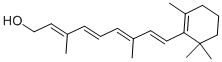
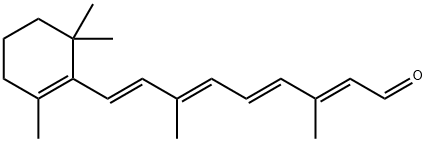
Retinal
Synonym(s):Vitamin A aldehyde
- CAS NO.:116-31-4
- Empirical Formula: C20H28O
- Molecular Weight: 284.44
- MDL number: MFCD00001550
- EINECS: 204-135-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:59
What is Retinal?
Chemical properties
Yellow Powder
The Uses of Retinal
Corotenoid component of the visual pigments. All-trans retinal is converted to retinoic acid in vivo by the action of retinal dehydrogenase.
The Uses of Retinal
retinaldehyde is a mild retinoid credited with increasing epidermal thickness without producing erythema.
The Uses of Retinal
All trans-Retinal has been used:
- in optogenetic experiments
- in electrophysiological experiment
- to study the effect of AKR1B10 (aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily member) on the conversion of retinal to retinol in the airway epithelium
- in decidual transformation of human endometrial stromal cells
What are the applications of Application
all-trans Retinal-14,15-13C2 is a carotenoid component of the visual pigments
What are the applications of Application
all-trans Retinal is an oxidized form of retinol, which is a corotenoid component of the visual pigments.
Definition
ChEBI: A retinal in which all four exocyclic double bonds have E- (trans-) geometry.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 29, p. 419, 1988 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)80111-2
General Description
All trans-Retinal is one of the major derivatives of vitamin A group. A variety of food serves as a source of vitamin A. It is predominant in liver and among the brightly colored vegetables.
Biological Activity
all-trans retinal, also known as vitamin a aldehyde or retinaldehyde, is one of the many forms of vitamin a and also the oxidation product of all-trans retinol [1]. all-trans retinal are associated with one of the two isoforms of cellular retinol-binding proteins (crbp-i and crbp-ii) with kd values of 50 and 90 nm, respectively [1].crbp-i and crbp-ii were the first intracellular retinoid-binding proteins. both proteins display a similar binding affinity towards retinal. they play important roles in retinoid biology and regulation of the metabolism of retinol and retinal. crbp-i is used to regulate vitamin a storage and synthesis of retinoic acid. and crbp-ii has a role in the initial processing of retinol from food [1].all-trans retinal is one form of vitamin a. all-trans retinal, the initial substrate of retinoid cycle, is a chemically reactive aldehyde that can form toxic conjugates with proteins and lipids, leading to degeneration of the retina [2].
Biochem/physiol Actions
All-trans retinal is converted to retinoic acid in vivo by the action of retinal dehydrogenase. Retinoic acid is a ligand for both the retinoic acid receptor (RAR) and the retinoid X receptor (RXR) that act as transcription factors to regulate the growth and differentiation of normal and malignant cells. Retinal isomers are also chromophores that bind to opsins, a family of G-protein-linked transmembrane proteins, to form photosensitive receptors in visual and nonvisual systems. All-trans retinal is a potent photosensitizer.
Purification Methods
The aldehyde is separated from retinol by column chromatography on water-deactivated alumina. Elute with 1-2% acetone in hexane, or on TLC plates of silica gel G and using the same eluting solvent. It crystallises from pet ether or n-hexane as yellow-orange crystals, and the UV in hexane has max at 373nm (A1cm 1% 1,548) and 368nm ( 48,000). It is an irritant and is light sensitive. Store it in sealed ampoules under N2. The semicarbazone forms yellow crystals from CHCl3/Et2O or EtOH, m 199-201o(dec). The 9-cis-isomer [514-85-2] and the 13-cis-isomer [472-86-6] [max at 375nm ( 1,250) in EtOH] are also available commercially. [Beilstein 7 III 1742.]
References
[1]. noy n. retinoid-binding proteins: mediators of retinoid action. biochem j. 2000 jun 15;348 pt 3:481-95.
[2]. kiser pd, golczak m, maeda a, et al. key enzymes of the retinoid (visual) cycle in vertebrate retina. biochim biophys acta. 2012 jan;1821(1):137-51.
Properties of Retinal
| Melting point: | 61-63°C |
| Boiling point: | 366.92°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0083 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | powder |
| color | yellow |
| Water Solubility | <70mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic, Light Sensitive, Temperature Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 116-31-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Retinal (116-31-4) |
Safety information for Retinal
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Retinal
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 All-trans-retinal 95% CAS 116-31-4View Details
All-trans-retinal 95% CAS 116-31-4View Details
116-31-4 -
 all trans-Retinal CAS 116-31-4View Details
all trans-Retinal CAS 116-31-4View Details
116-31-4 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6