3,4-Diaminopyridine
Synonym(s):3,4-Diaminopyridine
- CAS NO.:54-96-6
- Empirical Formula: C5H7N3
- Molecular Weight: 109.13
- MDL number: MFCD00006401
- EINECS: 200-220-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
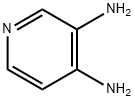
What is 3,4-Diaminopyridine?
Absorption
Orally-administered amifampridine is rapidly absorbed in humans to reach the peak plasma concentrations within by 0.6 to 1.3 hours . A single oral dose of 20 mg amifampridine in fasted individuals resulted in mean peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) ranging from 16 to 137 ng/mL . Bioavailability is approximately 93-100% based on recoveries of unmetabolised amifampridine and a major 3-N-acetylated amifampridine metabolite in urine . Food consumption decreases amifampridine absorption and exposure with a decrease in the time to reach maximum concentrations (Tmax) . It is approximated that food consumption lowers the Cmax on average by ~44% and lowers AUC by ~20%. based on geometric mean ratios .
Systemic exposure to amifampridine is affected by the overall metabolic acetylation activity of NAT enzymes and NAT2 genotype . The NAT enzymes are highly polymorphic that results in variable slow acetylator (SA) and rapid acetylator (RA) phenotypes. Slow acetylators are more prone to increased systemic exposure to amifampridine, and may require higher doses for therapeutic efficacy .
Toxicity
The approximate oral LD50 was >25mg/kg in rats and 100 mg/kg in mice. The approximate intravenous LD50 was 25 mg/kg in both rats and mice . Peritoneal and subcutaneous LD50 in mice were 20 mg/kg and 35 mg/kg, respectively . There is limited clinical experienced with amifampridine overdose. The manifestations of acute drug overdose may include abdominal pain, and should be responded with discontinuation of treatment and initiation of supportive care with close monitoring of viral signs. There is no specific antidote known for amifampridine .
In vitro, amifampridine showed no clinically relevant carcinogenic or genotoxic potential. However, in a 2-year rat study, amifampridine caused small but statistically significant dose-related increases in the incidence of Schwannomas in both genders and of endometrial carcinomas in females . At doses higher than the recommended daily dose for humans, amifampridine caused a dose-related increase in the percentage of pregnant rats with stillborn offspring . Effects on the central and autonomic nervous system, increased liver and kidney weights and cardiac effects (second degree atrioventricular block) were seen in a repeat-dose toxicity studies in rats and dogs .
Description
3,4-Diaminopyridine, or 3,4-DAP, is used to treat muscle diseases such as Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome. It has also been used to relieve the symptoms of botulinum neurotoxin type A (BoNT/A) poisoning (botulism), but it penetrates the blood–brain barrier and produces neurotoxic side effects.?K. J. Janda and coauthors have recently shown?that the 3,4-DAP derivative 3,4,5-triaminopyridine overcomes this problem and has anti-BoNT/A potency equal to 3,4-DAP.
Chemical properties
brownish to brown-grey crystalline powder
The Uses of 3,4-Diaminopyridine
It is a potassium channel blocker in nerve terminals. It inhibits potassium channel efflux, increasing the duration of the action potential, which results in an increase in the duration of calcium channel opening and enhanced acetylcholine (ACh) release. Increased ACh availability at the motor end plate allows muscles to contract.
Indications
Amifampridine is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) in adults and pediatric patients. Nevertheless, at the current time only the Firdapse brand of amifampridine is indicated for the treatment of LEMS in both adult and pediatric patients, while the Ruzurgi brand of amifampridine is indicated for the treatment of LEMS only in patients aged 6 to less than 17 years.
Background
Amifampridine, or 3,4-diaminopyridine (3,4-DAP), is a quaternary ammonium compound that blocks presynaptic potassium channels, and subsequently prolongs the action potential and increases presynaptic calcium concentrations . It was first discovered in Scotland in the 1970s and its clinical effectiveness for neuromuscular disorders, including Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS), has been investigated in the 1980s . Amifampridine phosphate is a more stable salt that serves as an active ingredient of EMA-approved Firdapse, which was previously marketed as Zenas. It is currently used as the first-line symptomatic treatment for LEMS in adult patients and is ideally given as oral tablets in divided doses, three or four times a day. Firdapse (amifampridine) was formally approved by the US FDA for the treatment of adults with LEMS as recently as November of 2018 .
LEMS is a rare auto-immune disorder of the neuromuscular junction that is characterized by proximal muscle weakness, depressed tendon reflexes, and posttetanic potentiation in addition to autonomic dysfunction . About 50-60% of the patients develop more rapidly progressive LEMS and small cell lung cancer, which influences the prognosis . Patients with LEMS develop serum antibodies against presynaptic P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channels, leading to decreased presynaptic calcium levels and reduced quantal release of acetylcholine, which is mainly responsible for causing symptoms of LEMS . Reduced acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction leads to decreased frequency of miniature endplate potentials of normal amplitude, and insufficient acetylcholine levels for the activation of postsynaptic muscle fibers following a single nerve impulse . This leads to the reduction of the compound muscle action potential (CMAP) . Treatment for LEMS include immunotherapy such as conventional immunosuppression or intravenous immunoglobulins, however such treatments are recommended in patients in whom symptomatic treatment would not suffice . Amifampridine is the nonimmune treatment options for LEMS.
