Isotretinoin
Synonym(s):13-cis-Retinoic acid;Isotretinoin
- CAS NO.:4759-48-2
- Empirical Formula: C20H28O2
- Molecular Weight: 300.44
- MDL number: MFCD00079542
- EINECS: 225-296-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:56
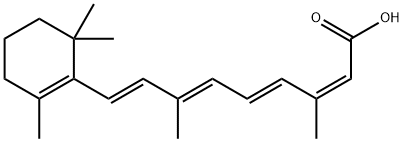
What is Isotretinoin?
Absorption
Patients reach a maximum concentration of 74-511ng/mL after 1-4 hours following a 100mg oral dose. Isotretinoin is better absorbed with a high fat meal and bioavailability may change from one brand to another.
Following a 40mg oral dose, fasted subjects reached a maximum concentration of 314ng/mL in 2.9 hours with an area under the curve of 4055ng/mL*hr. Subjects given a high fat meal and a 40mg oral doses reached a maximum concentration of 395ng/mL in 6.4 hours with an area under the curve of 6095ng/mL*mL.
Toxicity
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with vomiting, facial flushing, cheilosis, abdominal pain, headache, dizziness, and ataxia. These symptoms may rapidly resolve. Generally no treatment is required for these overdoses.
The oral lowest dose causing toxic effect (TDLO) for children is 30mg/kg/21W, oral TDLO for men is 24mg/kg/4W, oral TDLO for women is 56mg/kg/8W. The intraperitoneal LD50 for rats is 901mg/kg, oral LD50 for mice is 3389mg/kg, oral LD50 for rats is >4000mg/kg.
Isotretinoin is associated with major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortion, and premature birth. It is unknown if isotretinoin is expressed in breast milk but due to the associated hazards a decision should be made to either stop nursing or stop taking isotretinoin.
In animal studies, isotretinoin was associated with an increased risk of pheochromocytoma and adrenal medullary hyperplasia at doses above the recommended clinical dose. Isotretinoin was negative for the Ames test of mutagenicity once and weakly positive a second time. It has not been shown to be clastogenic. A study in dogs noted testicular atrophy after doses of 10-30 times the recommended clinical dose for 30 weeks. In trials with men there were no effects seen on sperm count, motility, morphology, ejaculate volume, and seminal plasma fructose.
Description
Isotretinoin is the 9-cis isomer of retinoic acid, a close relative of retinol, or vitamin A. It was originally developed to treat cystic acne, and today this is still its primary use despite several more modern applications of the drug, including a treatment for pancreatic and brain cancers. First shown to be an effective treatment for acne in 1982, its development stemmed from advances in knowledge of the effects of vitamin A to reduce or eliminate sebum production. Since that time, however, several instances of deleterious effects became well known, most notably birth defects arising from the use of isotretinoin.
Chemical properties
Yellow or orange crystalline powder or crystal, insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, very slightly soluble in ether, soluble in chloroform.
Originator
Accutane,Roche
The Uses of Isotretinoin
isotretinoin is a retinoid derivative with improved bioavailability and percutaneous absorption for acne treatment products. Presently being studied in conjuction with the treatment of photoaged skin.
Background
Isotretinoin is a retinoid derivative of vitamin A used in the treatment of severe recalcitrant acne. It was most widely marketed under the brand name Accutane, which has since been discontinued. Isotretinoin is associated with major risks in pregnancy and is therefore only available under the iPLEDGE program in the United States. The first isotretinoin-containing product was FDA approved on 7 May 1982.
Indications
Isotretinoin is indicated to treat severe recalcitrant nodular acne and patients ≥12 years enrolled in the iPLEDGE program.
What are the applications of Application
13-cis-Retinoic acid is a vitamin A analog that inhibits cell proliferation
Definition
ChEBI: Isotretinoin is a retinoic acid that is all-trans-retinoic acid in which the double bond which is alpha,beta- to the carboxy group is isomerised to Z configuration. A synthetic retinoid, it is used for the treatment of severe cases of acne and other skin diseases. It has a role as a keratolytic drug, an antineoplastic agent and a teratogenic agent. It is a conjugate acid of a 13-cis-retinoate.
Indications
Isotretinoin (Accutane) alters keratinization in the acroinfundibulum of sebaceous glands and shrinks them, thereby reducing sebum excretion and comedogenesis. These features underlie its usefulness in acne vulgaris, since sebum secretion is a hallmark of acneprone skin. Furthermore, the drug has antiinflammatory activity.
