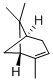
alpha-Pinene
Synonym(s):α-Pinene;(±)-2-Pinene;2,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene;alpha-Pinene
- CAS NO.:80-56-8
- Empirical Formula: C10H16
- Molecular Weight: 136.23
- MDL number: MFCD00001339
- EINECS: 201-291-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
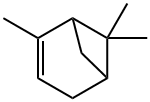
What is alpha-Pinene?
Description
Alpha-pinene is the major constituent of turpentine (about 80%). It exists as a levogyre form in European turpentines, and as a dextrogyre form in turpentines found in North America. Sensitization mainly occurs in painters, polishers and varnishers, and in those in the perfume and ceramics industry.
Chemical properties
liquid with a turpentine odour
Chemical properties
α-Pinene is the most widespread pinene isomer. (+)-α-Pinene, (1R,5R)-2,6,6-trimethylbicyclo[3.3.1]hept-2-ene, occurs, for example, in oil from Pinus
palustris Mill., at a concentration up to 65%; oil from Pinus pinaster Soland and
American oil from Pinus caribaea contain 70% and 70–80%, respectively, of the
laevorotatory isomer, (?)-α-Pinene, (1S,5S)-2,6,6-trimethylbicyclo[3.3.1]hept-2-ene.
α-Pinene undergoes many reactions, of which the following are used in the fragrance
industry: upon hydrogenation, α-pinene is converted to pinane, which has
become an important starting material in the industrial processes used in the fragrance
and flavor industry. α-Pinene can be isomerized to β-pinene with high
selectivity for β-pinene formation. Hydration with simultaneous ring opening
yields terpineol and cis-terpin hydrate. Pyrolysis of α-pinene yields a mixture
of ocimene and alloocimene.
Pure α-pinene is obtained by distillation of turpentine oils. As a fragrance substance,
it is used to improve the odor of industrial products.However, it is farmore
important as a starting material in industrial syntheses, for example, terpineols, borneol, and camphor.
Chemical properties
α-Pinene has a characteristic odor of pine. It is turpentine-like. The oxidized material has a resin-like odor.
Occurrence
The structure would account for the presence of four optically active and two optically inactive isomers; although only d-, l-, and dl-α-pinene are known, however; presence of one or more isomers has been reported in more than 400 essential oils; in the largest amounts it has been reported found in Achillea millefolium (d-), Artemisia tridentata (d-), Italian rosemary (l-), wild thyme (l-), French lavender (l-), coriander (d-, dl-), cumin (d, dl-), labdanum (l-), neroli (l-), lemon, Litsea cubeba (d-) and ylang-ylang (d-). It is also reported in over 200 natural products including apple, apricot, many citrus juices and peel oils, bilberry, cranberry, lingonberry, blackberry, currants, guava, raspberry, strawberry, orange, lime, grapefruit, mandarin, tangerine oils and juices, various spices, mint essential oils, carrot, celery, cooked potato, bell pepper, tomato, anise, cinnamon, cassia leaf, clove, cumin, ginger, Mentha oils, nutmeg, mace, pepper, parsley, thyme, Swiss and cheddar cheese, cream, fatty fish, fried chicken, beef fat, hop oil, rum, bourbon whiskey, tea, roasted filberts, pecans, oats, soybean, plum, mushroom, sweet and wild marjoram, starfruit, mango, tamarind, cardamom, coriander, gin, rice, litchi, calamus, dill, lovage, caraway seed, buckwheat, laurel, fennel, kiwifruit, myrtle leaf and berry, rosemary, buchu oil, Bourbon vanilla, Spanish and clary sage, nectarine, crayfish, clam, cape gooseberry, anise hyssop, angelica root oil, Roman and German chamomile oil, eucalyptus oil, bullock’s heart and mastic gum leaf and fruit oil.
The Uses of alpha-Pinene
α-Pinene was used as standard in headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatographic analysis of volatile compounds in virgin olive oils 1 . It was used in the synthesis of cesium-doped heteropolyacid having potential application in biodiesel synthesis.
The Uses of alpha-Pinene
Reference Standard in the analysis of herbal medicinal products
The Uses of alpha-Pinene
α-Pinene was used as standard in headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatographic analysis of volatile compounds in virgin olive oils. It was used in the synthesis of cesium-doped heteropolyacid having potential application in biodiesel synthesis.
