6-Gingerol
Synonym(s):[6]-Gingerol, Zingiber officinale - CAS 23513-14-6 - Calbiochem;1-(4ʹ-Hydroxy-3ʹ-methoxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-3-decanone;3-Decanone, 5-hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-, (5S)-;5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-decanone;6-Gingerol
- CAS NO.:23513-14-6
- Empirical Formula: C17H26O4
- Molecular Weight: 294.39
- MDL number: MFCD00210507
- EINECS: 607-241-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
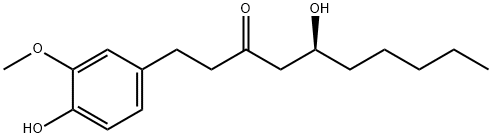
What is 6-Gingerol?
Description
Gingerol (correctly, [6]-gingerol) is the predominant phenol and most important of the pungent constituents in ginger oil. It was isolated by J. C. Thresh in 1879 from the rhizome of the ginger plant (Zingiber officinale). It and its dehydrated analogue [6]-shogaol are the primary ginger-derived bioactive compounds. Shogaol and the fragmented molecule zingerone are produced when fresh ginger is heated or cooked.?A recently synthesized azagingerol analogue?increases metabolism in mice and may reduce the risk of obesity-associated diseases.
Zingerone gives ginger a "hot" taste. It''s also an antioxidant, although it only weakly inhibits peroxidation of phospholipid liposomes in the presence of Fe(III) and ascorbate. Zingerone''s vanillin foundation and hydrocarbon tail make it a chemical relative of?eugenol?and capsaicin.
Chemical properties
Light yellow ceraceous solid
The Uses of 6-Gingerol
[6]-Gingerol has been used:
- to study its effects on transient receptor potential (TRP) channels
- to study its effects on experimental models of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- to determine its effects on microsomal prostaglandine E2 synthase 1 (mPGES-1), glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) and β-catenin pathway in A549 cell line
- to analyse the effects of 6-Shogaol (6-SG) on diabetic nephropathy (DN) in db/db mice
What are the applications of Application
Gingerol is an apoptosis inducing, anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory agent
Definition
ChEBI:Gingerol is a beta-hydroxy ketone that is 5-hydroxydecan-3-one substituted by a 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl moiety at position 1; believed to inhibit adipogenesis. It is a constituent of fresh ginger. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent and a plant metabolite. It is a beta-hydroxy ketone and a member of guaiacols.
General Description
6-Gingerol is a naturally occurring plant phenoland an active pungent constituent found in the rhizome of ginger, which is known to possess anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor and antioxidant properties and can hence, serve as a potential candidate in the treatment of cancer.
Biological Activity
6-Gingerol is the major pharmacologically-active component of ginger. It is known to exhibit a variety of biological activities including anticancer, anti-inflammation, and anti-oxidation. 6-Gingerol has been found to possess anticancer activities via its effect on a variety of biological pathways involved in apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, cytotoxic activity, and inhibition of angiogenesis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Bioactive compound found in ginger (Zingiber officinale) with antioxidant activity, which functions as an anti-inflammatory and antitumor agent. [6]-Gingerol down regulates proinflammatory cytokine release by macrophages. It has been shown to inhibit COX-2 expression by blocking the activation of p38 MAP kinase and NF-κB in phorbol ester-stimulated mouse skin.
Anticancer Research
6-Gingerol is a plant polyphenol and an active constituent of Zingiber officinale, whichshowed antioxidant, anti-inflammation, and antitumor properties. It has the capacityto inhibit NOS, TNF-α, and COX-2 enzymes which are regulated by NF-κB(Aggarwal and Shishodia 2004; Wang et al. 2012). It hinders the cell growth ofprostate, gastric, and breast cancer cells and suppresses the lung metastasis ofB16F10 melanoma. It exhibits antitumorigenic effect in human colorectal cancercells via upregulating NSAID-activated gene-1 (NAG-1) (Aggarwal et al. 2008). Italters ERK1/2/JNK/AP1 pathway and induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells in acaspase-dependent manner (Singh et al. 2016b). ROS levels were significantlyincreased in K562 and MOLT4 cells treated with gingerol, and apoptosis wasinduced in leukemia cells by mitochondrial pathway (Wang et al. 2012).
Properties of 6-Gingerol
| Melting point: | 31℃ |
| Boiling point: | 453.0±35.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.083±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | methanol: soluble1mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | Pale yellow oil |
| pka | 10.02±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to Light yellow |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C17H26O4/c1-3-4-5-6-14(18)12-15(19)9-7-13-8-10-16(20)17(11-13)21-2/h8,10-11,14,18,20H,3-7,9,12H2,1-2H3/t14-/m0/s1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 23513-14-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Gingerol(23513-14-6) |
Safety information for 6-Gingerol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for 6-Gingerol
| InChIKey | NLDDIKRKFXEWBK-AWEZNQCLSA-N |
| SMILES | C(C1=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C1)CC(=O)C[C@@H](O)CCCCC |
6-Gingerol manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
![[6]-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) [6]-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6View Details
[6]-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6View Details
23513-14-6 -
![[6]-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) [6]-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6View Details
[6]-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6View Details
23513-14-6 -
![[6]-Gingerol, Zingiber officinale CAS 23513-14-6](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) [6]-Gingerol, Zingiber officinale CAS 23513-14-6View Details
[6]-Gingerol, Zingiber officinale CAS 23513-14-6View Details
23513-14-6 -
 6-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6View Details
6-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6View Details
23513-14-6 -
![[6]-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) [6]-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6View Details
[6]-Gingerol CAS 23513-14-6View Details
23513-14-6 -
 Gingerol 99%View Details
Gingerol 99%View Details -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1