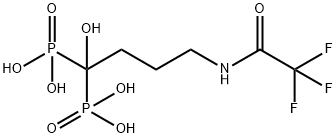
Alendronic acid
- CAS NO.:66376-36-1
- Empirical Formula: C4H13NO7P2
- Molecular Weight: 249.1
- MDL number: MFCD00868112
- EINECS: 204-352-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
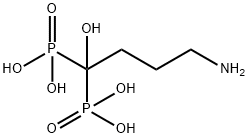
What is Alendronic acid?
Absorption
Mean oral bioavailability of alendronic acid in women is 0.64% and in men is 0.59%. Bioavailability of alendronic acid decreases by up to 40% if it is taken within an hour of a meal.
Toxicity
In clinical studies, ≥3% of patients experience abdominal pain, acid regurgitation, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, musculoskeletal pain, and nausea.
No information for treatment of overdose is available, however patients should be given milk or antacids to bind alendronic acid and vomiting should not be induced. Patients may experience hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, and upper gastrointestinal events..
There are currently no studies for safety and efficacy in pregnancy, though studies in pregnant rats show fetal and maternal complications at 4 times the clinical dose and pregnant rabbits do not show complications at as high as 10 times the clincal dose.
Excretion in breast milk, and therefore safety in lactation, is unknown.
Alendronic acid has been studied for use in pediatric patients. The oral bioavailability is similar to that in adult patients, but an increase in the portion of patients experiencing vomiting.
There is no significant difference in efficacy or safety of alendronic acid in geriatric populations, though there is potential for even greater sensitivity in patients at a further advanced age than those in the study.
Alendronic acid is not recommended for patients with creatinine clearance <35mL/min, but no dosage adjustment is necessary in hepatic impairment.
Originator
Adronat ,Neopharmed ,Italy
The Uses of Alendronic acid
Alendronate acid is an inhibitor of FDPS.
Background
Alendronic acid is a second generation bisphosphonate that is used for the treatment of some forms of osteoperosis and Paget's disease. It functions by preventing resorption of bone.
What are the applications of Application
Alendronate acid is an inhibitor of FDPS
Indications
Alendronic acid is indicated for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in men and postmenopausal women, treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, and Paget's disease of bone. However, alendronic acid is not indicated for use in pediatric populations or patients with a creatinine clearance <35mL/min.
Definition
ChEBI: A 1,1-bis(phosphonic acid) that is methanebis(phosphonic acid) in which the two methylene hydrogens are replaced by hydroxy and 3-aminopropyl groups.
Manufacturing Process
4-Amino-1-hydroxybutylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (ABDT).
Orthosphophorous acid (102.7 g; 1.25 moles) is introduced into a 2 liter-flask
with condenser, stirrer and dropping funnel, placed on a thermostatized bath;
the air is then removed with a nitrogen stream which is continued during all
the reaction. The acid is melted by heating the bath to 95°C. When melting is
complete, 4-aminobutyric acid (103.3; 1 mole) is added under stirring which
is continued till obtaining a doughy fluid. Phosphorous trihalide (176 ml; 2
moles) is added dropwise causing the mixture to boil and evolution of gaseous
hydrochloric acid which is damped by means of a suitable trap. The addition
rate is adjusted so as to keep a constant reflux for about 60 minutes. When
the addition is nearly over, the mixture swells, slowly hardening. Stirring is
continued as long as possible, whereafter the mixture is heated for further 3
hours. Without cooling, but removing the bath, water (300 ml) is added, first
slowly and then quickly. Heating and stirring are started again. Decolorizing
charcoal is added and the mixture is boiled for about 5 minutes, then hotfiltered
on paper and the filtrate is refluxed for 6 hours. After cooling is slowly
poured in stirred methanol (1500 ml) causing thereby the separation of a
white solid which collected and dried (161 g; 64.6%). The structure of ABDT
is confirmed by IR spectrum, proton magnetic and nuclear magnetic
resonance spectrum and elemental analysis.
The sodium salt of this acid may be prepared by adding of equivalent of
sodium hydroxide.
Therapeutic Function
Antiosteoporotic
Hazard
A reproductive hazard.
Pharmacokinetics
Alendronic acid tablets have a very low oral bioavialability. After administration it distributes into soft tissue and bone or is excreted in the urine. Alendronic acid does not undergo metabolism.
Clinical Use
Bisphosphonate:
Treatment and prophylaxis of osteoporosis
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Calcium salts: reduced absorption of alendronate.
Metabolism
Alendronate transiently distributes to soft tissues but is then rapidly redistributed to bone or excreted in the urine. There is no evidence that alendronate is metabolised in animals or humans. Following a single intravenous dose of [14C]-alendronate, approximately 50% of the radioactivity was excreted in the urine within 72 hours and little or no radioactivity was recovered in the faeces.
Metabolism
Urinary excretion is the sole method of elimination of alendronic acid and no metabolites are detected upon urine collection.
Properties of Alendronic acid
| Melting point: | 230-235°C |
| Boiling point: | 616.7±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.857±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Aqueous Base (Sparingly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Very Slightly) |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| form | powder to crystal |
| pka | pK1 2.72 ±0.05; pK2 8.73 ±0.05; pK3 10.5 ±0.1; pK4 11.6 ±0.1 at 25°, (0.1M KCl) |
| color | White to Light yellow |
| Merck | 14,229 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phosphonic acid, P,P'-(4-amino-1-hydroxybutylidene)bis- (66376-36-1) |
Safety information for Alendronic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Alendronic acid
Alendronic acid manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

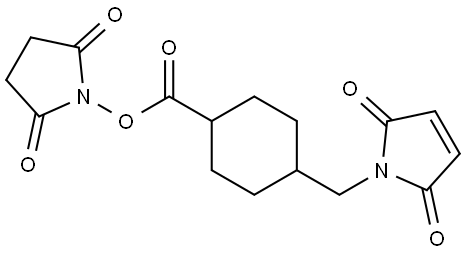
![Phosphonic acid, P,P'-[4-[[[4-[(2,5-dihydro-2,5-dioxo-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)methyl]cyclohexyl]carbonyl]amino]-1-hydroxybutylidene]bis-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20210111/GIF/1426523-52-5.gif)

You may like
-
 66376-36-1 Alendronic acid 98%View Details
66376-36-1 Alendronic acid 98%View Details
66376-36-1 -
 66376-36-1 98%View Details
66376-36-1 98%View Details
66376-36-1 -
 Alendronic acid 98%View Details
Alendronic acid 98%View Details
66376-36-1 -
 Alendronic acid 95% CAS 66376-36-1View Details
Alendronic acid 95% CAS 66376-36-1View Details
66376-36-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1