Acebutolol
- CAS NO.:37517-30-9
- Empirical Formula: C18H28N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 336.43
- MDL number: MFCD00599435
- EINECS: 253-539-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
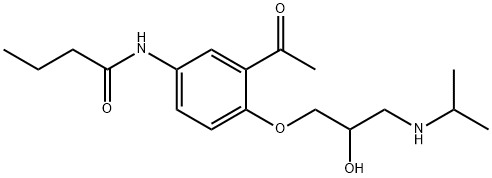
What is Acebutolol?
Absorption
Well absorbed from the Gl tract with an absolute bioavailability of approximately 40% for the parent compound. In
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include extreme bradycardia, advanced atrioventricular block, intraventricular conduction defects, hypotension, severe congestive heart failure, seizures, and in susceptible patients, bronchospasm, and hypoglycemia.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Sectral ,May and Baker ,UK ,1975
The Uses of Acebutolol
Cardioselective ?adrenergic blocker. Antihypertensive; antianginal; antiarrhythmic (class II)
The Uses of Acebutolol
Cardioselective β-adrenergic blocker. Antihypertensive; antianginal; antiarrhythmic (class II).
The Uses of Acebutolol
Acebutol is 3′-acetyl-4′-[2-hydroxy-3-(iso-propylamino)propoxy] butyranilide (12.1.6) [9,10].Acebutol is a selective β1-adrenoblocker. It possesses antianginal, antihypotensive, and antiarrhythmic action. It is used for arterial hypertension, preventing attacks of angina, and cardiac rhythm disturbances.
Background
A cardioselective beta-adrenergic antagonist with little effect on the bronchial receptors. The drug has stabilizing and quinidine-like effects on cardiac rhythm as well as weak inherent sympathomimetic action.
Indications
For the management of hypertension and ventricular premature beats in adults.
Definition
ChEBI: An ether that is the 2-acetyl-4-(butanoylamino)phenyl ether of the primary hydroxy group of 3-(propan-2-ylamino)propane-1,2-diol.
Manufacturing Process
Crude 5'-butyramido-2'-(2,3-epoxypropoxy)acetophenone (16 g),
isopropylamine (20 g) and ethanol (100 ml) were heated together under
reflux for 4 hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced
pressure and the residual oil was dissolved in N hydrochloric acid. The acid
solution was extracted with ethyl acetate, the ethyl acetate layers being
discarded. The acidic solution was brought to pH 11 with 2 N aqueous sodium
hydroxide solution and then extracted with chloroform. The dried chloroform
extracts were concentrated under reduced pressure to give an oil which was
crystallized from a mixture of ethanol and diethyl ether to give 5'-butyramido-
2'-(2-hydroxy-3-isopropylaminopropoxy)acetophenone (3 g), MP 119-123°C.
Crude 5'-butyramido-2'-(2,3-epoxypropoxy)acetophenone used as starting
material was prepared as follows: p-butyramidophenol (58 g; prepared
according to Fierz-David and Kuster, Helv. Chim. Acta 1939,2282), acetyl
chloride (25.4 g) and benzene (500 ml) were heated together under reflux
until a solution formed (12 hours). This solution was cooled and treated with
water. The benzene layer was separated and the aqueous layer was again
extracted with benzene.
The combined benzene extracts were dried and evaporated to dryness under
reduced pressure to give p-butyramidophenyl acetate (38 g) as an off-white
solid, MP 102-103°C. A mixture of p-butyramidophenyl acetate (38 g),
aluminum chloride (80 g) and 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane (250 ml) was heated
at 140°C for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled and treated with iced
water. The tetrachloroethane layer was separated and the aqueous layer was
extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layers were extracted with 2
N aqueous sodium hydroxide and the alkaline solution was acidified to pH 5
with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The acidified solution was extracted with
chloroform and the chloroform extract was dried and concentrated under
reduced pressure to give 5'-butyramido-2'-hydroxyacetophenone (15.6 g), MP
114-117°C. A solution of 5'-butyramido-2'-hydroxyacetophenone (15.6 g) in ethanol (100 ml) was added to an ethanolic solution of sodium ethoxide which
was prepared from sodium (1.62 g) and ethanol (100 ml). The resulting
solution was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure and
dimethylformamide (100 ml) was added to the solid residue. Approximately
10 ml of dimethylformamide was removed by distillation under reduced
pressure. Epichlorohydrin (25 ml) was added and the solution was heated at
100°C for 4 hours. The solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to
give a residual oil which was treated with water to give a solid. The solid was
dissolved in ethanol and the resulting solution was treated with charcoal,
filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give crude 5'-butyramido-
2'-(2,3-epoxypropoxy)acetophenone (16 g), MP 110-116°C.
