Aurothioglucose
Synonym(s):GGT;GGT 1;Gold thioglucose;GTG;Solganal
- CAS NO.:12192-57-3
- Empirical Formula: C6H11AuO5S
- Molecular Weight: 392.18
- MDL number: MFCD00056080
- EINECS: 235-365-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
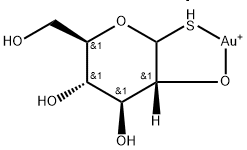
What is Aurothioglucose?
Absorption
In general, aurothioglucose is administered via intramuscular injection - preferably intragluteally - after which the resultant absorption is typically slow and erratic .
Gold is absorbed from injection sites, reaching peak concentration in blood in about 4 to 6 hours . After a single intramuscular injection of 50 mg of aurothioglucose suspension in two subjects, peak serum levels were observed at approximately 235 g/dL and 450 g/dL .
Storage of gold in human tissues depends upon organ mass as well as the concentration of gold .Subsequently, tissues having the highest gold levels (w/w) may not necessarily have the largest total amounts of gold . The highest concentrations of gold are generally found in the lymph nodes, adrenal glands, liver, kidneys, bone marrow, and spleen . Relatively small concentrations are actually found in the articular structures . In particular, following the administration of aurothioglucose doses, about 85% of the resultant plasma gold will be stored in the major bodily gold depots, which in decreasing order of total gold content are, the lymph nodes, bone marrow, liver, skin, and bone .
Toxicity
Overdose as a result of too rapid increases in dosing with aurothioglucose will be manifested by rapid appearance of toxic reactions, including those that are particular to renal damage, like hematuria and proteinuria, while hematologic effects include thrombocytopenia and granulocytopenia .
Other toxic effects, including fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and various skin disorders like papulovesicular lesions, urticaria, and exfoliative dermatitis, each of which are typically combined with severe pruritus can also develop .
The intramuscular TDLo for males is reported to be approximately 3.357 mg/kg when considering sense organs and special senses like eye vision and about 5.5 mg/kg for affects on the lungs, thorax, or respiration . For women, the intramuscular TDLo for effects on the liver, gastrointestinal tract, and cholestatic jaundice is between 2.6-2.7 mg/kg while the value for effects on the kidney, ureter, bladder, and acute renal failure, acute tubular necrosis, and other changes in urine composition is about 14.402 mg/kg .
Description
Aurothioglucose is highly water soluble, and its aqueous solutions decompose on long standing. It therefore is available as a suspension in sesame oil. Gold content is approximately 50%. Following IM injection, it is highly protein bound (95%), and peak plasma levels are achieved within 2 to 6 hours. Following a single 50-mg dose, the biological half-life ranges from 3 to 27 days, but following successive weekly doses, the half-life increases to 14 to 40 days after the third dose. The therapeutic effect does not correlate with serum plasma gold levels but appears to depend on total accumulated gold. Aurothioglucose is indicated for the adjunctive treatment of adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
Chemical properties
yellow crystals,
History
In 1927, aurothioglucose was found to relieve joint pain when used to treat bacterial endocarditis. The area of chrysotherapy had begun. Subsequent investigations led to an extensive study of gold compounds in Great Britain by the Empire Rheumatism Council, which reported in 1961 that sodium aurothiomalate was effective in slowing the development of progressive joint diseases. Both aurothioglucose and sodium aurothiomalate are orally ineffective and are administered by IM injection. In 1985, the first orally effective gold compound for arthritis, auranofin, was introduced in the United States. Several other gold compounds have been evaluated clinically but do not appear to offer advantages in terms of efficacy or toxicity.
The Uses of Aurothioglucose
Aurothioglucose hydrate has been used in redox stress survival assay in human cell lines and for inducing obese phenotype in mice.
The Uses of Aurothioglucose
To produce obesity in experimental animals.
Indications
Aurothioglucose is indicated for the adjunctive treatment of early active adult and juvenile type rheumatoid arthritis that is not adequately controlled by other anti-inflammatory agents and conservative measures like salicylate, glucocorticoids, etc. . In chronic, advanced cases of rheumatoid arthritis, such gold therapy is not demonstrated to be as valuable .
