Acitretin
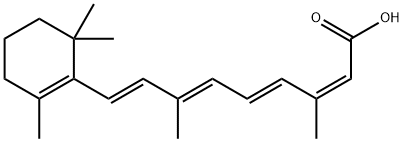
Synonym(s):9-(4-Methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethylnona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid;Acitretin
- CAS NO.:55079-83-9
- Empirical Formula: C21H26O3
- Molecular Weight: 326.43
- MDL number: MFCD00866632
- EINECS: 259-474-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36

What is Acitretin?
Absorption
Oral absorption of acitretin is optimal when given with food, and is linear and proportional with increasing doses from 25 to 100 mg. Approximately 72% (range 47% to 109%) of the administered dose was absorbed after a single 50 mg dose of acitretin was given to 12 healthy subjects.
Toxicity
Oral, rat: LD50 = >4000 mg/kg. Symptoms of overdose include headache and vertigo.
Description
Acitretin is the free acid form of etretinate useful in the treatment of severe psoriasis and other disorders of keratinization. Although the two compounds have virtually the same efficacy and teratogenic side-effects, acitretin is advantageous for child-bearing women, as its shorter half-life reduces the necessary contraception period from two years to only one month after treatment ceases.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Hoffmann-La Roche (Switzerland)
The Uses of Acitretin
Acitretin, a retinoid that binds to nuclear receptors and regulates gene expression, is a potent activator of the α-secretase ADAM10 gene expression and apoptosis inducer via the CD95 signalling pathway. Acitretin is a systemic retinoid drug used in the treatment of severe psoriasis.
The Uses of Acitretin
A synthetic retinoid which is the major metabolite of etretinate (E938000).
The Uses of Acitretin
antipsoriatic;binds to nuclear receptors that regulate gene transcription
What are the applications of Application
Acitretin is a synthetic retinoid - the major metabolite of etretinate
Background
An oral retinoid effective in the treatment of psoriasis. It is the major metabolite of etretinate with the advantage of a much shorter half-life when compared with etretinate.
Indications
For the treatment of severe psoriasis in adults.
Indications
Unlike isotretinoin, acitretin (Soriatane) is not primarily sebosuppressive. Rather, it promotes normalization of dysregulated keratinocyte proliferative activity in the epidermis and is also antiinflammatory. Oral absorption is optimal when acitretin is taken with a fatty meal; peak levels are reached approximately 3 hours after ingestion, while steady-state plasma levels are achieved after approximately 3 weeks of daily dosing. The mean terminal elimination half-life of the parent compound is 49 hours. However, when consumed with ethanol, acitretin may be transesterified to form etretinate, a retinoid that is stored in adipose tissue, resulting in a much longer half-life (3–4 months or longer).
Definition
ChEBI: All-trans-acitretin is an acitretin, a retinoid and an alpha,beta-unsaturated monocarboxylic acid. It has a role as a keratolytic drug.
Manufacturing Process
228 g of 5-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethyl-phenyl)-3-methyl-penta-2,4-diene-1-
triphenylphosphonium bromide was added under nitrogen to 910 ml of
dimethylformamide and treated at 5-10°C within 20 min. with 17.5 g of a
suspension of sodium hydride (about 50% by weight) in mineral oil. The
mixture was stirred for 1 hour at about 10°C, then 61.8 g of 3-formylcrotonic
acid butyl ester was added dropwise at 5-8°C, a mixture was heated for 2
hours at 65°C, subsequently introduced into 8 L of ice-water, then was added
300 g of sodium chloride, and the mixture thoroughly extracted with a total
18 L of hexane. The extract was washed 5 times with 1 L of methanol/water
(6:4 parts by volume) each time and 2 times with 1.5 L water each time,
dried over sodium sulphate and evaporated under reduced pressure to leave
9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-nona-2,4,6,8-tetraen-1-oic
acid butyl ester, m.p. 80-81°C.
125.8 g of this ester was introduced into 2 L of abs. ethanol and treated with
a solution of 125.6 g of hydroxide in 195 ml of water. The mixture was heated to boiling under nitrogen gassing for 30 minutes, then cooled, introduced into
10 L of ice-water and, after the addition of about 240 ml of conc. hydrochloric
acid (pH 2-4), thoroughly extracted with total 9 L methylene chloride. Extract
is washed with about 6 L water to neutrality, dried over calcium chloride and
evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue is taken up in 700 ml of
hexane. The precipitated 9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethyl-phenyl)-3,7-dimethylnona-
2,4,6,8-tetraen-1-oic acid melts at 228-230°C.
brand name
Soriatane (Connetics);Neotigason (r) 10;Neotigason roche 10 mg;Neotigason sauter kapsein 25 mg.
Therapeutic Function
Antipsoriatic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Acitretin, a retinol derivative, was introduced in 1989 for the treatment of severe psoriasis. By the end of 1990, acitretin was confirmed to be metabolized in part to etretinate. Marketing authorization was suspended temporarily in France while the product information was modified to conform to the recommendations issued by the Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products of the European Communities. Acitretin remains registered in several countries. See also WHO comment for etretinate.
General Description
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Acitretin is a major metabolite of etretinate and belongs to the class of retinoid and is typically used for treating psoriasis. Acitretin inhibits excessive cell growth and keratinisation which are the major symptoms of psoriasis, therefore reducing plaque formation and scaling.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Synthetic retinoid that is a metabolite of etretinate. Preferentially binds to cellular retinoic acid binding proteins (CRABPs).