Preparation
Preparation of isotretinoin in a single step from β-ionone and ethyl chloride are first reacted together after which the product is further reacted with triphenylphosphine to obtain Triphenyl salt. The Triphenyl salt is further reacted with cyclopentenone derivative to produce isotretinoin and its 8Z isomer. separate out the 8Z isomer and convert it to isotretinoin through isomerization with the help of nitric acid.
brand name
Accutane (Roche); Amnesteem (Genpharm); Claravis (Barr); Sotret (Ranbaxy);Accutane roche;Apsor;Isotretinoin;Neovamin a acid;Neovitamin a acid;Ro 4-3780;Roacutan.
Therapeutic Function
Antiacne, Keratolytic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Isotretinoin, a retinol derivative, was introduced in 1982 exclusively for the treatment of severe acne. Its use in pregnant women has resulted in major fetal abnormalities. The manufacturer's information emphasizes that the drug is teratogenic and must not be given to women who are pregnant, and that contraceptive measures must be maintained for at least four weeks after discontinuation of treatment. In some countries, blood banks are advised not to accept as donors persons who have taken isotretinoin within the previous four weeks. See also under retinol (vitamin A).
General Description
Yellow-orange to orange crystalline powder; orange-brown chunky solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
An organic acid and unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbon. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Isotretinoin are not available; however, Isotretinoin is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
13-cis-Retinoic acid (RA) has anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor action. The action of RA is mediated through RAR-β and RAR-α receptors. RA attenuates iNOS expression and activity in cytokine-stimulated murine mesangial cells. It induces mitochondrial membrane permeability transition, observed as swelling and as a decrease in membrane potential, and stimulates the release of cytochrome c implicating mechanisms through the apoptosis pathway. These activities are reversed by EGTA and cyclosporin A. RA also increases MMP-1 protein expression partially via increased transcription.
Mechanism of action
Isotretinoin binds to and activates nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs); activated RARs serve as transcription factors that promote cell differentiation and apoptosis. This agent also exhibits immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory responses and inhibits ornithine decarboxylase, thereby decreasing polyamine synthesis and keratinization. Isotretinoin is rapidly absorbed orally, with peak blood concentrations 3 hours after ingestion. It is not stored in tissue, and the elimination half-life is 10 to 20 hours, either after a single dose or during chronic therapy.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacodynamics of isotretinoin are poorly understood.
Clinical Use
Isotretinoin is most useful for the treatment of severe recalcitrant nodular acne vulgaris. It may also be helpful in other disorders of keratinization, but it is not useful for psoriasis. High doses of isotretinoin (2mg/kg/day) are effective as cancer chemoprevention agents to reduce the frequency of cutaneous malignancies in patients at increased risk, such as those with xeroderma pigmentosum, an inherited disorder in which DNA repair is deficient, or in immunosuppressed patients.
Side Effects
Isotretinoin is teratogenic to humans and should not be administered to pregnant women or women contemplating pregnancy. Concomitant use of isotretinoin with drugs of the tetracycline class increases the incidence of Pseudotumor cerebri. There have been recent reports of an increased risk of depression, suicide, and suicide attempts in individuals taking isotretinoin, but the causality has not been absolutely proved.
Isotretinoin, like many retinoids, can lead to increase in serum aminotransferase levels, but, unlike acitretin and etretinate, isotretinoin has not been clearly implicated in cases of clinically apparent acute liver injury with jaundice.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A human teratogen by ingestion with fetal developmental abnormalities of the skin and appendages and other postnatal effects. Human reproductive effects. Human systemic effects: decreased immune response, darrhea, hypermouhty, irritative dermatitis, sweating. Human mutation data reported. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Isotretinoin may be useful in treating a variety of dermatologicrelated
conditions,
including canine lamellar ichthyosis, cutaneus
T-cell lymphoma, intracutaneous cornifying epitheliomas,
multiple
epidermal inclusion cysts, comedo syndrome in Schnauzers,
and sebaceous adenitis seen in standard poodles.
Because of the concerns of teratogenic effects in humans, availability
to veterinarians may be restricted by the manufacturers and
drug distributors; obtaining the medication for veterinary patients
may be difficult.
Environmental Fate
In primates (including humans), isotretinoin (Accutane) is
metabolized to a more active form, 13-cis-4-oxo-retinoic acid,
which is able to move through the placental membrane. On
its own, however, Accutane (isotretinoin) is not particularly
motile across the placental barrier, and perhaps most interestingly
tends not to bind to cellular retinoid-binding proteins
or nuclear receptors. The rapid isomerization to the all-trans
isomer, the oxidation of Accutane (isotretinoin) to 13-cis-4-
oxo-retinoic acid, and the relatively high circulation times of
these compounds may be important in explaining the teratogenic
toxicity of Accutane (isotretinoin).