In phase III clinical trials of adult patients with LEMS, treatment of amifampridine significantly improved symptoms of LEMS compared to placebo with good tolerance . It was demonstrated in clinical studies involving healthy volunteers that the pharmacokinetics and systemic exposure to amifampridine is affected by the genetic differences in N-acetyl-transferase (NAT) enzymes (acetylator phenotype) and NAT2 genotype, which is subject to genetic variation . Slow acetylators were at higher risk for experiencing drug-associated adverse reactions, such as paresthesias, nausea, and headache .
What are the applications of Application
3,4-Diaminopyridine is a potassium channel blocker in nerve terminals
Indications
3,4-diaminopyridine has been used to treat Lambert Eaton myasthenia (LEM) for thirty years despite the lack of conclusive evidence of efficacy.
Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome is characterized by muscle weakness, hyporeflexia, and autonomic dysfunction, which result from impaired release of acetylcholine from cholinergic nerve terminals. It is frequently associated with cancer, it is autoimmune-mediated, and treatment has been unsatisfactory.
The drug 3,4-diaminopyridine (3,4-DAP) increases neurotransmitter release and also the action potential (by blocking potassium conductance); these actions lead to a nonspecific excitatory effect on the cholinergic system, and provide benefit. It should be taken orally, 4-5 times per day. Adverse effects due to CNS excitation (insomnia, seizures) can occur.
Definition
ChEBI: Amifampridine is an aminopyridine.
Pharmacokinetics
Administration of amifampridine to patients with LES in clinical trials resulted in improvement of the compound muscle action potential (CMAP), muscle function, and quantitative myasthenia gravis (QMG) score . One case of a slight prolongation of the QTc interval in male patient with LEMS and euthyroid Hashimoto’s disease treated with 90 mg of amifampridine in combination with 100 mg azathioprine was reported . In vitro, amifampridine was shown to modulate cardiac conduction and induce phasic contractions in different arteries from several species . In addition, it stimulated potassium-evoked dopamine and noradrenaline release in rat hippocampal slices and upregulate acetylcholine release in the brain . It may also potentiate adrenergic and cholinergic neuromuscular transmission in the gatrointestinal tract . In a single pharmacokinetic study, no effect was observed of amifampridine phosphate on cardiac repolarization as assessed using the QTc interval . There were no changes in heart rate, atrioventricular conduction or cardiac depolarization as measured by the heart rate, PR and QRS interval durations .
Metabolism
Amifampridine is extensively metabolized by N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2) to 3-N-acetyl-amifampridine, which is considered an inactive metabolite.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from *benzene and is stored under N2 because it is deliquescent and absorbs CO2. [Beilstein 22/11 V 266.]
Properties of 3,4-Diaminopyridine
| Melting point: | 216-218 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 194.6°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1118 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5340 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 240 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 30g/l |
| pka | 9.17±0.12(Predicted) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | Brownish to brown-gray |
| Water Solubility | 24 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,2986 |
| BRN | 110232 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C5H7N3/c6-4-1-2-8-3-5(4)7/h1-3H,7H2,(H2,6,8) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 54-96-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for 3,4-Diaminopyridine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for 3,4-Diaminopyridine
| InChIKey | OYTKINVCDFNREN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1=NC=CC(N)=C1N |
3,4-Diaminopyridine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 54-96-6 3,4-Diaminopyridine 98%View Details
54-96-6 3,4-Diaminopyridine 98%View Details
54-96-6 -
 54-96-6 3,4-Diaminopyridine 99%View Details
54-96-6 3,4-Diaminopyridine 99%View Details
54-96-6 -
 Amifampridine 98%View Details
Amifampridine 98%View Details
54-96-6 -
 Amifampridine 54-96-6 98%View Details
Amifampridine 54-96-6 98%View Details
54-96-6 -
 3,4-Diaminopyridine CAS 54-96-6View Details
3,4-Diaminopyridine CAS 54-96-6View Details
54-96-6 -
 3,4-Diaminopyridine CAS 54-96-6View Details
3,4-Diaminopyridine CAS 54-96-6View Details
54-96-6 -
 3,4-Diaminopyridine CAS 54-96-6View Details
3,4-Diaminopyridine CAS 54-96-6View Details
54-96-6 -
 3,4-Diaminopyridine CAS No: 54-96-6, Grade Standard: Reagent GradeView Details
3,4-Diaminopyridine CAS No: 54-96-6, Grade Standard: Reagent GradeView Details
54-96-6