Antirheumatic measures such as salicylate and other anti-inflammatory drugs (both steroidal and non steroidal) may be continued after initiation of gold therapy . After improvement commences, these measures may be discontinued slowly as symptoms permit .
Background
Aurothioglucose, also known as gold thioglucose, was formerly used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Contemporary research on the effect of gold salts treatment began in 1935, primarily to reduce inflammation and to slow disease progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis . The use of gold compounds has decreased since the 1980s owing to numerous side effects, limited efficacy, and slow onset of action. Many if not most gold compounds that were indicated for rheumatoid arthritis therapy have since been replaced with the use of various current disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate and others, which are far more effective.
brand name
Solganal (Schering, USA, Yugoslavia), Aureotan (BYK Gulden, Germany).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Aurothioglucose, a gold compound used clinically to treat rheumatoid arthritis, has recently been found to be a potent PKCiota-Par6 interaction inhibitor, with an IC50 approximately 1 μM. Disruption of this interaction disrupts a rac1 signaling pathway that is required for transformed growth in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Pharmacokinetics
After administration, patient serum levels of gold rise sharply but decline over the following week . Peak levels with aqueous preparations are higher and decline faster than those with oily preparations . Regular weekly administration produces a continuous rise in the basal value for several months, after which the serum level becomes relatively stable . After a standard weekly dose, considerable individual variation in the levels of gold can be observed . A steady decline in gold levels occurs when the interval between injections is lengthened, and small amounts may be found in the serum for months after discontinuation of therapy . The incidence of toxic reactions is seemingly unrelated to the plasma level of gold, but may perhaps be more associated with the total cumulative content of gold in the body .
Clinical Use
Aurothioglucose is highly water soluble, and its aqueous solutions decompose on long standing. It therefore is available as a suspension in sesame oil. Gold content is approximately 50%. Following IM injection, it is highly protein bound (95%), and peak plasma levels are achieved within 2 to 6 hours. Following a single 50-mg dose, the biological half-life ranges from 3 to 27 days, but following successive weekly doses, the half-life increases to 14 to 40 days after the third dose. The therapeutic effect does not correlate with serum plasma gold levels but appears to depend on total accumulated gold. Aurothioglucose is indicated for the adjunctive treatment of adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and neoplastigenic data. A deadly human poison by an unspecified route. An experimental poison by intramuscular route. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous and intravenous routes. Human systemic effects: nausea or vomiting, cholestatic jaundlce, and eye effects. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. See also GOLD COMPOUNDS. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx. Used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Synthesis
Synthesis: gold thioglucose is prepared by
adding a solution of gold bromide to an aqueous
solution of thioglucose that contains sulfur dioxide. After heating, the product is precipitated by
the addition of ethanol.
Metabolism
Although the exact metabolic fate of aurothioglucose is not formally understood, the principal gold species that can be found in the urine and blood of a patient following the administration of the drug is [Au(CN)2]- .
Purification Methods
Purify it by dissolving it in H2O (0.05g in 1mL) and precipitating it by adding EtOH. It yields yellow crystals with a slight mercaptan odour. It decomposes slowly in H2O, and is soluble in propylene glycol but insoluble in EtOH and other common organic solvents. [Caterson & Taylor FEBS Lett 98 351 1979, Cooney et al. Biochem J 259 651 1989.]
Dosage
Aurothioglucose is an antirheumatic used to treat active progressing rheumatoid arthritis and nondisseminated lupus erythematosus. The drug is administered at weekly intervals by intramuscular injection (10 mg, 25 mg, then 50 mg) until 800 mg to 1 g has been given. If improvement takes place, the drug is then administered at levels that balance the urinary excretion of gold. During this maintenance therapy the interval between injections is lengthened to 3 – 4 weeks.
Properties of Aurothioglucose
| Melting point: | >107oC (dec.) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble5mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
| Merck | 13,887 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic, Light Sensitive |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 13, Sup 7) 1987 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Aurothioglucose (12192-57-3) |
Safety information for Aurothioglucose
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Aurothioglucose
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Aurothioglucose CAS 12192-57-3View Details
Aurothioglucose CAS 12192-57-3View Details
12192-57-3 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1