Calcium acetate
Synonym(s):Calcium acetate
- CAS NO.:62-54-4
- Empirical Formula: C4H6CaO4
- Molecular Weight: 158.17
- MDL number: MFCD00012448
- EINECS: 200-540-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
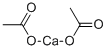
What is Calcium acetate?
Absorption
40% is absorbed in the fasting state and approximately 30% is absorbed in the nonfasting state following oral administration.
Toxicity
Oral, rat: LD50 = 4280 mg/kg. Symptoms of overdose include mild hypercalcemia (constipation; loss of appetite; nausea and vomiting), and severe hypercalcemia (confusion; full or partial loss of consciousness; incoherent speech).
Description
Calcium acetate is a chemical compound which is calcium salt of acetic acid. It has the formula Ca(C2H3O2)2. Its standard name is calcium acetate, while calcium ethanoate is the systematic name. An older name is acetate of lime. The anhydrous form is very hygroscopic; therefore the monohydrate (Ca(CH3COO)2?H2O) is the common form.
Chemical properties
Calcium acetate occurs as a white or almost white, odorless or almost odorless, hygroscopic powder.
The Uses of Calcium acetate
Calcium Acetate is the calcium salt of acetic acid which functions as a sequestrant and mold control agent. it contains approximately 25% calcium. it is a white odorless powder which is readily soluble in water with a solubility of approximately 37 g in 100 g water at 0°c. its solubility decreases with increasing temperature, with a sol- ubility of approximately 29 g in 100 g of water at 100°c.
The Uses of Calcium acetate
Calcium Acetate is the salt of acetic acid which is used as a preservative and sequestrant.
The Uses of Calcium acetate
Calcium Acetate is a salt of acetic acid (A167640), a common chemical reagent used in a multitude of organic reactions. It is the primary constituent of vinegar, contributing to its distinct taste and odor. It is used in the synthesis of dye-sensitized solar cells.
Indications
Calcium acetate is one of a number of calcium salts used to treat hyperphosphatemia (too much phosphate in the blood) in patients with kidney disease.
Background
The chemical compound calcium acetate is the calcium salt of acetic acid. It has been commonly referred to as the acetate of lime. The anhydrous form is very hygroscopic, therefore the monohydrate is the common form.
Definition
ChEBI: The calcium salt of acetic acid. It is used, commonly as a hydrate, to treat hyperphosphataemia (excess phosphate in the blood) in patients with kidney disease: the calcium ion combines with dietary phosphate to form (insoluble) calcium phosphate, which is excreted in the faeces.
Production Methods
Calcium acetate can be prepared by soaking calcium carbonate (found in eggshells, or in common carbonate rocks such as lime stone or marble) in vinegar:
CaCO3 + 2CH3COOH → Ca(CH3COO)2 + H2O + CO2
Since both reagents would have been available pre-historically, the chemical would have been observable as crystals then.
Preparation
Produced by calcium hydroxide neutralization of acetic acid.
General Description
Calcium Acetate belongs to the group of calcium salts, widely used as phosphorus binders in patients with chronic renal failure.
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Calcium acetate is used as a preservative in oral and topical
formulations.
Therapeutically, parenteral calcium acetate acts as a source of
calcium ions for hypocalcemia or electrolyte balance. Oral
calcium acetate is used as a complexing agent for hyperphosphatemia
in dialysis patients. Calcium acetate is also used in the
food industry as a stabilizer, buffer and sequestrant.
Clinical Use
Phosphate binding agent
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Mutation data reported. See also CALCIUM COMPOUNDS. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Safety
Calcium acetate is used in oral and topical formulations. The pure
form of calcium acetate is toxic by IP and IV routes.
LD50 (mouse, IP): 0.075 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 0.052 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 4.28 g/kg
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Calcium acetate can be used for oral administration to treat hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic renal failure. Secondary to its phosphorus binding efficiency and lower concentration of elemental calcium, calcium acetate is considered the most effective and having the lowest potential for causing hypercalcemia of the calcium-based phosphorus-binding agents. When compared to calcium carbonate, calcium acetate binds approximately twice as much phosphorus per gram of elemental calcium administered. Unlike calcium citrate, calcium acetate does not promote aluminum absorption.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Can impair absorption of some drugs, e.g. iron,
ciprofloxacin.
The Uses of Calcium acetate
Calcium acetate is used to control high blood levels of phosphorus in people with kidney disease who are on dialysis (medical treatment to clean the blood when the kidneys are not working properly). Calcium acetate is in a class of medications called phosphate binders. It binds phosphorus that you get from foods in your diet and prevents it from being absorbed into your blood stream.
Metabolism
The residual acetate will be metabolised through bicarbonate, which will be further excreted via normal metabolic routes. Any unbound calcium not involved in the binding of phosphate will be variable and may be absorbed. Calcium is absorbed mainly from the small intestine by active transport and passive diffusion. About one-third of ingested calcium is absorbed although this can vary depending upon dietary factors and the state of the small intestine. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol), a metabolite of vitamin D, enhances the active phase of absorption. Excess calcium is mainly excreted renally. Unabsorbed calcium is eliminated in the faeces, together with that secreted in the bile and pancreatic juice. Minor amounts are lost in the sweat, skin, hair, and nails.
storage
Calcium acetate is stable although very hygroscopic, and so the
monohydrate is the common form. It decomposes on heating (above
1608℃) to form calcium carbonate and acetone.
Store in well-closed airtight containers.
Purification Methods
Recrystallise it from water (3mL/g) by partial evaporation in a desiccator. [Beilstein 2 IV 113.]
Incompatibilities
Calcium acetate is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and moisture.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral suspensions and tablets; topical emulsions, lotions, and creams). Included in nonparenteral medicines (oral tablets) licensed in the UK.
Properties of Calcium acetate
| Melting point: | 160°C (dec.) |
| Density | 1,5 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.5500 |
| FEMA | 2228 | CALCIUM ACETATE |
| Flash point: | 160°C |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, Room Temperature, under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Powder |
| color | white |
| Specific Gravity | 1.50 |
| PH | 8(1 mM solution);8.43(10 mM solution);8.77(100 mM solution);9.13(1000 mM solution) |
| Odor | mild acetic |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Decomposition | 160 ºC |
| Stability: | Stable. Non-flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 62-54-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Calcium acetate (62-54-4) |
Safety information for Calcium acetate
Computed Descriptors for Calcium acetate
| InChIKey | VSGNNIFQASZAOI-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Calcium acetate manufacturer
Vasa Pharmachem Pvt Ltd. (VPPL)
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 CALCIUM ACETATE USP 99%View Details
CALCIUM ACETATE USP 99%View Details -
 CALCIUM ACETATE 99%View Details
CALCIUM ACETATE 99%View Details -
 Calcium acetate 99%View Details
Calcium acetate 99%View Details -
 CALCIUM DI ACETATE 99%View Details
CALCIUM DI ACETATE 99%View Details -
 Calcium acetate 99%View Details
Calcium acetate 99%View Details -
 Calcium Acetate 99%View Details
Calcium Acetate 99%View Details -
 Calcium acetate 99%View Details
Calcium acetate 99%View Details -
 Calcium acetate 98%View Details
Calcium acetate 98%View Details
