Metoprolol
- CAS NO.:51384-51-1
- Empirical Formula: C15H25NO3
- Molecular Weight: 267.36
- MDL number: MFCD00599534
- EINECS: 257-166-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
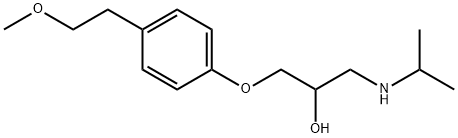
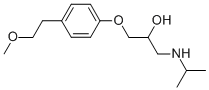
What is Metoprolol?
Absorption
When metoprolol is administered orally, it is almost completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum serum concentration is achieved 20 min after intravenous administration and 1-2 hours after oral administration. The bioavailability of metoprolol is of 100% when administered intravenously and when administered orally it presents about 50% for the tartrate derivative and 40% for the succinate derivative.
The absorption of metoprolol in the form of the tartrate derivative is increased by the concomitant administration of food.
Toxicity
Oral administration of metoprolol to rats presents an LD50 in the range of 3090 to 4670 mg/kg. Cases of overdose have reported bradycardia, hypotension, bronchospasm, and cardiac failure. In the case of an overdose, gastric lavage is recommended followed by specific treatment according to symptoms.
Metoprolol is not reported to be carcinogenic nor mutagenic nor to impair fertility. The only event registered is the increase of macrophages in pulmonary alveoli and slight biliary hyperplasia. When metoprolol was given for long periods of time on the highest dose, there was evidence of small benign lung tumors.
The Uses of Metoprolol
rac Metoprolol is a β1 selective aryloxypropanolamine andrenergic antagonist. Used in the treatment of a variety of cardiovascular disorder.
The Uses of Metoprolol
Anti-adrenergic.
What are the applications of Application
1-[4-(2-methoxyethyl)phenoxy]-3-propan-2-ylamino-propan-2-ol is a selective adrenergic β-1-blocking agent
Background
Metoprolol is a selective beta-1 blocker commonly employed as the succinate and tartrate derivatives depending if the formulation is designed to be of immediate release or extended release. The possibility of the generation of these formulations comes from the lower systemic bioavailability of the succinate derivative. To this date, it is one of the preferred beta-blockers in general clinical guidelines and it is widely prescribed in the Netherlands, New Zealand, and the US. Metoprolol was developed since 1969 by US Pharmaceutical Holdings I and FDA approved in 1978.
Indications
Metoprolol is indicated for the treatment of angina, heart failure, myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter and hypertension.
Some off-label uses of metoprolol include supraventricular tachycardia and thyroid storm.
All the indications of metoprolol are part of cardiovascular diseases. These conditions correspond to a number of diseases that involve the function of the heart and blood vessels. The underlying causes of these conditions are variable and can be due to genetic disposition, lifestyle decisions such as smoking, obesity, diet, and lack of exercise, and comorbidity with other conditions such as diabetes. The cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death on a global scale.
Definition
ChEBI: Metoprolol is a propanolamine that is 1-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol substituted by a 4-(2-methoxyethyl)phenoxy group at position 1. It has a role as a beta-adrenergic antagonist, an antihypertensive agent, a xenobiotic, an environmental contaminant and a geroprotector. It is a propanolamine, an aromatic ether, a secondary alcohol and a secondary amino compound.
Pharmacokinetics
Administration of metoprolol in normal subjects is widely reported to produce a dose-dependent reduction on heart rate and cardiac output. This effect is generated due to a decreased cardiac excitability, cardiac output, and myocardial oxygen demand. In the case of arrhythmias, metoprolol produces its effect by reducing the slope of the pacemaker potential as well as suppressing the rate of atrioventricular conduction.
The Metoprolol Atherosclerosis Prevention in Hypertensives (MAPHY) trial showed a significant improvement in sudden cardiac death and myocardial infarction when patients were given with metoprolol as compared with diuretics. As well, in clinical trials performed in 1990, metoprolol reduces mortality and re-infarction in 17% of the individuals when administered chronically after an episode of myocardial infarction.
Metabolism
Metoprolol goes through significant first-pass hepatic metabolism which covers around 50% of the administered dose. The metabolism of metoprolol is mainly driven by the activity of CYP2D6 and to a lesser extent due to the activity of CYP3A4. The metabolism of metoprolol is mainly represented by reactions of hydroxylation and O-demethylation.
Properties of Metoprolol
| Melting point: | 35 °C |
| Boiling point: | 398.6±37.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.033±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 9.56± 0.01(H2O,t =25,I=0.15(KCl))(Approximate) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 51384-51-1 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Propanol, 1-[4-(2-methoxyethyl)phenoxy]-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]- (51384-51-1) |
Safety information for Metoprolol
Computed Descriptors for Metoprolol
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


![METOPROLOL SUCCINATE IMP. E (EP): (2RS)-1-[2-(2-METHOXYETHYL)PHENOXY]-3-(ISOPROPYLAMINO)PROPAN-2-OL MM(CRM STANDARD)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)


![METOPROLOL RELATED COMPOUND A(+/-)1-ETHYLAMINO-3-[4-(2-METHOXYETHYL)PHENOXY]-PROPAN-2-OL USP(CRM STANDARD)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)

You may like
-
 Metoprolol 96% CAS 51384-51-1View Details
Metoprolol 96% CAS 51384-51-1View Details
51384-51-1 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1