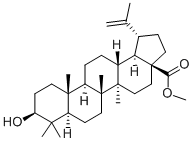
Betulinic acid
Synonym(s):3β-Hydroxy-20(29)-lupaene-28-oic acid;Lupatic acid;Mairin
- CAS NO.:472-15-1
- Empirical Formula: C30H48O3
- Molecular Weight: 456.71
- MDL number: MFCD00009619
- EINECS: 207-448-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
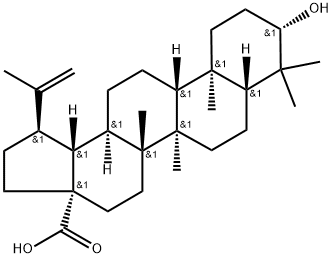
What is Betulinic acid ?
Description
Betulinic acid (472-15-1) is a natural Lupane triterpenoid from white birch tree (Betula pubescens). Induces apoptosis in a variety of cell lines.1 Induces mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening.2 ?Acts as a chemosensitizer for anticancer drug treatment in chemoresistant colon cancer cell lines.3 Cell permeable.
Description
Betulinic acid is a naturally-occurring triterpene found in the bark of the white birch tree. Research has found betulinic acid to be particularly useful against melanoma, a dangerous form of skin cancer, by targeting tumors without destroying healthy cells.
Chemical properties
colorless Needles
The Uses of Betulinic acid
Betulinic Acid is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid. Betulinic Acid displays anti-inflammatory and anti-HIV activity. Betulinic Acid selectively induces apoptosis in tumor cells by directly activati ng the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis through a p53- and CD95-independent mechanism. Betulinic Acid also exhibits TGR5 agonist activity
The Uses of Betulinic acid
antineoplastic
The Uses of Betulinic acid
Betulinic acid (BetA) has been used:
- to test its effects as an antiviral agent against Dengue virus (DENV)
- as a sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) inhibitor to repress the lipid metabolism and proliferation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) cells
- as a treatment to test its anti-tumor properties for cell viability and apoptotic cell death assays in multiple myeloma models
Background
Betulinic Acid has been used in trials studying the treatment of Dysplastic Nevus Syndrome.
What are the applications of Application
Betulinic Acid is a cytotoxic, cell apoptosis causing agent that upregulates caspase-8
Definition
ChEBI: A pentacyclic triterpenoid that is lupane having a double bond at position 20(29) as well as 3beta-hydroxy and 28-carboxy substituents. It is found in the bark and other plant parts of several species of plants including Syzygium cla iflorum. It exhibits anti-HIV, antimalarial, antineoplastic and anti-inflammatory properties.
General Description
Betulinic acid is a lupane-type triterpene, which can be prepared from betulin via oxidation using chromium oxide (VI). Along with anti-HIV-1 and anti-tumor activity, it also shows other bioactivities such as anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, in vitro antimalarial, anthelmintic and antioxidant activities.
Biological Activity
Natural triterpenoid that displays anti-HIV and antitumor activity. Induces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and activates NF- κ B. Exhibits TRG5 agonist activity (EC 50 = 1.04 μ M).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Betulinic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene, selectively induces apoptosis in tumor cells by directly activating the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis through a p53- and CD95-independent mechanism.
Anticancer Research
This compound is a pentacyclic triterpene obtained from Betula and Zizyphus species,which shows selective cytotoxicity against human melanoma cells (Shoeb2006). It generates reactive oxygen species, activates MAPK cascade, inhibitstopoisomerase I, inhibits angiogenesis, modulates pro-growth transcriptionalactivators, modulates the activity of aminopeptidase-N, and thereby inducesapoptosis in cancer cells (Desai et al. 2008; Fulda 2008).
Metabolism
Not Available
Storage
+4°C
References
1) Ehrhardt et al. (2004) Betulinic acid-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells; Leukemia, 18 1406 2) Mullauer et al. (2009) Betulinic acid induces cytochrome c release and apoptosis in Bax/Bak-independent, permeability transition pore dependent fashion.; Apoptosis, 14 191 3) Jung et al. (2007) Effect of betulinic acid on anticancer drug-resistant colon cancer cells; Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 101 277
Properties of Betulinic acid
| Melting point: | 295-298 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 550.0±33.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D25 +7.5° (c = 0.37 in pyridine) |
| Density | 1.065±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| refractive index | 7.8 ° (C=0.9, Pyridine) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 25 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 25 mg/ml). |
| form | neat |
| pka | 4.61±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White or off-white |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +7.8°, c = 0.9 in pyridine |
| Merck | 14,1190 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 2 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 472-15-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Betulinic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H413:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. |
Computed Descriptors for Betulinic acid
| InChIKey | QGJZLNKBHJESQX-FZFNOLFKSA-N |
Betulinic acid manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

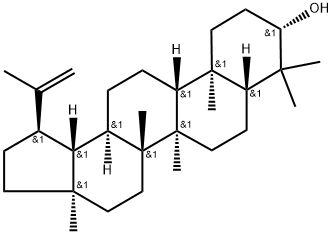

You may like
-
 472-15-1 Betulinic Acid 98%View Details
472-15-1 Betulinic Acid 98%View Details
472-15-1 -
 Betulinic Acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
Betulinic Acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
472-15-1 -
 Betulinic acid, 97% CAS 472-15-1View Details
Betulinic acid, 97% CAS 472-15-1View Details
472-15-1 -
 Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
472-15-1 -
 Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
472-15-1 -
 Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
472-15-1 -
 Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
472-15-1 -
 Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
Betulinic acid CAS 472-15-1View Details
472-15-1
