1,3,5-trioxane
Synonym(s):1,3,5-Trioxane;Metaformaldehyde;sym.-Trioxane;Trioxymethylene
- CAS NO.:110-88-3
- Empirical Formula: C3H6O3
- Molecular Weight: 90.08
- MDL number: MFCD00006563
- EINECS: 203-812-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
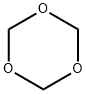
What is 1,3,5-trioxane?
Description
1,3,5-trioxane is a stable, solid, easy to handle source of anhydrous formaldehyde. Under acidic conditions 1,3,5-trioxane decomposes to form three molecules of formaldehyde.
Chemical properties
Trioxane is a most unusual chemical. It is an excellent solvent for many classes of materials. Concentrated aqueous solutions of trioxane have solvent properties which are not possessed by trioxane itself. Molten trioxane dissolves numerous organic compounds, such as naphthalene, urea, camphor, dichlorobenzene, etc. It is stable in alkaline or neutral solutions, yet it is depolymerized to formaldehyde by small amounts of strong acid or acid-forming materials, and the rate of depolymerization can be readily controlled.
Chemical properties
Paraformaldehyde is a white crystalline solid. Irritating odor. The term “trioxane” applies specifically to this trimer (CH2O)3 but paraformaldehyde is applied both to trioxane and other low polymers or oligomers of formaldehyde.
The Uses of 1,3,5-trioxane
1,3,5-Trioxane is used in organic chemical processes such as aldol condensation of amides and syntheses of chloromethyl esters or other plastics.
The Uses of 1,3,5-trioxane

The reaction was carried out 32 times. A mixture of the SM (2.0 g, 5.3 mmol) and 1,3,5-trioxane (2.38 g, 26.4 mmol) in CHCl3 (20 mL) was treated with TFA (10 mL), and the reaction was heated at 50 C for 50 min. The reaction mixture was poured into cooled sat aq NaHCO3 (500 mL) and extracted with DCM (2 x 300 mL). The combined organic layers were washed with sat aq brine (400 mL), dried, and concentrated in vacuo. Purification by silica gel chromatography (20-33% EtOAc/PE) provided the product as a yellow solid. From 1H NMR analysis, the compound was assumed to exist as a mixture of two rotamers. [combined yield: 28 g, 72 mmol, 42%]
The Uses of 1,3,5-trioxane
1,3,5-Trioxane is widely used as a source of anhydrous formaldehyde.
It can be used to synthesize:
- Polyoxymethylene and hyperbranched polyesters.
- Calixarenes such as calix[4]resorcinarene, calix[6]resorcinarene and para-tert-butylcalix[8] and [9]arene.
- Various natural products including (?)-motuporin, (+)-sundiversifolide, (+)-lyconadin A and (?)-lyconadin B.
Definition
ChEBI: A saturated organic heteromonocyclic parent that is cyclohexane in which the carbon atoms at positions 1, 3 and 5 are replaced by oxygen atoms.
General Description
Transparent crystals or white crystalline solid with a pleasant odor resembling the odor of chloroform. Melts at 62°C; boils at 115°C without polymerization. The cyclic trimer of formaldehyde.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
s-Trioxane is stable under normal laboratory conditions but is unstable in the presence of acids, which initiate polymerization. Sublimes readily. May react with oxidizing matter . A stable polymeric product of formaldehyde that in the presence of strong aqueous acids will depolymerize (reforming the parent formaldehyde). Inert to strong alkalis. Readily converted in non aqueous solutions to the monomeric formaldehyde by small concentrations of acid---the rate of conversion is directly proportional to the concentration of the acid.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: s-Trioxane is toxic and flammable. It can emit toxic fumes on contact with acid or acid fumes.
Fire Hazard
s-Trioxane is combustible.
Safety Profile
Mutation data reported. Can evolve toxic formaldehyde fumes when heated strongly or in contact with strong acids or acid fumes. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidzers. May explode when heated. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. Explodes on impact, possibly due to peroxide contamination. Mixtures with hydrogen peroxide are explosives sensitive to heat, shock, or contact with lead. Mixtures with liquid oxygen are highly explosive. Incompatible with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, or dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also FORMALDEHYDE.
Potential Exposure
Paraformaldehyde is used in polyacetal resin manufacture; as a food additive; and as an odorless fuel.
Shipping
UN2213 Paraformaldehyde, Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid.
Purification Methods
Crystallise 1,3,4-trioxane from sodium-dried diethyl ether or water, and dry it over CaCl2. It can also be purified by zone refining. [Beilstein 19 H 381, 19 II 392, 19 III/IV 4710, 19/9 V 103.]
Incompatibilities
Paraformaldehyde dust forms an explosive mixture with air. Decomposes on contact with oxidizers, strong acids; acid fumes; and bases; with elevated temperatures, forming formaldehyde. May explode when heated. May explode on impact if peroxide contamination develops. Mixtures with hydrogen peroxide or liquid oxygen are explosives sensitive to heat, shock, or contact with lead.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Properties of 1,3,5-trioxane
| Melting point: | 59-62 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 112-115 °C |
| Density | 1.17 |
| vapor pressure | 7.5 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4168 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 113 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 221g/l |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Flakes |
| appearance | White solid |
| color | Colorless to white |
| explosive limit | 3.6-28.7%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 221 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9734 |
| Sublimation | 115 ºC |
| BRN | 102769 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-88-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,3,5-Trioxane(110-88-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,3,5-Trioxane (110-88-3) |
Safety information for 1,3,5-trioxane
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 1,3,5-trioxane
| InChIKey | BGJSXRVXTHVRSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 1,3,5-Trioxane, 99% CAS 110-88-3View Details
1,3,5-Trioxane, 99% CAS 110-88-3View Details
110-88-3 -
 s-Trioxane CAS 110-88-3View Details
s-Trioxane CAS 110-88-3View Details
110-88-3 -
 1,3,5-Trioxane CAS 110-88-3View Details
1,3,5-Trioxane CAS 110-88-3View Details
110-88-3 -
 1,3,5-Trioxane CAS 110-88-3View Details
1,3,5-Trioxane CAS 110-88-3View Details
110-88-3 -
 1,3,5-Trioxane CAS 110-88-3View Details
1,3,5-Trioxane CAS 110-88-3View Details
110-88-3 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1