2-Hexanone
Synonym(s):2-Hexanone in dimethyl sulfoxide;2-Hexanone solution;Butyl methyl ketone
- CAS NO.:591-78-6
- Empirical Formula: C6H12O
- Molecular Weight: 100.16
- MDL number: MFCD00009482
- EINECS: 209-731-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
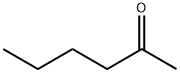
What is 2-Hexanone?
Description
2-Hexanone has been used as a solvent for both cellulose- and resin-based coating systems. In the early 1970s, a number of workers in the print department of a coated fabrics plant developed severe peripheral neuropathy from an unknown cause. In search of an etiological agent, and in the absence of other neurotoxicants, 2-hexanone was implicated as it was recently substituted for methyl isobutyl ketone in the manufacturing process. Similar observations in workers exposed to 2-hexanone may have resulted in the decline in production and use in the United States.
Chemical properties
2-Hexanone is a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a sharp odor. It dissolves very easily in water and is miscible in ethanol, methanol, and benzene. 2-Hexanone evaporates easily into the air as a vapor. It is stable, flammable, and incompatible with oxidizing agents, strong bases, and reducing agents. 2-Hexanone is a waste product of wood pulping, coal gasifi cation, and oil shale operations. Formerly, 2-hexanone was in use as a paint and paint thinner with other chemical substances, and to dissolve oils and waxes.and is used as a solvent and organic syn- thesis intermediates. However, the industrial uses of 2-hexanone is now very much restricted.
Chemical properties
MNBK is a colorless liquid with an acetonelike odor. The odor threshold is 0.08 ppm.
Physical properties
Clear, colorless to pale yellow, flammable liquid with an odor resembling acetone and 2-butanone. Nagata and Takeuchi (1990) reported an odor threshold concentration of 24 ppbv. Amoore and Hautala (1983) reported odor threshold concentrations of 250 μg/L and 76 ppbv in water and air, respectively.
The Uses of 2-Hexanone
2-Hexanone is used in various organic chemical syntheses. It is used in the synthesis of (+/-)-monomorine. It is also used in the preparation of alcohols by transfer hydrogenation of ketones.
The Uses of 2-Hexanone
Methyl butyl ketone (MBK) is used as asolvent for nitrocellulose, resins, lacquers,oils, fats, and waxes.
The Uses of 2-Hexanone
As industrial solvents for adhesives, lacquers, paint removers, and acrylic coatings
Production Methods
MnBK can be produced by a reaction between acetic acid and ethylene under pressure MnBK can be produced by a reaction between acetic acid and ethylene under pressure.
Definition
ChEBI: 2-Oxohexane is a ketone.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 24, p. 5181, 1983 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)88391-4
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 89, p. 5708, 1967 DOI: 10.1021/ja00998a040
General Description
A clear colorless liquid. Flash point 95°F. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
2-Hexanone is incompatible with oxidizing agents. 2-Hexanone may also react with strong bases and reducing agents.
Hazard
Flammable, moderate fire risk, explosive limits 1.2–8% in air. Irritant to eyes and mucous membranes, narcotic in high concentration, absorbed by skin. Causes peripheral neuropathy and testicular damage.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of high concentrations of vapor may result in narcosis; peripheral neuropathy may develop. Ingestion of large amounts may cause some systemic injury. Contact with eyes causes mild to moderate irritation. Liquid irritates skin; prolonged or repeated contact may cause defatting of the skin with resultant dermatitis.
Health Hazard
Chronic exposure to MBK via inhalationor skin absorption can cause disordersof the peripheral nervous system andneuropathic diseases. The symptoms inhumans, depending on the severity ofexposure, were parasthesias in the handsor feet, muscle weaknesses, weakness inankles and hand, and difficulty in grasping heavy objects. Animal studies indicatethat prolonged exposure to this compoundat a concentration of 200–1300 ppm for4–12 weeks can result in neuropathy.Neurotoxicity is attributed to its primarymetabolite, 2,5-hexanedione. Improvementin conditions can occur slowly over monthsafter cessation of exposure. Acute exposureto high concentrations, 1000 ppm, for severalminutes can cause irritation of the eyes andnose in humans. Inhalation to 20,000 ppmfor 30 minutes caused narcosis in guineapigs and prolonged exposure for 70 minuteswas lethal. The acute oral toxicity in ratswas low.