Some studies have more fully explored the metabolic
products of isotretinoin. For example, isotretinoin can be
metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 microsomal
enzyme system – more specifically the CYP2C8, CYP2C,
CYP3A4, and CYP2B6 isoenzymes. The metabolites produced
are numerous, including retinoic acid (tretinoin), 4-oxo-isotretinoin,
and 4-oxo-retinoic acid (4-oxo-tretinoin). This relatively
large array of retinoid metabolites may produce a variety
of effects, most notably due to their higher potency as retinoids
compared to the parent compound (isotretinoin).
It is possible that these additional metabolites are capable
of binding to a variety of retinoid receptors in order to alter
gene expression and further transcription or transrepression in
protein synthesis, which may be responsible for the toxic effects
of isotretinoin.
Metabolism
Isotretinoin, or 13-cis-retinoic acid can undergo reversible cis-trans isomerization to all-trans-retinoic acid. Isotretinoin undergoes 4-hydroxylation to 4-hydroxy-13-cis-retinoic acid, which is oxidized to the main metabolite 4-oxo-13-cis-retinoic acid.. All-trans-retinoic acid undergoes 4-hydroxylation to 4-hydroxy-all-trans-retinoic acid, which is oxidized to 4-oxo-all-trans-retinoic acid. 4-oxo-13-cis-retinoic acid can undergo reversible cis-trans isomerization to 4-oxo-all-trans-retinoic acid.
Toxicity evaluation
Direct studies focused on the environmental fate of Accutane (isotretinoin) are rare in the literature. The pure compound is insoluble in water, and highly lipophilic. Powders do not aerosolize readily, and volatilization is extremely low. Isotretinoin released into the environment would not be expected to have high mobility in water or soil, and will most likely become deposited in organic materials. Bioaccumulation is possible, but isotretinoin is readily oxidized to form other retinoids or metabolites that are expected to be mitigated via natural biological pathways.
Properties of Isotretinoin
| Melting point: | 172-175 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 381.66°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0597 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, soluble in methylene chloride, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It is sensitive to air, heat and light, especially in solution. Carry out all operations as rapidly as possible and avoid exposure to actinic light; use freshly prepared solutions. |
| form | Fine Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 4.76±0.33(Predicted) |
| color | Yellow-orange to orange |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| λmax | 354nm(EtOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,5228 |
| Stability: | Stable, but probably air and light sensitive. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 4759-48-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isotretinoin (4759-48-2) |
Safety information for Isotretinoin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Isotretinoin
| InChIKey | SHGAZHPCJJPHSC-YCNIQYBTSA-N |
Isotretinoin manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

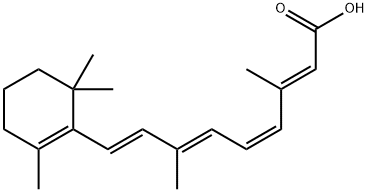
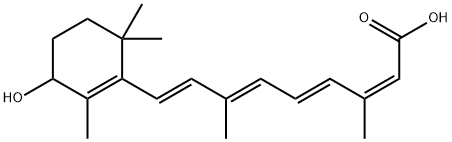
![2-[[(3aS,4R,6S,6aR)-4-[7-[[(1R,2S)-2-(3,4-Difluorophenyl)cyclopropyl]amino]-5-(propylthio)-3H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-3-yl]-2,2-dimethyl-tetrahydro-3aH-cyclopenta[d][1,3]dioxol-6-yl]oxy]ethanol](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/274693-26-4.gif)
You may like
-
 Isotretinoin 98%View Details
Isotretinoin 98%View Details -
 Isotretinoin 99%View Details
Isotretinoin 99%View Details -
 Isotretinoin 99%View Details
Isotretinoin 99%View Details -
 13-cis-Retinoic Acid CAS 4759-48-2View Details
13-cis-Retinoic Acid CAS 4759-48-2View Details
4759-48-2 -
 Isotretinoin >98% (HPLC) CAS 4759-48-2View Details
Isotretinoin >98% (HPLC) CAS 4759-48-2View Details
4759-48-2 -
 Isotretinoin 95.00% CAS 4759-48-2View Details
Isotretinoin 95.00% CAS 4759-48-2View Details
4759-48-2 -
 Isotretinoin CAS 4759-48-2View Details
Isotretinoin CAS 4759-48-2View Details
4759-48-2 -
 Isotretinoin CAS 4759-48-2View Details
Isotretinoin CAS 4759-48-2View Details
4759-48-2
