Adenine
Synonym(s):6-Aminopurine;Adenine;Adenine - CAS 73-24-5 - Calbiochem;Vitamin B4
- CAS NO.:73-24-5
- Empirical Formula: C5H5N5
- Molecular Weight: 135.13
- MDL number: MFCD00041790
- EINECS: 200-796-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-05-28 21:18:33

What is Adenine?
Description
adenine is one of the purine nitrogenous bases that composes DNA and RNA; composed of two carbon–nitrogen rings. Adenine bonds with thymine in DNA and with uracil in RNA (see base pairing rule); it is also a major component of other molecules such as adenosine triphosphate.
Chemical properties
Adenine is a prominent member of the family of naturally occurring purines. Adenine occurs not only in ribonucleic acids (RNA), and deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA), but in nucleosides, such as adenosine, and nucleotides, such as adenylic acid, which may be linked with enzymatic functions quite apart from nucleic acids. Adenine, in the form of its ribonucleotide, is produced in mammals and fowls endogenously from smaller molecules and no nutritional essentiality is ascribed to it. In the nucleosides, nucleotides, and nucleic acids, the attachment or the sugar moiety is at position 9.
The purines and pyrimidines absorb ultraviolet light readily, with absorption peaks at characteristic frequencies. This has aided in their identification and quantitative determination.
Physical properties
Adenine is a white to almost white crystalline powder that is an important biological compound found in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), ribonucleic acid (RNA), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It was once commonly referred to as vitamin B4 but is no longer considered a vitamin. Adenine is derived from purine. Purine is a heterocyclic compound.
History
Adenine is one of the two purines found in DNA and RNA. The other is guanine. Adenine and guanine are called bases in reference to DNA and RNA. A nucleic acid base attached to ribose forms a ribonucleoside. Adenine combined with ribose produces the nucleoside adenosine.
The Uses of Adenine
Adenine is used as an active component of boron-deficient media to grow yeast in order to assess whether yeast growth is stimulated by boron. It is useful as a local antiseptic and vitamin B4. Further, it is used in the microbial determination of niacin. It is also employed as a food supplement for adult rats to investigate the effects of dietary adenine overload. In addition to this, it is used in the production of nucleotides of the nucleic acids.
Background
A purine base and a fundamental unit of adenine nucleotides.
Indications
For nutritional supplementation, also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance
Definition
ChEBI: Adenine is the parent compound of the 6-aminopurines, composed of a purine having an amino group at C-6. It has a role as a human metabolite, a Daphnia magna metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a purine nucleobase and a member of 6-aminopurines. It derives from a hydride of a 9H-purine.
What are the applications of Application
Widespread throughout animal and plant tissues combined with niacinamide, d-ribose, and phosphoric acids; a constituent of nucleic acids and coenzymes, such as codehydrase I and II, adenylic acid, coa laninedehydrase. It is used in microbial determination of niacin; in research on heredity, virus diseases, and cancer.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 88, p. 3829, 1966 DOI: 10.1021/ja00968a028
General Description
Adenine is a purine nucleobase. It is part of DNA, and RNA. Adenine is also a component of cofactors (NAD, FAD) and signaling molecules (cAMP). It is a nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA. It is also a constituent of certain coenzymes and when combined with the sugar ribose it forms the nucleoside adenosine found in AMP, ADP, and ATP. Adenine has a purine ring structure. It is one of the major component bases ofnucleotides and the nucleic acidsDNA and RNA.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Adenine is essential for many in vivo and in vitro biochemical processes. Adenine is converted to adenosine with ribose. On phosphorylation, it forms AMP, ADP and ATP. ATP is the energy currency of the cell and is required during cellular metabolism. Adenine is metabolized to is 2,8-dihydroxyadenine, which on accumulation in proximal tubules leads to the induction of chronic kidney disease (CKD) with severe anemia in rats. Adenine based derivatives elicit antiviral functionality against dsDNA viruses and are exploited for generating antiviral scaffolds.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx,.
