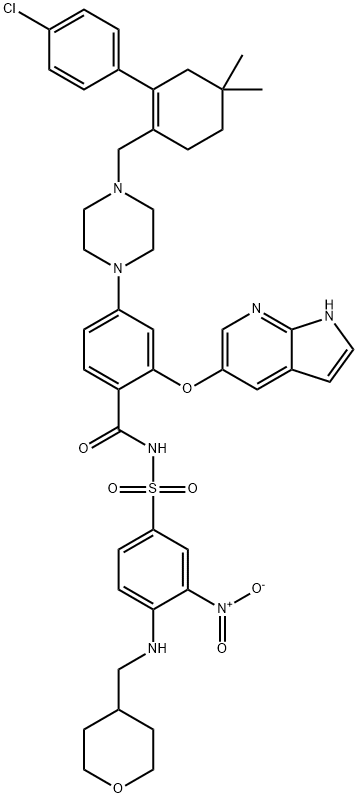
ABT-199
- CAS NO.:1257044-40-8
- Empirical Formula: C45H50ClN7O7S
- Molecular Weight: 868.44
- MDL number: MFCD23160052
- EINECS: 820-130-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-22 22:33:46
What is ABT-199?
Absorption
Following several oral administrations after a meal, the maximum plasma concentration of venetoclax was reached 5-8 hours after the dose . Venetoclax steady state AUC (area under the curve) increased proportionally over the dose range of 150-800 mg. After a low-fat meal, venetoclax mean (± standard deviation) steady-state Cmax was 2.1 ± 1.1 μg/mL and AUC0-24 was 32.8 ± 16.9 μg?h/mL at the 400 mg once daily dose .
When compared with the fasted state, venetoclax exposure increased by 3.4 times when ingested with a low-fat meal and 5.2 times with a high-fat meal. When comparing low versus high fat, the Cmax and AUC were both increased by 50% when ingested with a high-fat meal. The FDA label indicataes that venetoclax should be taken with food , .
Toxicity
Acute toxicity: oral toxicity (LD50) >2001 mg/kg (mouse) .
Venetoclax may cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Patients should avoid pregnancy during treatment. A risk to human male fertility exists based on the results of testicular toxicity (germ cell loss) seen in dogs at exposures as low as 0.5 times the human AUC exposure at the recommended dose .
Carcinogenicity studies have not yet been performed with venetoclax .
Venetoclax was not shown to be mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial mutagenicity (Ames) assay, did not induce aberrations in an in vitro chromosome aberration assay with human peripheral blood lymphocytes. It was not clastogenic in an in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay at doses up to 835 mg/kg. The M27 metabolite was negative for genotoxic activity during both in vitro Ames and chromosome aberration assays .
Description
Venetoclax, codeveloped by AbbVie (previously Abbott Laboratories) and Genentech/ Roche, was approved in the US for treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). To meet qualifications for venetoclax treatment, patients must have received prior therapy and possess the 17p deletion genetic mutation, as determined by USFDA testing. Venetoclax functions as a selective inhibitor of B cell lymphoma subtype 2 (BCL-2), which is often overexpressed on malignant cells and thus leads to impairment of the apoptotic pathway. Along these lines, the orally dosed small molecule drug restores the ability of malignant cells to undergo apoptosis as its mechanism of action.90 Although other BCL-2 inhibitors are known, development of similar agents such as navitoclox have been pursued and halted due to undesired inhibition of BCL-XL, leading to significant thrombocytopenia and demonstrating the need for more selective inhibitors. Venetoclax is also currently being considered for approval in Europe and Canada for similar indications and is in various stages of development for the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), multiple myeloma (MM), and several other disorders, either as a combination therapy or a stand-alone treatment.
The Uses of ABT-199
ABT 199 (>99%) is a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor that achieves potent antitumour activity while sparing platelets. It’s practical application is to treat chronic lymphocytic leukaemic cells and estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.
Background
Venetoclax is a BCL-2 inhibitor that was initially approved by the FDA in April 2016 . Proteins in the B cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) family are important regulators of the apoptotic (programmed cell death) process , . Venetoclax is used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and certain types of small lymphocytic lymphoma . CLL is the most prevalent leukemia diagnosed in Western countries . Venetoclax was developed through reverse engineering of the BCL-2 protein family inhibitor, navitoclax . Venetoclax is approximately 10 times more potent than navitoclax with regard to induction of apoptosis in CLL cells . A new indication was approved in 2018 for the treatment patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), with or without 17p deletion, who have received at least one prior therapy . Previously, this drug was indicated only for patients with 17p gene deletion .
Indications
Venetoclax is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). It is also used in combination with azacitidine, or decitabine, or low-dose cytarabine for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in adults 75 years or older, or who have comorbidities that preclude use of intensive induction chemotherapy.
What are the applications of Application
ABT-199 is a BH3 mimetic and a Bcl-2-selective inhibitor with a subnanomolar affinity Ki of
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of pyrrolopyridines that is a potent inhibitor of the antiapoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma 2. It is used for treamtment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with 17p deletion.
Pharmacokinetics
Venetoclax induces rapid and potent onset apoptosis of CLL cells, powerful enough to act within 24h and to lead to tumor lysis syndrome , , . Selective targeting of BCL2 with venetoclax has demonstrated a manageable safety profile and has been shown to induce significant response in patients with relapsed CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) or SLL (small lymphocytic leukemia), including patients with poor prognostic features . This drug is not expected to have a significant impact on the cardiac QT interval . Venetoclax has demonstrated efficacy in various types of lymphoid malignancies, including relapsed/ refractory CLL harboring deletion 17p, with an overall response rate of approximately 80% .