LD50 value, oral (rats): 2600 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
2-Hexanone is flammable.
Potential Exposure
The material is used as a solvent
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Using the BOD technique to measure biodegradation, the mean 5-d BOD value (mM
BOD/mM 2-hexanone) and ThOD were 5.22 and 61.4%, respectively (Vaishnav et al., 1987).
Photolytic. A second-order photooxidation rate constant of 8.97 x 10-12 cm3/molecule?sec for the
reaction of 2-hexanone and OH radicals in the atmosphere at 299 K was reported by Atkinson
(1985).
Chemical/Physical. 2-Hexanone will not hydrolyze because it has no hydrolyzable functional
group (Kollig, 1995).
storage
2-Hexanone should be kept stored in a tightly closed container, in a cool, dry place, away from sources of ignition.
Shipping
UN1224 Ketones, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid, Technical Name Required
Toxicity evaluation
Regardless of the route of exposure, both human and animal studies indicate that the nervous system is the target organ of 2-hexanone toxicity with its metabolite, 2,5-hexanedione, serving as the neurotoxic agent. 2,5-Hexanedione binds covalently to axonal components of the nerve tissue. In vitro studies have shown that this metabolite reacts with the nucleophilic lysine 3-amino groups to ultimately form 2,5-dimethylpyrrole adducts with neurofilaments. Neurofilament aggregates concentrate in the distal subterminal axon, resulting in axonal swelling, or distal axonopathy, just proximal to the nodes of Ranvier. These reactions may lead to the manifestation of peripheral neuropathy.
Incompatibilities
Violent reaction with oxidizers. May form unstable peroxides. Attacks plastics.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Precautions
Occupational workers should be careful when using and handling 2-hexanone. Workers should wash thoroughly after handling the chemical substance. Workers should avoid contact of 2-hexanone with the eyes, skin, and clothing and also avoid contact with heat, sparks, and flame.
Properties of 2-Hexanone
| Melting point: | -57 °C |
| Boiling point: | 127 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.812 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 10 mm Hg ( 39 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 95 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in acetone, ethanol, and ether (Weast, 1986) |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | -8.30 (quoted, Riddick et al., 1986) |
| color | Clear colorless to light yellow |
| Odor | at 1.00 % in dipropylene glycol. fruity fungal meaty buttery |
| Odor Threshold | 0.024ppm |
| Water Solubility | 2 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,6033 |
| BRN | 1737676 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 24.4 at 37 °C (static headspace-GC, Bylaite et al., 2004) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 1 ppm (4 mg/m3), IDLH 1,600 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA
100 ppm (410 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 ppm, STEL 10 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 14.6(15℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, strong bases, reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 591-78-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Hexanone(591-78-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Hexanone (591-78-6) |
Safety information for 2-Hexanone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Hexanone
| InChIKey | QQZOPKMRPOGIEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
2-Hexanone manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 591-78-6 98%View Details
591-78-6 98%View Details
591-78-6 -
 2-Hexanone, 98% 591-78-6 99%View Details
2-Hexanone, 98% 591-78-6 99%View Details
591-78-6 -
 2-Hexanone CAS 591-78-6View Details
2-Hexanone CAS 591-78-6View Details
591-78-6 -
 2-Hexanone CAS 591-78-6View Details
2-Hexanone CAS 591-78-6View Details
591-78-6 -
 2-Hexanone CAS 591-78-6View Details
2-Hexanone CAS 591-78-6View Details
591-78-6 -
 Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
 609-15-4View Details
609-15-4View Details
609-15-4 -
 27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3View Details
27143-07-3
