2-Hydroxyethyl salicylate
Synonym(s):(2-Hydroxyethyl)-salicylate;Ethylene glycol salicylate;Salicylic acid (2-hydroxyethyl) ester;Salicylic acid 2-hydroxyethyl ester;Salicylic acid ethylene glycol ester
- CAS NO.:87-28-5
- Empirical Formula: C9H10O4
- Molecular Weight: 182.17
- MDL number: MFCD00002862
- EINECS: 201-737-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:45
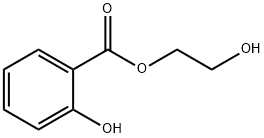
What is 2-Hydroxyethyl salicylate?
Absorption
Salicylate absorption follows first-order kinetics with an absorption half-life ranging from 5 to 16 minutes .
Toxicity
Acute ingestion of > 150 mg/kg of salicylates may result in severe toxicity. Salicylate tablets may form stomach bezoars, prolonging absorption of the drug and toxicity. Chronic toxicity can occur after several days or more of high therapeutic doses; it is common, often undiagnosed, and often more serious than acute toxicity. Chronic toxicity is likely to occur in elderly patients .
Treatment for salicylate poisoning consists of activated charcoal and alkaline diuresis with extra KCl .
Unless contraindicated (eg, by altered mental status), activated charcoal is administered as soon as possible and, if bowel sounds are active and there is adequate gastrointestinal motility, may be repeated every 4 hours until charcoal appears in the stool .
After volume and electrolyte abnormalities are corrected and maintained, alkaline diuresis can be used to increase urine pH, ideally to ≥ 8. Alkaline diuresis is advised for patients with any symptoms of poisoning and should not be delayed until salicylate levels are determined. This process is usually safe and greatly increases the rate of salicylate excretion. Because hypokalemia can interfere with alkaline diuresis, patients are often given a solution composed of 1 L of 5% D/W, 3 50-mEq ampules of NaHCO3, and 40 mEq of KCl at 1.5 to 2 times the maintenance IV fluid rate. Serum potassium levels are monitored. Due to the fact that fluid overload can lead to the occurrence of pulmonary edema, patients are monitored for respiratory findings .
Drugs that increase urinary HCO3 (eg, acetazolamide) must be avoided because they worsen metabolic acidosis and decrease blood pH. Drugs that decrease respiratory drive should be avoided when possible because they may impair hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis, decreasing blood pH .
Chemical properties
Colorless oily liquid or low melting solid
The Uses of 2-Hydroxyethyl salicylate
Glycol Salicylate, is a derivative of salicylic acid that has been proved to be able to improve the aesthetic appearance of the skin. It is also a building block used in various chemical synthesis.
Background
Glycol salicylate, also known as 2-hydroxyethyl salicylate, is a benzoate ester formed from the condensation of the carboxy group of salicylic acid with one of the hydroxy groups of ethylene glycol. It is found as an active ingredient and topical analgesic in patches used to provide relief for mild to moderate muscle and joint pain .
This drug belongs to the salicylate group of drugs, which are used as analgesic agents for the treatment of mild to moderate pain .
Glycol salicylate (GS), composed of salicylic acid (SA) and ethylene glycol, is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug .
This ingredient is an important component of many topical creams and sprays for the relief of aches, pains, and stiffness of the muscles, joints, and tendons .
Indications
This drug is only recommended for topical usages for the relief of muscular and rheumatic pain in human and animals .
Definition
ChEBI: A benzoate ester obtained by the formal condensation of carboxy group of salicylic acid with one of the hydroxy groups of ethylene glycol
Pharmacokinetics
Temporarily relieves minor to moderate aches and pains . Works with ingredients such as menthol, which has counter-irritant properties . Counter-irritants are externally applied, and lead to irritation or mild inflammation of the skin to relieve pain in muscles or joints by reducing inflammation in deeper adjacent structures . Counter-irritants relieve pain by disrupting the brain from receiving pain signals resulting from conditions such as osteoarthritis (OA) or injuries such as sprains or strains. These agents may cause vasodilatation or skin irritation, leading to a false sensation of heat or warmth .
Metabolism
The metabolism of glycol salicylate is similar to that of Aspirin at other salicylates .
Metabolism of salicylic acid occurs through glucuronide formation (to produce salicyl acyl glucuronide and salicyl phenolic glucuronide), conjugation with glycine (to produce salicyluric acid), and oxidation to gentisic acid. The rate of formation of salicyl phenolic glucuronide and salicyluric acid are readily saturated at low salicylic acid concentrations and their formation is described by Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The larger the dose administered, the longer it will take to reach steady-state concentrations of salicylates. There is also evidence that enzyme induction of salicyluric acid formation occurs during the metabolism of salicylates .
Properties of 2-Hydroxyethyl salicylate
| Melting point: | 25°C |
| Boiling point: | 166 °C13 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.244 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0.0001 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 13.1g/l |
| form | Oily Liquid or Low Melting Solid |
| pka | 8.00±0.30(Predicted) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.244 (20/4℃) |
| color | Colorless |
| PH | 4.0 (13.1g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Merck | 14,4499 |
| BRN | 2255685 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 87-28-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Hydroxyethyl salicylate(87-28-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, 2-hydroxyethyl ester (87-28-5) |
Safety information for 2-Hydroxyethyl salicylate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Hydroxyethyl salicylate
| InChIKey | LVYLCBNXHHHPSB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 87-28-5 Ethyleneglycol monosalicylate 98%View Details
87-28-5 Ethyleneglycol monosalicylate 98%View Details
87-28-5 -
 2-Hydroxyethyl salicylate CAS 87-28-5View Details
2-Hydroxyethyl salicylate CAS 87-28-5View Details
87-28-5 -
 2-Hydroxyethyl Salicylate CAS 87-28-5View Details
2-Hydroxyethyl Salicylate CAS 87-28-5View Details
87-28-5 -
 Ethylene glycol monosalicylate CAS 87-28-5View Details
Ethylene glycol monosalicylate CAS 87-28-5View Details
87-28-5 -
 Glycol Salicylate Cas 87 28 5View Details
Glycol Salicylate Cas 87 28 5View Details
87-28-5 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