Mechanism of action
Acitretin (Soriatane) is a synthetic derivative of vitamin A that is particularly effective in treating the pustular and erythrodermic forms of psoriasis. It is the main metabolite of etretinate; ingestion of alcohol with acitretin increases the amount of detectable etretinate. It is accumulated in fatty tissue with a prolonged elimination half-life of approximately 120 days. Most patients show improvement within 2 to 4 weeks, although some patients may need as long as 6 months of therapy before a response is noted.
Pharmacokinetics
Acitretin is a retinoid. Retinoids have a structure similar to vitamin A and are involved in the normal growth of skin cells. Acitretin works by inhibiting the excessive cell growth and keratinisation (process by which skin cells become thickened due to the deposition of a protein within them) seen in psoriasis. It therefore reduces the thickening of the skin, plaque formation and scaling.
Pharmacology
Like other systemic retinoids, acitretin is a serious teratogen and should not be prescribed for women of childbearing potential unless no acceptable alternative is available and the patient has acknowledged in writing that she understands the need to use two effective forms of contraception during therapy and for 3 years following discontinuation of therapy. Because of the much longer half-life of etretinate, which may be formed when ethanol is ingested with acitretin, female patients of childbearing potential must also agree not to ingest alcohol during treatment and for 2 months following its discontinuation. Other toxicities are similar to those of isotretinoin; they include cutaneous irritation and inflammation, bone and joint pain, hyperlipidemia, hepatic enzyme elevation, and tendinous and ligamentous calcifications.Alopecia (hair loss) may also occur in some patients.
Clinical Use
Acitretin is most useful for the treatment of severe psoriasis, particularly the pustular and erythrodermic variants. Psoriatic nail changes and arthritis also may respond. Combining the drug with ultraviolet light therapy (Re-UVB, in the case of ultraviolet B radiation, or Re-PUVA, with psoralen plus ultraviolet A radiation) permits the use of lower doses of both acitretin and ultraviolet radiation. Other conditions for which the drug may be especially useful include congenital and acquired hyperkeratotic disorders, such as the ichthyoses and palmoplantar keratodermas, and severe lichen planus.
Side Effects
Side effects are dose dependent and include elevation of triglycerides, hepatitis, hair loss, thinning of the nails, cheilitis, xerosis, and stickiness of the skin. Gemfibrozil (300 mg b.i.d.) corrects elevated lipid levels on this therapy.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Acitretin may be useful in the treatment of canine lamellar ichthyosis,
solar-induced
precancerous lesions in Dalmatians or bull
Terriers, actinic keratoses, squamous cell carcinomas,
and intracutaneous
cornifying epitheliomas (multiple keratoacanthomas).
While the drug has provided effective treatment of idiopathic
seborrhea (particularly in cocker spaniels), it is not effective in treating
the ceruminous otitis that may also be present. Results have
been disappointing
in treating idiopathic seborrheas seen in basset
hounds and West Highland terriers.
Acitretin’s usage in cats is very limited, but etretinate has shown
some usefulness in treating paraneoplastic
actinic keratosis, solarinduced
squamous cell carcinoma and Bowen’s Disease in this
species.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Alcohol: increased risk of teratogenicity in women.
Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of benign
intracranial hypertension with tetracyclines - avoid
concomitant use.
Anticoagulants: possible antagonism of the
anticoagulant effect of coumarins.
Cytotoxics: increased concentration of methotrexate
(also increased risk of hepatotoxicity) - avoid
concomitant use.
Vitamin A: risk of hypervitaminosis - avoid
concomitant use.
Metabolism
Following oral absorption, acitretin undergoes extensive metabolism and interconversion by simple isomerization to its 13-cis form (cis-acitretin). Both parent compound and isomer are further metabolized into chain-shortened breakdown products and conjugates, which are excreted.
Metabolism
Acitretin is metabolised by isomerisation into its 13-cis isomer (cis acitretin), which is also a teratogen, by glucuronidation and cleavage of the side chain. Acitretin is excreted entirely in the form of its metabolites, in approximately equal parts via the kidneys and the bile.
Properties of Acitretin
| Melting point: | 228-230°C |
| Boiling point: | 404.46°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1348 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4700 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in tetrahydrofuran, slightly soluble in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent), very slightly soluble in cyclohexane. |
| form | powder |
| pka | 4.72±0.33(Predicted) |
| color | Light yellow to yellow |
| λmax | 352nm(MeOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,112 |
| Stability: | LIGHT SENSITIVE |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 55079-83-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Acitretin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H360:Reproductive toxicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Acitretin
Acitretin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 55079-83-9 Acitretin 98%View Details
55079-83-9 Acitretin 98%View Details
55079-83-9 -
 Acitretin 98%View Details
Acitretin 98%View Details
55079-83-9 -
 Acitretin CAS 55079-83-9View Details
Acitretin CAS 55079-83-9View Details
55079-83-9 -
 Acitretin, 98% (HPLC) CAS 55079-83-9View Details
Acitretin, 98% (HPLC) CAS 55079-83-9View Details
55079-83-9 -
 Acitretin CAS 55079-83-9View Details
Acitretin CAS 55079-83-9View Details
55079-83-9 -
 CAS 55079 83 9 ACITRETIN APIView Details
CAS 55079 83 9 ACITRETIN APIView Details
55079-83-9 -
 Acitretin CAS: 55079-83-9View Details
Acitretin CAS: 55079-83-9View Details
55079-83-9 -
 AcitretinView Details
AcitretinView Details
55079-83-9
