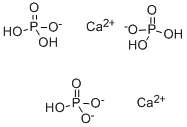
Calcium phosphate monobasic
Synonym(s):Calcium bis(dihydrogenphosphate) monohydrate;Calcium dihydrogenphosphate monohydrate;Primary calcium phosphate monohydrate
- CAS NO.:10031-30-8
- Empirical Formula: CaH7O5P
- Molecular Weight: 158.1
- MDL number: MFCD00149602
- EINECS: 600-059-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52

What is Calcium phosphate monobasic ?
Chemical properties
white, large, shining, tricl plates, crystal(s) powder(s) or granules; not hygroscopic [MER06] [STR93]
The Uses of Calcium phosphate monobasic
Calcium phosphate monobasic monohydrate may be used in the preparation of calcium polyphosphate (CPP) powders.
The Uses of Calcium phosphate monobasic
calcium phosphate monobasic is an acidulant, leavening agent, and nutritional supplement that exists as white crystals or granular powder. It is sparingly soluble in water. It is used as an acidulant in breads and dry-mix beverages; as a source of calcium in fruit jellies, preserves, and cereals; and as a component of dough conditioners. It is also of restricted use as a chemical leavening agent because it releases about 67% of the carbon dioxide during the initial mixing and this is generally too rapid. It is also termed calcium acid phosphate, monocalcium phosphate, calcium biphosphate, and acid calcium phosphate.
The Uses of Calcium phosphate monobasic
Monocalcium phosphate monohydrate was the first acidic phosphate used as a leavening acid. A patent for its use in baking powders was issued in 1956. The early MCP· H2 0 was prepared by ashing bones to form a crude product. This phosphate is classed as a fast-acting leavening acid; approximately 60% of the theoretical C02 is released by reaction of the MCP· H2 0 with soda during the mixing stage of batter or dough preparation. No further gas is then released until the product is placed in the oven and the temperature has reached approximately l40°F. The reason for this is that MCP· H2 0 disproportionates upon contact with water to form some dicalcium phosphate according to the following equation: Ca(H2PO4)2.H2O+H2O=CaHPO4.2H2O+H3PO4.
Because of the speed of its reaction, MCP· H20 has limited applications by itself. Although it is commonly used in the preparation of phosphated flour at levels of 0.25 to 0.75% of the weight of the finished product and in the preparation of cookies, most of its applications are in combination with other slower-acting phosphate leavening acids. It is expected to release gas during the mixing stages to assist in forming bubble nucleii, while the other slower-acting acids release gas during bench action or baking.
What are the applications of Application
Calcium phosphate monobasic monohydrate is a synthetic reagent
General Description
Calcium phosphate monobasic monohydrate is mainly used in the manufacture of fertilizers and as an acidulant in food industry. Aqueous solution of calcium phosphate monobasic monohydrate (MCPM) mixed with α-tertiary calcium phosphate forms dicalcium phosphate dihydrate cement. It is also used in composing brushite cement.
Agricultural Uses
Apatite treated with sulphuric acid gets converted to mono calcium dihydrogen phosphate [Ca(H2PO4)2] which is called superphosphate. Calcium dihydrogen phosphate is more water-soluble than apatite.
Agricultural Uses
Soil is made of particles of various sizes. Silt, a
constituent of soil, comprises particles of sizes between
those of clay and sand. According to the international
particle-size system, a silt particle size is about 2 to 50μm
in diameter. It is further divided into fine silt (2 to 20μm)
and coarse silt (20 to 50μm). The percentage of silt
particles in a particular soil is taken into consideration
while defining soil texture.
Silt is often carried as suspended particles in running
water and deposited on riverbeds, riverbanks or in lakes
as alluvial sediments.
A soil that contains 40% or more of clay and 40% or
more of silt is called silt clay. A soil with 27 to 40% clay
and less than 20% sand is known as silt-clay loam. Silt
loam has 30% or more silt and 12 to 27% clay. Similarly,
silt loam soil consists of 50 to 80% silt, less than 12%
clay and the rest sand.
Properties of Calcium phosphate monobasic
| Melting point: | 100°C |
| Boiling point: | 203°C |
| Density | 2.220^1^6 |
| Flash point: | 203°C |
| solubility | slightly soluble in H2O; soluble in dilute acid solutions |
| form | Powder |
| color | white |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | moderately soluble H2O; soluble dilute HCl, HNO3, acetic acid [MER06] |
| Merck | 14,1693 |
| Dielectric constant | 14.0(Ambient) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10031-30-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Monocalcium phosphate monohydrate (10031-30-8) |
Safety information for Calcium phosphate monobasic
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Calcium phosphate monobasic
| InChIKey | ZBZJARSYCHAEND-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Calcium phosphate monobasic manufacturer
Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd
Pd Navkar Bio Chem Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Calcium phosphate monobasic monohydrate 98%View Details
Calcium phosphate monobasic monohydrate 98%View Details -
 10031-30-8 98%View Details
10031-30-8 98%View Details
10031-30-8 -
 Calcium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate extrapure CAS 10031-30-8View Details
Calcium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate extrapure CAS 10031-30-8View Details
10031-30-8 -
 Calcium bis(dihydrogenphosphate), GR CAS 10031-30-8View Details
Calcium bis(dihydrogenphosphate), GR CAS 10031-30-8View Details
10031-30-8 -
 CALCIUM DIHYDROGEN PHOSPHATE MONOHYDRATE Extra Pure CAS 10031-30-8View Details
CALCIUM DIHYDROGEN PHOSPHATE MONOHYDRATE Extra Pure CAS 10031-30-8View Details
10031-30-8 -
 Calcium phosphate monobasic monohydrate CAS 10031-30-8View Details
Calcium phosphate monobasic monohydrate CAS 10031-30-8View Details
10031-30-8 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1