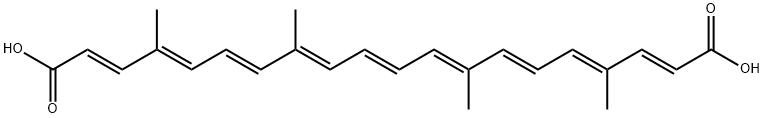
Bixin
Synonym(s):6-Methyl hydrogen (9Z)-6,6′-diapocarotene-6,6’-dioate;9-cis-6,6′-Diapo-ψ,ψ-carotenedioic acid 6-methyl ester;Natural orange 4
- CAS NO.:6983-79-5
- Empirical Formula: C25H30O4
- Molecular Weight: 394.5
- MDL number: MFCD00016545
- EINECS: 230-248-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
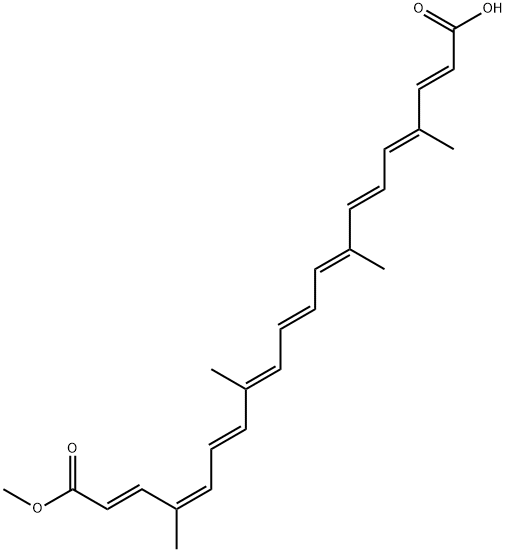
What is Bixin?
Description
Bixin [CAS: 6983-79-5] (CI Natural Orange 4; CI 75120) is found in the seed of the plant Bixa orellana, native to India. Later it was found growing in South America, where the Indians used the red dye from the seeds as a body paint. An extract of the seeds appears on the market as annatto. This extract is used in coloring butter, margarine, and cheese such as Leicester cheese. In Mexican and South American cuisine, it finds special use as a flavor and coloring matter. Annato is available as an aqueous solution, as an oleaginous dispersion, and a spray-dried powder.
Description
Bixin is a natural product found in the seeds of the achiote tree (Bixa orellana) that grows in Latin America, India, and East Africa. Like the carotenes, it contains nine conjugated double bonds, but with carboxyl groups rather than hexene rings at both ends.
Bixin is sometimes referred to as cis-bixin because of the lone (Z)-configuration of the second double bond from its ester terminus. When bixin is isolated, the thermodynamically unstable (Z)-bond isomerizes, coverting the molecule to all-trans-bixin.1 Both bixins are insoluble in water; but base hydrolysis of either produces the water-soluble diacid norbixin.2 All three molecules have vivid red-orange colors.
Indigenous peoples have long ground B. orellana seeds into a powder or paste called annatto, of which bixin is the principal ingredient. Annatto is used as a food colorant and flavoring agent; it is also extracted with hot water or oil to make liquids that are used for the same purposes. In modern times, annatto has become a commercial ingredient for coloring dairy products, margarine, baked goods, processed meats, and other foods.
Aqueous annatto extracts, which primarily contain norbixin, are frequently used to produce uniformly colored cheeses such as cheddars. Cheeses may have color inconsistencies from batch to batch because of multiple milk sources and seasonal variations in dairy-cow feed. January 20 is National Cheese Lovers Day, so as you slice your cheddar, be thankful for bixin and the achiote tree.
1. CAS Reg. No. 39937-23-0.
2. CAS Reg. No. 542-40-5.
Chemical properties
orange,purple lustrous crystalline solid plates
Occurrence
Bixin (CI Natural Orange 4; CI 75120) is found in the seed of the plant Bixa orellana, native to India. Later it was found growing in South America, where the Indians used the red dye from the seeds as a body paint. An extract of the seeds appears on the market as annatto. This extract is used in coloring butter, margarine, and cheese such as Leicester cheese. In Mexican and South American cuisine, it finds special use as a flavor and coloring matter. Annato is available as an aqueous solution, as an oleaginous dispersion, and a spray-dried powder.
The Uses of Bixin
Bixin is a carotenoid that is the main coloring component of annatto. it is obtained from the bixa orellana tree. bixin is soluble in fats and oils and the produced color is found in the fat fraction of the food. it has a yellow hue, very good oxidation stability, fair light stability, and good heat stability, but it is poor at very high temperatures, such as above 125°c. one part bixin is equivalent to 1.5 parts caro- tene. it is used at 0.5–10 ppm in finished foods, such as margarine, salad dressings, popcorn oil, and baked goods. it is also termed annatto extract. see annatto.
Definition
ChEBI: A carotenoic acid that is the 6'-monomethyl ester of 9'-cis-6,6'-diapocarotene-6,6'-dioic acid.
General Description
Bixin is a methyl ester of a dibasic fatty acid. On treating with alkali, it is hydrolyzed to form water soluble norbixin. It is obtained in pure form from annatto seeds. Bixin is a carotenoid and estimated as yolk and skin pigmenter.
Purification Methods
Crystallise bixin from Me2CO (violet prisms) [Pattenden et al. J Chem Soc (C) 235 1970]. [Beilstein 2 III 2020, 2 IV 2455, H 30 110.]
Properties of Bixin
| Melting point: | 217°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 438.7°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0659 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4460 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| Colour Index | 75120 |
| pka | 4.69±0.10(Predicted) |
| appearance | red-orange crystals |
| color | Dark Red to Very Dark Red |
| λmax | λ: 465-475 nm Amax |
| Stability: | Air Sensitive, Light Sensitive, Temperature Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 6983-79-5 |
Safety information for Bixin
Computed Descriptors for Bixin
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Bixin CAS 6983-79-5View Details
Bixin CAS 6983-79-5View Details
6983-79-5 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4