Biological function
Adenine (sometimes known as vitamin B4) combines with the sugar ribose to form adenosine, which can be bonded from one to three phosphoric acid units, yielding AMP, ADP and ATP. These adenine derivatives perform important functions in cellular metabolism. Adenine is one of four nitrogenous bases utilized to synthesize nucleic acids. A modified form of adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP) is an important secondary messenger in the propagation of many hormonal stimuli. Adenine is an integral part of the structure of many coenzymes. Adenosine (adenine with a ribose group) causes transient heart block in the AV node of the heart. In individuals suspected of suffering from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify the rhythm. Certain SVTs can be successfully terminated with adenosine.
Metabolism
Not Available
Purification Methods
Crystallise adenine from distilled water. [Beilstein 26 III/IV 3561.]
Properties of Adenine
| Melting point: | >360 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 238.81°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3795 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7000 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 220°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 0.5 M HCl: soluble20mg/mL, Grade III, colorless to faint yellow or tan |
| pka | 4.12(at 25℃) |
| form | Liquid or Solid |
| color | Clear colorless to light yellow |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 7 |
| Water Solubility | 0.5 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sublimation | 220 ºC |
| Merck | 14,152 |
| BRN | 5777 |
| Stability: | Stable. Moisture-sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 73-24-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Adenine(73-24-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Adenine (73-24-5) |
Safety information for Adenine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Adenine
| InChIKey | GFFGJBXGBJISGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Adenine manufacturer
New Products
N-Boc-3-pyrrolidinone Carbamic acid, (3-oxocyclobutyl)-, 1,1-dimethylethyl ester (9CI) 3-(3-PYRIDYL)ACRYLIC ACID 6-chloro-4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)pyridin-3-amine Milvexian 3-Iodophenylacetic acid Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Lamotrigine Cetirizine Dihydrochloride Clopidogrel Bisulfate/Clopidogrel Hydrogen Sulfate Form-II S-amlodipine Besylate 9-Bromo-7,7-diethyl-7H-benzo[c]fluoren-5-ol methyl 3-hydroxy-6-methylpyridazine-4-carboxylate 2,3-Dimethoxy-7,7-dipropyl-9-(trifluoromethyl)7H-benzo[c]fluoren-5-ol N1-(3,5-diisopropylbiphenyl-4-yl)benzene-1,2-diamine 9-(4-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-methoxy-7,7-dipropyl-7H-benzo[c]fluoren-5-ol N-(4-bromo-2-chlorobenzyl)propionamide Efinaconazole N-Oxide Impurity 2 Efinaconazole D6 Glycolyl-Phenylalanyl Octreotide Enclomiphene D10 Citrate N-Nitroso Vildagliptin Impurity Vibegron D7 PolycaprolactoneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

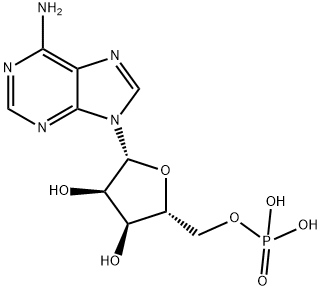
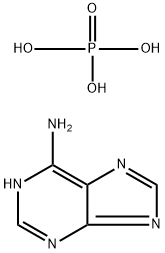
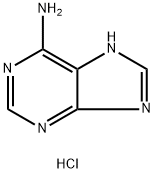
You may like
-
 Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
73-24-5 -
 Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
73-24-5 -
 Adenine extrapure CAS 73-24-5View Details
Adenine extrapure CAS 73-24-5View Details
73-24-5 -
 Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
73-24-5 -
 Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
73-24-5 -
 ADENINE For Biochemistry CAS 73-24-5View Details
ADENINE For Biochemistry CAS 73-24-5View Details
73-24-5 -
 Adenine 99% CAS 73-24-5View Details
Adenine 99% CAS 73-24-5View Details
73-24-5 -
 Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
Adenine CAS 73-24-5View Details
73-24-5
