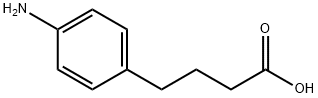
4-Phenylbutyric acid
- CAS NO.:1821-12-1
- Empirical Formula: C10H12O2
- Molecular Weight: 164.2
- MDL number: MFCD00004403
- EINECS: 217-341-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-22 14:18:24
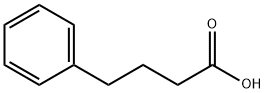
What is 4-Phenylbutyric acid?
Absorption
Following oral administration of a single 5g dose of sodium phenylbutyrate, the Cmax was 195-218 μg/mL under fasting conditions and the Tmax was one hour. The effect of food on drug absorption is unknown.
Toxicity
In animals, lethality was seen at a dose of 1586 mg/kg sodium phenylbutyrate; however, this is a supra-therapeutic dose and acute toxicity is unlikely. No adverse experiences have been reported involving overdoses of sodium phenylbutyrate in patients with urea cycle disorders. High levels of phenylacetate, the active metabolite of phenylbutyric acid, can cause nausea, headache, emesis, fatigue, weakness, lethargy, somnolence, dizziness, slurred speech, memory loss, confusion, and disorientation.
In the event of an overdose, discontinue the drug and institute supportive measures. Hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis may be beneficial. Animal studies in the scientific literature have demonstrated the embryo-fetal toxicity potential of phenylacetate, the major metabolite of phenylbutyrate.
Chemical properties
4-Phenylbutyric acid is white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder. It is slightly soluble in chloroform and methanol. Its solubility in water is 5.3 g/l (at 40 °C).
The Uses of 4-Phenylbutyric acid
4-Phenylbutyric acid is used as a chemical chaperone involved in protein-folding disorders. It is involved in the synthesis of dyes and an active pharmaceutical ingredient intermediate.
Indications
Phenylbutyric acid is used for the treatment of various conditions, including urea cycle
disorders, neonatal-onset deficiency, late-onset deficiency disease in patients with a history of hyperammonemic encephalopathy. Phenylbutyric acid must be combined with dietary protein restriction and, in some cases, essential amino acid supplementation.
Phenylbutyric acid, as sodium phenylbutyrate, is used in combination with tauroursodeoxycholic acid to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in adults.
Background
Phenylbutyric acid is a fatty acid and a derivative of butyric acid naturally produced by colonic bacteria fermentation. It demonstrates a number of cellular and biological effects, such as relieving inflammation and acting as a chemical chaperone. It is used to treat genetic metabolic syndromes, neuropathies, and urea cycle disorders.
What are the applications of Application
4-Phenylbutyric acid is a chemical chaperone that suppresses oxidative stress
Definition
4-Phenylbutyric acid is a monocarboxylic acid the structure of which is that of butyric acid substituted with a phenyl group at C-4. It is a histone deacetylase inhibitor that displays anticancer activity. It inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration and induces apopto is in glioma cells. It also inhibits protein isoprenylation, depletes plasma glutamine, increases production of foetal haemoglobin through transcriptional activation of the gamma-globin gene and affects hPPARgamma activation.
Preparation
4-phenylbutyric acid is obtained by the reaction of benzene with butyrolactone in the presence of aluminum chloride, followed by neutralization with base.
Synthesis of 4-phenylbutyric acid
What are the applications of Application
4-Phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) is used in the treatment of urea cycle disorders under the trade name Buphenyl. 4-PBA has been used as a selective inhibitor of endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS).
4-Phenylbutyric acid is used as organic intermediates. It can also be used as a reactant in the synthesis of:
1-Tetralone using Lewis acid catalyst.
4,N-diphenylbutyramide.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 32, p. 3309, 1991 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)92693-5
General Description
4-Phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) is a small-molecular-weight fatty acid with a terminal aromatic group, and its sodium salt (sodium 4-phenyl butyrate) has been used for the treatment of urea cycle disorders. This molecule is also used for the treatment of sickle cell diseases and thalassemia owing to its ability to activate β-globin transcription. Moreover, 4-PBA is employed as an orally bioavailable agent for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and tumors.
Neuroprotective Effects of 4-phenylbutyric Acid and Its Derivatives: Possible Therapeutics for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Pharmacokinetics
Phenylbutyric acid decreases elevated plasma ammonia glutamine levels in patients with urea cycle disorders. It increases waste nitrogen excretion in the form of phenylacetylglutamine.
In the intestines, phenylbutyric acid was shown to reduce mucosal inflammation, regulate transepithelial fluid transport, and improve oxidative status. Some studies report antineoplastic properties of phenylbutyric acid, showing that phenylbutyric acid can promote growth arrest and apoptosis of cancer cells. It is suggested that phenylbutyric acid can act as an ammonia scavenger, chemical chaperone, and histone deacetylase inhibitor.
Metabolism
The major sites for metabolism of sodium phenylbutyrate are the liver and kidney. Phenylbutyric acid is rapidly metabolized to phenylacetate via beta-oxidation. Phenylacetate is conjugated with phenylacetyl-CoA, which in turn combines with glutamine via acetylation to form phenylacetylglutamine.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the acid from pet ether (b 40-60o). [Beilstein 9 IV 1811.]
Properties of 4-Phenylbutyric acid
| Melting point: | 49-51 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 165 °C10 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.0326 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5405 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | 5.3g/l |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 4.76(at 25℃) |
| color | White to slightly yellow |
| Water Solubility | 5.3 g/L at 40 ºC |
| BRN | 638180 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1821-12-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 4-Phenylbutanoic acid(1821-12-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 4-Phenylbutyric acid (1821-12-1) |
Safety information for 4-Phenylbutyric acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for 4-Phenylbutyric acid
| InChIKey | OBKXEAXTFZPCHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
4-Phenylbutyric acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
ASM Organics
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 4-Phenylbutyric acid 98%View Details
4-Phenylbutyric acid 98%View Details -
 4-Phenylbutyric acid 98%View Details
4-Phenylbutyric acid 98%View Details -
 4-Phenyl Butyric Acid pure CAS 1821-12-1View Details
4-Phenyl Butyric Acid pure CAS 1821-12-1View Details
1821-12-1 -
 4-Phenylbutyric acid CAS 1821-12-1View Details
4-Phenylbutyric acid CAS 1821-12-1View Details
1821-12-1 -
 4-Phenylbutyric acid CAS 1821-12-1View Details
4-Phenylbutyric acid CAS 1821-12-1View Details
1821-12-1 -
 4 Phenylbutyric Acid, 5kgView Details
4 Phenylbutyric Acid, 5kgView Details
1821-12-1 -
 4-PHENYLBUTYRIC ACID CAS Number: 1821-12-1, 25kgView Details
4-PHENYLBUTYRIC ACID CAS Number: 1821-12-1, 25kgView Details
1821-12-1 -
 4-Phenylbutyric acid 98+View Details
4-Phenylbutyric acid 98+View Details
1821-12-1
