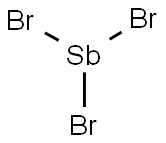
Antimony trichloride
Synonym(s):Antimonous acid, Antimony trichloride;Antimony trichloride;Antimony(III) chloride
- CAS NO.:10025-91-9
- Empirical Formula: Cl3Sb
- Molecular Weight: 228.119
- MDL number: MFCD00011212
- EINECS: 233-047-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
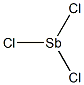
What is Antimony trichloride?
Description
Antimony trichloride is a noncombustible,clear, colorless, crystalline solid with an acrid, pungentodor. Molecular weight= 228.10; Boiling point= 223.3℃;Freezing/Melting point= 73℃; Specific gravity (H2O:1)=3.14 at 20℃; Heat of solution=2 1.6 3 105 J/kg; Heat offusion= 13.3 cal/g; Vapor pressure= 0.119 mmHg at 20℃.Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M RatingSystem): Health 3, Flammability 0, Reactivity 2. Soluble inwater; solubility=10%[d]; reaction.
Chemical properties
Colourless Crystal Or Flakes,fuming in moist air.
Chemical properties
Antimony trichloride is a noncombustible, clear, colorless, crystalline solid. Acrid, pungent odor.
Physical properties
Colorless crystalline solid; orthorhombic crystal; hygroscopic; density 3.14 g/cm3; melts at 73.4°C; boils at 220.3°C; readily dissolves in water undergoing hydrolysis; soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid, ethanol, acetone, benzene, dioxane and CS2.
The Uses of Antimony trichloride
Antimony Trichloride is used as a chlorinating agent, as a fireproofing agent in textiles; in bronzing steel and as a mordant in dyeing as well as a caustic in medicine. It is also used as an apoptosis agent that is used to detect cholesterols and carotenoids.
The Uses of Antimony trichloride
Used in the chemical microscopy of drugs.
The Uses of Antimony trichloride
Bronzing iron, especially gun barrels; mordant for patent leather and in dyeing; coloring zinc black; manufacture of lakes, particularly from dye woods; furniture polishes.
What are the applications of Application
Antimony (III) Chloride is an apoptosis agent that is used to detect cholesterols and carotenoids.
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic chloride salt with formula SbCl3. It is used as a reagent for detecting vitamin A and related carotenoids, reacting with the carotenoid to form a blue complex that can be measured by colorimetry (the Carr-Price test). Solu ions of antimony trichloride were formerly used for dissolving and removing horn stubs from calves and goats.
Definition
A white deliquescent solid, formerly known as butter of antimony. It is prepared by direct combination of antimony and chlorine. It is readily hydrolyzed by cold water to form a white precipitate of antimony(III) chloride oxide (antimonyl chloride, SbOCl): SbCl3 + H2O = SbOCl + 2HCl.
Preparation
SbCl3 is prepared by reaction of chlorine with antimony, antimony trioxide or antimony trisulfide. It also may be made by treating antimony trioxide with concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Production Methods
Although manufacture from antimony metal and chlorine is expensive, it is feasible on a small scale. The best procedure is to react chlorine with antimony metal in liquid antimony trichloride or concentrated hydrochloric acid. In the first case the temperature can be as high as 200 ℃. Equally good results are obtained by dissolving antimony oxides in hot, concentrated hydrochloric acid. Distillation of the crude product or its solution in strong hydrochloric acid in the presence of some metallic antimony or iron (to reduce antimony(V) and iron(III) compounds) then yields pure antimony trichloride.
General Description
Antimony trichloride is a colorless crystalline solid. Antimony trichloride is shipped as a solid or liquid solution. Antimony trichloride is decomposed slowly by water to hydrochloric acid and antimony oxychloride. Antimony oxychloride is soluble in hydrochloric acid but insoluble in water. Antimony trichloride is corrosive to metals and tissue.
Air & Water Reactions
Fumes in air to form hydrochloric acid [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. Decomposed by water to form hydrochloric acid and antimony oxychloride.
Reactivity Profile
Acidic salts, such as ANTIMONY TRICHLORIDE, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions.