What are the applications of Application
α-Pinene is a standard in headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatographic analysis
Definition
ChEBI: A pinene that is bicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene substituted by methyl groups at positions 2, 6 and 6 respectively.
Preparation
From turpentine, by distillation.
Production Methods
α-Pinene occurs naturally in a variety of trees and shrubs, including more than 400 essential oils, and air concentrations near pine forests may reach 500–1200 mg/m3. Total U.S. emission of α-pinene from deciduous and coniferous forests amounts to 6.6 million tons annually. An estimated emission rate of α-pinene from natural sources to the atmosphere is 1.84×10 -10 g/cm3/s.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 2.5 to 62 ppb. Aroma characteristics at 1.0%: terpy citrus and spicy, woody pine and turpentinelike with a slight cooling camphoraceous nutmeglike nuance, a fresh herbal lift and a tropical fruit top note.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 10 ppm: intense, woody, piney and terpy with camphoraceous and turpentine notes. It has herbal, spicy and slightly tropical mango nuances.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a turpentine odor. Flash point 91°F. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air. Used as a solvent.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
alpha-Pinene may react vigorously with strong oxidizing agents. May react exothermically with reducing agents to release gaseous hydrogen.
Health Hazard
Harmful if swallowed, inhaled or absorbed through skin. High concentrations are extremely destructive to mucous membrane and upper respiratory tract, eyes and skin. Symptoms of exposure may include burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis, shortness of breath, headache, nausea and vomiting.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Vapor may travel considerable distance to source of ignition and flashback. Container explosion may occur during fire conditions. Forms explosive mixtures in air.
Contact allergens
Alpha-pinene is the major constituent of turpentine (about 80%). It exists in levogyre form in European turpentine and in dextrogyre form in turpentine found in North-Americans. Sensitization occurs mainly in painters, polishers, and varnishers, and in those in the perfume and in the ceramics industry.
Safety Profile
A deadly poison by inhalation. Moderately toxic by ingestion. An eye, mucous membrane, and severe human skin irritant. Flammable liquid. A dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use foam, Co2, dry chemical. Explodes on contact with nitrosyl perchlorate.
Properties of alpha-Pinene
| Melting point: | -55°C |
| Boiling point: | 155-156 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.858 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 6.9hPa at 20℃ |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2902 | ALPHA-PINENE |
| Flash point: | 90 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in ethanol; |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Odor | at 10.00 % in dipropylene glycol. fresh camphor sweet pine earthy woody |
| Odor Threshold | 0.018ppm |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| JECFA Number | 1329 |
| Merck | 13,7527 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.7(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 80-56-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | «alpha»-Pinene(80-56-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | .alpha.-Pinene (80-56-8) |
Safety information for alpha-Pinene
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H304:Aspiration hazard H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
Computed Descriptors for alpha-Pinene
alpha-Pinene manufacturer
New Products
3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Iodophenylacetic acid Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine Pivalic anhydride,98% Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride, 98% Glyoxylic acid solution, 50% in water tert-Butyl glycinate,97% 4-Ethoxybenzoic acid, 99% Sodium 1-octanesulfonate monohydrate 7-Ethyl Tryptophol 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) 5-Cyanophthalide 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 3-Methoxybenzonitrile Dibenzoyl Peroxide 4-Methoxybenzonitrile Titanium Dioxide Chloral PentachlorobenzonitrileRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![PINENE 1G [R]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)



You may like
-
 80-56-8 Alpha Pinene 99%View Details
80-56-8 Alpha Pinene 99%View Details
80-56-8 -
 alpha-Pinene 98%View Details
alpha-Pinene 98%View Details
80-56-8 -
 Alpha-pinene 97% CAS 80-56-8View Details
Alpha-pinene 97% CAS 80-56-8View Details
80-56-8 -
 80-56-8 98%View Details
80-56-8 98%View Details
80-56-8 -
 alpha-Pinene 98%View Details
alpha-Pinene 98%View Details
80-56-8 -
 80-56-8 alpha-Pinene 98%View Details
80-56-8 alpha-Pinene 98%View Details
80-56-8 -
 α-Pinene CAS 80-56-8View Details
α-Pinene CAS 80-56-8View Details
80-56-8 -
 α-Pinene CAS 80-56-8View Details
α-Pinene CAS 80-56-8View Details
80-56-8
