor | at 10.00 % in dipropylene glycol. camphor minty phenolic herbal woody |
| optical activity | [α]25/D +44°, c = 10 in ethanol |
| explosive limit | 3.5% |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (0.1 g/L at 20°C). |
| JECFA Number | 1395 |
| Merck | 14,1732 |
| BRN | 2042745 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong reducing agents, strong oxidizing agents, chlorinated solvents. Protect from direct sunlight. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 464-49-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Camphor (464-49-3) |
Safety information for D-CAMPHOR
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H371:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for D-CAMPHOR
D-CAMPHOR manufacturer
New Products
Tetrabutylammonium iodide (3,3-DIFLUOROCYCLOBUTYL)METHANOL 4,4-DIFLUOROCYCLOHEXANAMINE Cyclobutylamine (S)-3-Fluoro-pyrrolidine hydrochloride 3-Oxocyclobutanecarboxylic acid N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide L-tert-Leucine,97% 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% Aluminum oxide, basic Calcium hydroxide, 95% Diallylamine, 99% 2-Iodobenzoic Acid 3-Methoxybenzonitrile Pentachlorobenzonitrile Chloral Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide O-Benzylhydroxylamine Hydrochloride 2-Nitrobenzaldehyde 2-Picolylamine (2-Aminomethylpyridine) 2-Venylpyridine Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 4-Dimethylamine PyridineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




![methyl N,N,N-trimethyl-4-[(4,7,7-trimethyl-3-oxobicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ylidene)methyl]anilinium sulphate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/52793-97-2.gif)

You may like
-
 464-49-3 D-(+)-Camphor 98%View Details
464-49-3 D-(+)-Camphor 98%View Details
464-49-3 -
 (+)-Camphor CAS 464-49-3View Details
(+)-Camphor CAS 464-49-3View Details
464-49-3 -
 Camphor CAS 464-49-3View Details
Camphor CAS 464-49-3View Details
464-49-3 -
 1126-74-5 3-Pyridineacrylic acid 98+View Details
1126-74-5 3-Pyridineacrylic acid 98+View Details
1126-74-5 -
 tert-Butyl carbazate 98+View Details
tert-Butyl carbazate 98+View Details
870-46-2 -
 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 10442-39-4 98+View Details
TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 10442-39-4 98+View Details
10442-39-4 -
 91419-52-2 98+View Details
91419-52-2 98+View Details
91419-52-2 -
 19752-84-2 TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 98+View Details
19752-84-2 TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 98+View Details
19752-84-2
