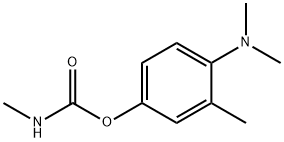
AMINOCARB
- CAS NO.:2032-59-9
- Empirical Formula: C11H16N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 208.26
- MDL number: MFCD00055440
- EINECS: 217-990-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 15:16:40
What is AMINOCARB?
Chemical properties
Tan; crystalline; slightly water-soluble; melting point 93–94C.
The Uses of AMINOCARB
Aminocarb is a carbamate insecticide.
The Uses of AMINOCARB
Insecticide.
The Uses of AMINOCARB
Nonsystemic, broad-spectrum insecticide used to control the spruce budworm in forests; molluscicide
Definition
ChEBI: A carbamate ester that is phenyl methylcarbamate substituted by a dimethylamino group at position 4 and a methyl group at position 3.
Hazard
Highly poisonous.
Environmental Fate
Plant/Surface Water. Several transformation products reported by Day (1991) include
4-amino-m-tolyl-N-methylcarbamate (AA), 4-amino-3-methylphenol (AC), 4-formamidom-tolyl-N-methylcarbamate (FA), N-(4-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl)-N-methylformamide
(FC), 4-methylformamido-m-tolyl-N-methylcarbamate (MFA), 4-methylamino-m-tolyl-Nmethylcarbamate (MAA), 3-methyl-4-(methylamino)phenyl-N-methylcarbamate (MAC),
phenol, methylamine and carbon dioxide. MAA was not detected in natural water but was
detected in fish tissues following exposure to aminocarb-treated water in the laboratory.
The metabolites FA, AC and MAC were detected in Canadian forests treated with aminocarb but the metabolites AA, MAA and FC were not detected (Day, 1991)
On and/or in bean plants, aminocarb degrades with the carbamate moiety remaining
intact. Methylcarbamate derivatives identified include the 4-methylamino, 4-amino, 4-
methylformamido and 4-formamido analogs (Abdel-Wahab et al., 1966)
Photolytic. When aminocarb in ethanol was irradiated by UV light, extensive degradation was observed. No degradation products were identified; however, two unidentified
cholinesterase inhibitors were reported (Crosby et al., 1965).
Chemical/Physical. Aminocarb is hydrolyzed in purified water to 4-(dimethylamino)-
3-methylphenol which is then converted to 2-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone. This compound
was then oxidized to form the following compounds: 6-(dimethylamino)-2-methyl-1,4-
benzoquinone, 6-(methylamino)-2-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone, 5-(dimethylamino)-2-
methyl-1,4-benzoquinone and 5-(methylamino)-2-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone (Leger and
Mallet, 1988). When aminocarb was irradiated by a high pressure xenon-mercury lamp
(λ = 253.7 nm) in aerated and degassed ethyl alcohol and cyclohexene solutions, 4-
dimethylamino-3-methyl phenol formed as the major product. A duplicate run using an
excitation wavelength of >300 nm yielded that same phenol as the major product. Sinceaminocarb absorbs radiation in the solar region (at λ >300 nm), this compound would be
expected to undergo photochemical degradation in the environment (Addison et al., 1974)
Emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition (Sax and Lewis,
1987)
Metabolic pathway
Aminocarb in purified water is hydrolyzed to 4- (dimethylamino)-3-methylphenol which is in turn converted to 2-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone either by direct means or via 2-methyl-1,4-dihydroquinone. The benzoquinone reacts readily with methylamine and diethylamine present in solution to give four red chemicals. In addition, mono- and diepoxides of 2-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone are formed.
Properties of AMINOCARB
| Melting point: | 93-94℃ |
| Boiling point: | 347.46°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.095 |
| refractive index | 1.5000 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| pka | 12.25±0.46(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | 915mg/L(20 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,432 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Aminocarb (2032-59-9) |
Safety information for AMINOCARB
Computed Descriptors for AMINOCARB
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
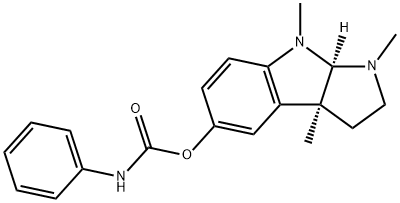
 Aminocarb CAS 2032-59-9View Details
Aminocarb CAS 2032-59-9View Details
2032-59-9 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4