Hazard
Corrosive liquid or solid. Very irritating to eyes, skin.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or contact (skin, eyes) with vapors, dusts or substance may cause severe injury, burns or death. Reaction with water or moist air will release toxic, corrosive or flammable gases. Reaction with water may generate much heat that will increase the concentration of fumes in the air. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Vapors may accumulate in confined areas (basement, tanks, hopper/tank cars etc.). Substance will react with water (some violently), releasing corrosive and/or toxic gases and runoff. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated or if contaminated with water.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human pulmonary system effects by inhalation. Corrosive by vigorous reaction with moisture, generating heat and hydrogen chloride gas (a strong irritant), whch can cause pulmonary edema when inhaled. Systemic effects can be caused by the antimony. See also ANTIMONY COMPOUNDS. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of chlorine and antimony. It can react violently with aluminum, potassium, sodmm.
Potential Exposure
It is used to make antimony salts and drugs; to fireproof textiles; and as a catalyst in many organic reactions; as a reagent for chloral, aromatic hydrocarbons, vitamin A, and for drug identification.
First aid
his chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek med ical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, includ ing resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medi cal attention. If victim is conscious, administer water or252 Antimony trichloridemilk. Do not induce vomiting. Medical observation isrecommended for 24°48 h after breathing overexposure, aspulmonary edema may be delayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor or authorized paramedic may consideradministering a corticosteroid spray.
Storage
(1) Color Code—White: Corrosive or ContactHazard; Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location.(2) Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store in asecure poison location. Prior to working with this chemicalyou should be trained on its proper handling and storage.Store in tightly closed containers under nitrogen in a cool,well-ventilated area away from water or moisture, heat andincompatible substances, such as strong bases, aluminum,potassium, and sodium.
Shipping
UN1733 Antimony trichloride, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
Dry the trichloride over P2O5 or by mixing it with toluene or xylene and distilling (water is carried off with the organic solvent), then distil it twice under dry nitrogen at 50mm, and sublime it twice in a vacuum into ampoules and seal. It can be crystallised from CS2 and is deliquescent. It fumes in moist air and is decomposed by H2O with precipitation of the basic chloride, but forms a clear solution in dilute HCl.
Incompatibilities
Decomposes in water, forming hydrochloric acid and antimony oxychloride. Reacts violently with strong bases; ammonia, alkali metals; aluminum, potassium, sodium. Forms explosive mixture with perchloric acid when hot. Reacts with air forming hydrochloric acid. Attacks metals in the presence of moisture, forming explosive hydrogen gas.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of Antimony trichloride
| Melting point: | 73.4 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 223 °C |
| Density | 3,14 g/cm3 |
| vapor density | 7.9 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 49 °C) |
| Flash point: | 223.5°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | Powder, Crystals and/or Chunks |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 3.14 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water, hydrochloric acid, alcohol, benzene, carbon disulfide, dioxane, chloroform, ether, acetone and carbon tetrachloride. Insoluble in organic bases. |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,707 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 50 mg/m3; TWA 0.5 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 5.3(0.0℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Hygroscopic. Reacts violently with water. Incompatible with metals. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10025-91-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Antimony trichloride (10025-91-9) |
Safety information for Antimony trichloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Antimony trichloride
| InChIKey | FAPDDOBMIUGHIN-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
Antimony trichloride manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Mincometsal
Jaiswal S Cyber Shop
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
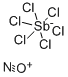
You may like
-
 Antimony trichloride 99%View Details
Antimony trichloride 99%View Details -
 Antimony(III) chloride CAS 10025-91-9View Details
Antimony(III) chloride CAS 10025-91-9View Details
10025-91-9 -
 Antimony(III) chloride CAS 10025-91-9View Details
Antimony(III) chloride CAS 10025-91-9View Details
10025-91-9 -
 Antimony(III) chloride CAS 10025-91-9View Details
Antimony(III) chloride CAS 10025-91-9View Details
10025-91-9 -
 Antimony(III) chloride, For analysis ACS CAS 10025-91-9View Details
Antimony(III) chloride, For analysis ACS CAS 10025-91-9View Details
10025-91-9 -
 Antimony(III) chloride, For analysis ACS CAS 10025-91-9View Details
Antimony(III) chloride, For analysis ACS CAS 10025-91-9View Details
10025-91-9 -
 Antimony(III) chloride, For analysis ACS CAS 10025-91-9View Details
Antimony(III) chloride, For analysis ACS CAS 10025-91-9View Details
10025-91-9 -
 Antimony (III) chloride, Ultra dry CAS 10025-91-9View Details
Antimony (III) chloride, Ultra dry CAS 10025-91-9View Details
10025-91-9
