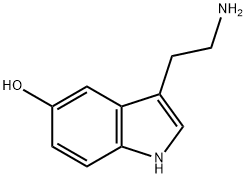
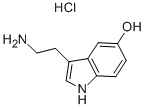
5-Hydroxytryptamine
Synonym(s):3-(2-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole;5-HT;5-Hydroxytryptamine
- CAS NO.:50-67-9
- Empirical Formula: C10H12N2O
- Molecular Weight: 176.22
- MDL number: MFCD00055054
- EINECS: 200-058-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is 5-Hydroxytryptamine?
Description
Serotonin is the baby boomer of neurotransmitters: It was identified in the late 1940s, its adolescence was troubled and turbulent, it made the drug scene in the 1960s, and it nearly died of an overdose in the early 1970s. At one point, the remark was made that serotonin doesn't do anything. On reaching its middle years, serotonin has matured and become an important topic of study, a household name, and more complicated than ever. Serotonin has been associated with, among other things, anxiety, depression, schizophrenia, drug abuse, sleep, dreaming, hallucinogenic activity, headache, cardiovascular disorders, and appetite control, and it is now dabbling in acupuncture and transcendental meditation.
Serotonin was independently identified in the late 1940s by two groups of investigators: In the United States, it was called serotonin, whereas in Italy, it was
called enteramine. Its total synthesis in the early 1950s confirmed that both substances were 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT ). Serotonin (5-HT ) was detected in
numerous plant and animal species and, in the mid-1950s, was identified in the central nervous system (CNS) of animals. A neurotransmitter role was
subsequently proposed for this substance. Later, 5-HT was implicated in a variety of central and peripheral physiologic actions. It seemed to be involved in
vasoconstriction and vasodilation, regulation of body temperature, sleep, and hormonal regulation, and evidence suggested that it might be involved in
depression. The structural similarity between 5-HT and the then recently discovered hallucinogenic agent (+)-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) intrigued
investigators. This observation led to speculation that 5-HT might be involved in the mechanism of action of psychoactive substances and that it might play a
seminal role in various mental disorders.
Description
Serotonin is a monoamine neurotransmitter found in blood, the gastrointestinal tract, and the central nervous system in humans. It also occurs in other animals and many plants. M. M. Rapport and co-workers isolated it from beef serum in 1948.
Serotonin is biosynthesized from tryptophan. Its first reported lab synthesis (M. E. Speeter and co-workers, 1951) started with 5-benzyloxyindole.
As a neurotransmitter, serotonin regulates a wide range of functions, depending on the animal or plant. Most of the serotonin in humans is found in the gut, where it regulates intestinal activity. It also regulates mood, appetite, and sleep in humans. But serotonin can be a double-edged sword: Earlier this year, W. H. Kaye at the University of California, San Diego, and others implicated elevated levels of serotonin in the brain in eating disorders, such as anorexia and bulimia.
The Uses of 5-Hydroxytryptamine
neurotransmitter
Definition
ChEBI: A primary amino compound that is the 5-hydroxy derivative of tryptamine.
Biological Functions
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, or 5HT) is present in the brain as well as in the periphery. In humans, about 90% of the total serotonin in the body is in enterochromaffin cells in the gastrointestinal tract; the remaining 10% occurs primarily in the platelets and brain. The physiological significance of the vast amounts of serotonin constantly synthesized and metabolized in the periphery still remains an enigma. Brain serotonin has been implicated as a potential neurotransmitter in the mediation of a wide variety of phenomena.
Clinical Use
Initially, serotonin was thought to be a sleep-promoting neurotransmitter or an “antiwaking” agent. The recognition of the numerous 5-HT receptor subtypes, often with unique anatomical distribution, has required that a more complex role for serotonin be developed. Current studies indicate that conditions for sleep are now met when the serotoninergic system becomes inactive. The serotonin agonists for the 5-HT1 (via the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B types at the hypothalamic level), 5-HT2, and 5-HT3 receptors cause wakefulness and inhibit sleep. Blockade of the 5-HT2 receptors (e.g., the 5-HT2 antagonist ritanserin) results in increased NREM sleep and inhibition of REM sleep. It has been proposed that the 5-HT1A and 5- HT2 may be involved in sleep by regulation of sleep-promoting substances in the hypothalamus. With the development of newer and more selective ligands for use in studying the numerous serotonin receptor subtypes, a better understanding of the role of serotonin in sleep will evolve.
Metabolism
The major route of metabolism for 5-HT is oxidative deamination by monoamine oxidase (MAO-A) to the unstable 5-hydroxyindole- 3-acetaldehyde, which is either reduced to 5-hydroxytryptophol (~15%) or oxidized to 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (~85%). In the pineal gland, 5-HT is acetylated by 5-HT N-acetyltransferase to N-acetylserotonin, which undergoes O-methylation by 5-hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase to melatonin.
References
Petrova, Men'shikov,J. Gen. Chern. USSR, 31,2413 (1961)
Properties of 5-Hydroxytryptamine
| Melting point: | 167.5 °C |
| Boiling point: | 307.83°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1102 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7110 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 9.8(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| form | neat |
| color | White to off-white |
| BRN | 143524 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-67-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Serotonin (50-67-9) |
Safety information for 5-Hydroxytryptamine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H361:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for 5-Hydroxytryptamine
5-Hydroxytryptamine manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 MELATONINE EP IMP A 90 % AboveView Details
MELATONINE EP IMP A 90 % AboveView Details
50-67-9 -
 Serotonin, 98% CAS 50-67-9View Details
Serotonin, 98% CAS 50-67-9View Details
50-67-9 -
 Serotonin CAS 50-67-9View Details
Serotonin CAS 50-67-9View Details
50-67-9 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1