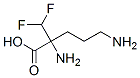
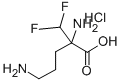
2-(Difluoromethyl)-DL-ornithine
- CAS NO.:70050-56-5
- Empirical Formula: C6H12F2N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 182.17
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:41
What is 2-(Difluoromethyl)-DL-ornithine?
Definition
ChEBI: Eflornithine is a fluoroamino acid that is ornithine substituted by a difluoromethyl group at position 2. It has a role as a trypanocidal drug. It is a fluoroamino acid and an alpha-amino acid. It is functionally related to an ornithine.
Antimicrobial activity
Cultured bloodstream trypomastigotes of T. brucei are relatively
insensitive, but high doses are effective against bloodstream
and CNS infections of T. brucei brucei and T. brucei
gambiense in rodents, provided a strong antibody response
is also present. Eflornithine entry into the CNS can be
enhanced with suramin. T. brucei rhodesiense
infections do not respond. Synergy with some arsenicals has
been demonstrated.
Eflornithine is active against P. falciparum in experimental
models and against Leishmania promastigotes and Giardia
lamblia in culture.
Acquired resistance
Acquired resistance in T. brucei gambiense in West Africa has not been reported. East African T. brucei rhodesiense strains are innately less sensitive. Reported treatment failures are thought to be associated with severity of disease.
Pharmaceutical Applications
An analog of ornithine, formulated as the hydrochloride for intravenous infusion. It is freely soluble in water.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: 55%
Cmax 10 mg/kg oral: c. 7 mg/L after 4 h
200 mg/kg intravenously: 15.9 mg/L (87.5 nmol/mL) (mean)
Plasma half-life: 3.3 h
Volume of distribution: 0.34 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: Very low
Renal clearance is 83%, with most eliminated unchanged.
In a study in Zaire the mean serum concentration in children
under 12 years old was half that of adults, probably due
to more rapid renal clearance. CNS penetration is good in
adult patients, with a CSF:plasma ratio of 0.91 at the end of
administration for 14 days. However, the CSF:plasma ratio
in children under 12 years old was 0.58. Relapses have been
recorded in patients in whom CSF levels dropped below
9 mg/L (50 nmol/mL) at the end of treatment.
Clinical Use
2-(Difluoromethyl)-DL-ornithine has been used speculatively for treatment of Pn. jirovecii infections in AIDS patients. Co-administration with oral nifurtimox has been added to the World Health Organization (WHO) List of Essential Medicines for second-stage sleeping sickness caused by T. brucei gambiense.
Side Effects
Osmotic diarrhea and bone marrow suppression are common, and up to 50% of sleeping sickness patients develop leukopenia. Reversible anemia and thrombocytopenia have been observed. Convulsions and seizures, different from those observed in melarsoprol-induced encephalopathy, have been reported in 4–18% of treated sleeping sickness patients but not in patients treated for Pn. jirovecii pneumonia. This difference might be due to the CNS inflammation associated with sleeping sickness.
Properties of 2-(Difluoromethyl)-DL-ornithine
| Melting point: | 181-184 ºC |
Safety information for 2-(Difluoromethyl)-DL-ornithine
Computed Descriptors for 2-(Difluoromethyl)-DL-ornithine
2-(Difluoromethyl)-DL-ornithine manufacturer
Ralington Pharma
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 67037-37-0 / 70052-12-9 Eflornithine 98%View Details
67037-37-0 / 70052-12-9 Eflornithine 98%View Details
67037-37-0 / 70052-12-9 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1