Berberine hydrochloride
Synonym(s):Natural Yellow 18
- CAS NO.:633-65-8
- Empirical Formula: C20H18NO4.Cl
- Molecular Weight: 371.81
- MDL number: MFCD00011939
- EINECS: 211-195-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 12:42:02
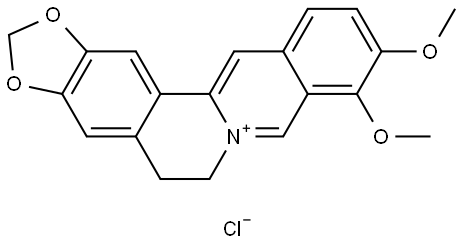
What is Berberine hydrochloride?
Chemical properties
yellow crystalline powder
Indications
Studies of berberine hydrochloride have indicated that it can treat several metabolic health conditions, including diabetes, obesity, and heart problems. It may also improve gut health.
The Uses of Berberine hydrochloride
antiarrhythmic, alpha2 agonist, anticonvulsant, antiinflammatory, antibacterial, antifungal, antitrypanosomal, antineoplastic, immunostimulant
The Uses of Berberine hydrochloride
An isoqinoline alkaloid shown to have a chemopreventive property against colon tumor formation by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (cox-2) which is abundantly expressed in colon cancer cells. Al so inhibits Activator Protein 1 (AP-1), a transcription factor that plays a critical role in inflammation and carcinogenesis. Treatment with berberine potentially results in the reduced accumulation o f chemotherapeutic drugs.
The Uses of Berberine hydrochloride
An ingredient in some commercial eyewash products.
Definition
ChEBI: Berberine chloride (TN) is an organic molecular entity.
Definition
Berberine Chloride is the orally bioavailable, hydrochloride salt form of berberine, a quaternary ammonium salt of an isoquinoline alkaloid and active component of various Chinese herbs, with potential antineoplastic, radiosensitizing, anti-inflammatory, anti-lipidemic and antidiabetic activities. Berberine is a naturally occurring yellow alkaloid in some plants. Berberine HCL is the native form combine with hydrogen chloride to make it more stable.
Biological Functions
Although the mechanisms of action through which berberine exerts its effects are not yet fully elucidated, upon administration this agent appears to suppress the activation of various proteins and/or modulate the expression of a variety of genes involved in tumorigenesis and inflammation, including, but not limited to transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB), myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl-1), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xl), cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-12, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), E-selectin, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), C-X-C motif chemokine 2 (CXCL2), cyclin D1, activator protein (AP-1), hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR), arylamine N-acetyltransferase (NAT), and DNA topoisomerase I and II. The modulation of gene expression may induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and inhibit cancer cell proliferation. In addition, berberine modulates lipid and glucose metabolism.
General Description
A highly potent and selective oxysterol EBI2 (GPR183) agonist (Kd) = 450 pM in a saturation binding assay, and EC50 = 140 pM over EC50 = 2.1 nM for its enantiomer, 7β,25-OHC, in a GTP-γS binding assay). Dose-dependently suppresses forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation in an EBI2-expressing SK-N-MC/CRE-β-galactosidase cell line (IC50 = 2 nM), but not in control cells. Stimulates migration of LPS-activated spleen B-cells and anti-CD3/CD28-activated CD4+ T-cells in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, pharmacological inhibition of its biosynthesis in vivo by Clotrimazole, a CYP7B1inhibitor, promotes the migration of adoptively transferred pre-activated B cells to the T/B boundary, mimicking the phenotype of pre-activated B cells in EBI2-deficient mice.
Biochem/physiol Actions
An alkaloid with weak antibiotic properties. Substrate for MDR efflux pumps. Antimicrobial activities of berberine is potentiated by the MDR inhibitor 5′-methoxyhydnocarpin (5′-MHC). Berberine upregulates the expression of Pgp in hepatoma cells. Treatment with berberine potentially results in the reduced accumulation of chemotherapeutic drugs.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route.Slightly toxic by ingestion. Mutation data reported. Whenheated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx andCl-.
Mechanism of action
Berberine hydrochloride might cause stronger heartbeats. It also might also be able to kill bacteria.
Side Effects
Side effects can include upset stomach and nausea.
Purification Methods
Berberine chloride crystallises from water to give the dihydrate. The anhydrous salt may be obtained by recrystallisation from EtOH/Et2O, wash the crystals with Et2O and dry them in a vacuum. The iodide has m 250o(dec) (from EtOH). [Perkin J Chem Soc 113 503 1918, Kametani et al. J Chem Soc(C) 2036 1969, Beilstein 27 I 515, 27 II 567.]
Clinical claims and research
People most commonly use berberine for diabetes, high levels of cholesterol or other fats in the blood, and high blood pressure. It is also used for burns, canker sores, liver disease, and many other conditions but there is no good scientific evidence to support many of these uses.
Properties of Berberine hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 204-206 °C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | methanol: soluble |
| form | Yellow powder |
| Colour Index | 75160 |
| color | Yellow powder |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE IN COLD WATER |
| BRN | 3836585 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C20H18NO4.ClH/c1-22-17-4-3-12-7-16-14-9-19-18(24-11-25-19)8-13(14)5-6-21(16)10-15(12)20(17)23-2;/h3-4,7-10H,5-6,11H2,1-2H3;1H/q+1;/p-1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 633-65-8 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Berberine chloride (633-65-8) |
Safety information for Berberine hydrochloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P330:Rinse mouth. P362:Take off contaminated clothing and wash before reuse. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Berberine hydrochloride
| InChIKey | VKJGBAJNNALVAV-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| SMILES | C12C=C3C(C(OC)=C(OC)C=C3)=C[N+]=1CCC1=CC3=C(OCO3)C=C21.[Cl-] |
Berberine hydrochloride manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 633-65-8 98%View Details
633-65-8 98%View Details
633-65-8 -
 Berberine Chloride 95% CAS 633-65-8View Details
Berberine Chloride 95% CAS 633-65-8View Details
633-65-8 -
 Berberine chloride, 97% CAS 633-65-8View Details
Berberine chloride, 97% CAS 633-65-8View Details
633-65-8 -
 Berberine chloride CAS 633-65-8View Details
Berberine chloride CAS 633-65-8View Details
633-65-8 -
 Berberine chloride CAS 633-65-8View Details
Berberine chloride CAS 633-65-8View Details
633-65-8 -
 Berberine Hydrochloride PowderView Details
Berberine Hydrochloride PowderView Details
633-65-8 -
 Berberine Hydrochloride PowderView Details
Berberine Hydrochloride PowderView Details
633-65-8 -
 Berberine HydrochlorideView Details
Berberine HydrochlorideView Details
633-65-8
