4,4'-METHYLENEBIS(PHENYL ISOCYANATE)
- CAS NO.:26447-40-5
- Empirical Formula: C15H10N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 250.25
- MDL number: MFCD00036131
- EINECS: 247-714-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
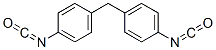
What is 4,4'-METHYLENEBIS(PHENYL ISOCYANATE)?
Description
Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) is a white, odorless diisocyanate that may also occur in crystalline form. It exists in three isomers, (2,20-MDI,2,40-MDI, and 4,40-MDI), however, the primary technical/commercial form of MDI is actually polymeric MDI, which is a mixture that contains 25–80% monomeric 4,40-MDI as well as oligomers containing three to six rings and other minor isomers, such as the 2,20-isomer the 4,40 isomer. MDI is most widely used and accounted for 62% of the global market in 2000.
The Uses of 4,4'-METHYLENEBIS(PHENYL ISOCYANATE)
MDI is used to produce polyurethane foams for application in a wide range of retail, commercial, and industrial uses to protect cement, wood, fiberglass, steel, and aluminum surfaces such as truck beds, trailers, boats, foundations, and decks. MDI is also used as a high strength adhesive in industrial and consumer applications.
Definition
ChEBI: Diphenylmethane-4,4'-diisocyanate is a diisocyanate consisting of diphenylmethane with two isocyanate groups at the 4- and 4'-positions. It has a role as a hapten and an allergen. It derives from a hydride of a diphenylmethane.
Environmental Fate
MDI is the least hazardous of the commonly available isocyanates, however, it is not without toxicity. It has low vapor pressure, which reduces hazards during handling compared to the other major isocyanates, e.g., TDI, HDI. The complex nature of MDI composition and reactions in the environment often makes interpretation difficult. Release of MDI to the atmosphere is low due to its low volatility and since MDI readily degrades to inorganic compounds in the presence of hydroxyl radicals, its atmospheric half-life is short. High exposures involving MDI in ambient environments are expected to be rare. There is no information about levels of various forms of MDI in the ambient air. When MDI is released to water, it reacts readily with water to form mixtures of diisocyanates and amines, which then readily react with more MDI to produce inert, solid, insoluble polyurea. MDI has a transient existence due to its reaction with the water to produce predominantly insoluble polyureas. The evidence indicates that MDI accumulation through the aquatic food chain is extremely unlikely, as might be expected considering the very low solubility and high reactivity of MDI with hydroxyl radicals in aqueous solution.
Toxicity evaluation
A definitive mechanism of MDI toxicity is unknown; however, it is speculated that humoral and cellular immunity may be involved in the pathogenesis of hypersensitivity due to isocyanate sensitization responses of both animals and humans.
Properties of 4,4'-METHYLENEBIS(PHENYL ISOCYANATE)
| Melting point: | 42-45℃ |
| Density | 1.18 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| form | Flakes |
| color | White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 26447-40-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diphenylmethane diisocyanate (26447-40-5) |
Safety information for 4,4'-METHYLENEBIS(PHENYL ISOCYANATE)
Computed Descriptors for 4,4'-METHYLENEBIS(PHENYL ISOCYANATE)
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8