The crude compound may be purified by recrystallization from ethyl acetate,
after treatment with decolorizing charcoal, to give pure 5'-butyramido-2'-(2,3-
epoxypropoxy)acetophenone, MP 136-138°C.
brand name
Sectral (Dr. Reddy’s).
Therapeutic Function
beta-Adrenergic blocker
General Description
Acebutolol is one of the very few β-blockers whosemetabolite plays a significant role in its pharmacological actions.This drug is absorbed well from the gastrointestinaltract, but it undergoes extensive first-pass metabolic conversionto diacetolol by hydrolytic conversion of the amidegroup to the amine, followed by acetylation of the amine. After oral administration, plasma levels of diacetololare higher than those of acebutolol. Diacetolol is also aselective β1-blocker with partial agonistic activity; it has littlemembrane-stabilizing activity. It has a longer half-life (8–12hours) than the parent drug and is excreted by the kidneys.
Pharmacokinetics
Acebutolol is a cardioselective, beta-adrenoreceptor blocking agent, which possesses mild intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) in its therapeutically effective dose range. In general, beta-blockers reduce the work the heart has to do and allow it to beat more regularly. Acebutolol has less antagonistic effects on peripheral vascular ?2-receptors at rest and after epinephrine stimulation than nonselective beta-antagonists. Low doses of acebutolol produce less evidence of bronchoconstriction than nonselective agents like propranolol but more than atenolol.
Clinical Use
Acebutolol (Sectral) is a cardioselective 1-adrenoceptor blocking agent that also has some minor membrane stabilizing effects on the action potential. Acebutolol is effective in the management of the patient with essential hypertension, angina pectoris, and ventricular arrhythmias. Antiarrhythmic effects are observed with the patient both at rest and taking exercise.
Side Effects
Adverse effects include bradycardia, gastrointestinal upset, dizziness, and headache.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intravenousroute. Human systemic effects by ingestion: developmentalabnormalities of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;effects on newborn in biochemical and metabolicabnormalities and reduced growth statistics. A humanter
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: NSAIDs antagonise hypotensive effect.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of myocardial
depression and bradycardia; increased risk of
bradycardia, myocardial depression and AV block
with amiodarone; increased risk of myocardial
depression and bradycardia with flecainide.
Antidepressants: enhanced hypotensive effect with
MAOIs.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect;
increased risk of withdrawal hypertension with
clonidine; increased risk of first dose hypotensive
effect with post-synaptic alpha-blockers such as
prazosin.
Antimalarials: increased risk of bradycardia with
mefloquine.
Antipsychotics enhanced hypotensive effect with
phenothiazines.
Calcium-channel blockers: increased risk of
bradycardia and AV block with diltiazem;
hypotension and heart failure possible with
nifedipine and nisoldipine; asystole, severe
hypotension and heart failure with verapamil.
Cytotoxics: possible increased risk of bradycardia
with crizotinib.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Fingolimod: possibly increased risk of bradycardia.
Moxisylyte: possible severe postural hypotension.
Sympathomimetics: severe hypertension with
adrenaline and noradrenaline and possibly with
dobutamine.
Metabolism
Subject to extensive first-pass hepatic biotransformation (primarily to diacetolol).
Metabolism
About half of an orally administered dose of acebutolol (Sectral) is absorbed. Approximately 25% of the drug is bound to plasma proteins, and its plasma halflife is about 4 hours.Metabolism of acebutolol produces a metabolite with -blocking activity whose half-life is 10 hours.
Precautions
Acebutolol should not be administered in cardiogenic shock, uncontrolled heart failure, or severe bradycardia or to patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug.
Properties of Acebutolol
| Melting point: | 119-123°C |
| Boiling point: | 472.9°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1748 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5700 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMF: 10 mg/mL,DMSO: 5 mg/mL,Ethanol: 5 mg/mL,PBS (pH 7.2): 0.3 mg/mL |
| pka | pKa 9.40 (Uncertain) |
| form | A solid |
| color | Crystals |
| Water Solubility | 259 mg/L |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 37517-30-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acebutolol(37517-30-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Butanamide, N-[3-acetyl-4-[2-hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propoxy]phenyl]- (37517-30-9) |
Safety information for Acebutolol
Computed Descriptors for Acebutolol
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 37517-30-9 Acebutolol 98%View Details
37517-30-9 Acebutolol 98%View Details
37517-30-9 -
 Acebutolol 98%View Details
Acebutolol 98%View Details -
 Acebutolol 98%View Details
Acebutolol 98%View Details
37517-30-9 -
 Acebutolol 95% CAS 37517-30-9View Details
Acebutolol 95% CAS 37517-30-9View Details
37517-30-9 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