Clinical Use
Selective inhibitor of B-cell lymphoma protein:
Treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Synthesis
The manufacturing route to venetoclax takes place by
coupling of three key structural subunits: azaindole 162,
sulfonamide 165, and piperazine 172. The first of these
subunits was generated in two steps from commercially
available 4-bromo-2-fluoro-1-iodo-benzene (159).
Grignard formation of iodide 159 (i-PrMgCl) followed by
quenching with Boc2O provided the desired tert-butyl ester 160
without the need for chromatographic purification. Aromatic
substitution of crude 160 with azaindole 161 provided access to
162 in 86% yield after recrystallization from EtOAc/heptane. Sulfonamide 165 was
formed in 91% yield and 99.9% purity via aromatic substitution
of commercially available 163 with amine 164 at 80 ??C
(DIPEA, MeCN).

Synthesis of the third venetoclax subunit, piperazine amine
hydrochloride salt 172, began with commercial cyclohexanone
166. Vilsmeier-Haack formylation of the
sterically more accessible enol tautomer of 166 delivered vinyl
chloride 167 in quantitative yield. Coupling of this chloride
with commercial aryl boronate 168 gave rise to transient enal
169 in 87% assay yield, which was not isolated. Crude 169 was
then carried into a reductive amination reaction with
commercial N-Boc piperazine (170). Precipitation and
recrystallization from acetonitrile ultimately furnished piperazinyl
alkene 171 in 74% yield from 167. Finally, subunit 172
was obtained via Boc removal with concentrated HCl in IPA at
65 ??C and subsequent filtration, conditions that provided a 95%
yield of high purity intermediate 172 (>99.5%).
The final approach to venetoclax involved a palladiumcatalyzed
coupling of amine 172 with aryl bromide 162, ester
hydrolysis, and coupling of the resulting carboxylic acid with
sulfonamide 165. In practice, Buchwald-Hartwig amination of 162 with 172 proceeded smoothly and
relied upon workup with cysteine to enable cleansing of
residual palladium from the reaction mixture. This reaction
gave rise to advanced intermediate 173 in 89% yield after
crystallization from cyclohexane. Treatment of 173 with t-
BuOK/H2O/2-MeTHF at 55 ??C provided the corresponding
free acid, which was immediately activated with EDC/DMAP/
Et3N to promote coupling with sulfonamide 165 at room
temperature. The final drug target could be accessed by
crystallization from EtOAc and washing with 1:1 DCM/EtOAc,
yielding venetoclax (XVIII) in free base form in 71% over
the two final steps. This synthetic route was capable of
fashioning the drug target in 52% overall yield based on the
longest linear sequence (7 steps).
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: concentration possibly increased by
ciprofloxacin, clarithromycin and erythromycin -
reduce venetoclax dose; avoid with rifampicin.
Anticoagulants: avoid with dabigatran; concentration
of warfarin increased.
Antidepressants: avoid with St John’s wort.
Antiepileptics: concentration possibly reduced by
carbamazepine, fosphenytoin and phenytoin - avoid.
Antifungals: concentration possibly increased by
fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole
and voriconazole - reduce venetoclax dose.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of agranulocytosis
with clozapine - avoid.
Antivirals: concentration possibly reduced by
efavirenz and etravirine - avoid; concentration
possibly increased by ritonavir - reduce venetoclax
dose.
Bosentan: concentration of venetoclax possibly
reduced by bosentan - avoid.
Calcium channel blockers: concentration possibly
increased by diltiazem and verapamil - reduce
venetoclax dose.
Cardiac glycosides: avoid with digoxin.
Cytotoxics: avoid with everolimus.
Grapefruit juice: avoid concomitant use.
Modafinil: concentration of venetoclax possibly
reduced - avoid.
Sirolimus: avoid concomitant use.
Vaccines: avoid with live vaccines.
Metabolism
In vitro studies demonstrated that venetoclax is predominantly metabolized as a substrate of CYP3A4/5 , , .
Metabolism
In vitro studies show that venetoclax is mainly
metabolised by cytochrome P450 CYP3A4. M27 was
identified as a major metabolite in plasma with an
inhibitory activity against BCL-2 that is at least 58-fold
lower than venetoclax in vitro.
Excretion is mainly by the faecal route (>99.9
%; 20.8
%
unchanged).
Storage
Store at -20°C
Properties of ABT-199
| Melting point: | >150°C (dec.) |
| Density | 1.340±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly) |
| form | Yellow solid. |
| pka | 4.09±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Light Yellow to Yellow |
Safety information for ABT-199
Computed Descriptors for ABT-199
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 1257044-40-8 Venetoclax 98%View Details
1257044-40-8 Venetoclax 98%View Details
1257044-40-8 -
 1257044-40-8 98%View Details
1257044-40-8 98%View Details
1257044-40-8 -
 Venetoclax 98%View Details
Venetoclax 98%View Details
1257044-40-8 -
 Venetoclax 1257044-40-8 98%View Details
Venetoclax 1257044-40-8 98%View Details
1257044-40-8 -
 ABT-199 >95% CAS 1257044-40-8View Details
ABT-199 >95% CAS 1257044-40-8View Details
1257044-40-8 -
 Venetoclax 95% CAS 1257044-40-8View Details
Venetoclax 95% CAS 1257044-40-8View Details
1257044-40-8 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details