Zolpidem tartrate
- CAS NO.:99294-93-6
- Empirical Formula: C23H27N3O7
- Molecular Weight: 457.48
- MDL number: MFCD31561831
- EINECS: 629-694-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
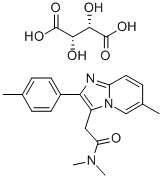
What is Zolpidem tartrate?
Chemical properties
White or almost white, hygroscopic, crystalline powder.
Originator
Ambien,Sanofi-Synthelabo,France
The Uses of Zolpidem tartrate
Sedativehypnotic.
Definition
ChEBI: The hemitartrate salt of zolpidem.
Manufacturing Process
18.6 g (84.8 mmol) of 3-(4-methylbenzoyl)propyldimethylamide are dissolved
in 50 ml of glacial acetic acid. A solution of 13.55 g (84.8 mmol) of bromine
and 45 ml of glacial acetic acid is added dropwise within 50 min at ambient
temperature and the mixture is then stirred overnight. The suspension formed
is filtered and washed with 30 ml of glacial acetic acid. The filter residue is
added to 200 ml of distilled water, triturated thoroughly and stirred for 1 hour.
The product is filtered again and washed with another 200 ml of water. The
crystals obtained (21.16 g) are dried for 6 hours in a vacuum at 70°C. Yield of
3-(4-methylbenzoyl)-2-bromopropyldimethylamide is 18.18 g of white crystals
(71.9% of theory), melting point: 119-121°C.
Synthesis of N,N,6-trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-
acetamide
1). 50 g (167.7 mmol) of 3-(4-methylbenzoyl)-2-bromopropyldimethylamide
are placed in 500 ml of acetonitrile. A solution of 36.27 g (335.4 mmol) of 6-
amino-3-picoline and 350 ml of acetonitrile is added dropwise at 60°C within
1.75 hours and once the solution has all been added the mixture is stirred for
another 4 hours. The resulting solution is diluted with 1000 ml of
dichloromethane and washed three times with 2000 ml of distilled water. Then
the organic phase is extracted three times with 1000 ml of 2 N hydrochloric
acid. The combined acid phases are adjusted to pH 8 with 20% sodium
hydroxide solution and, after being cooled, extracted three times with 1 L of
dichloromethane. The organic phases are combined, dried with magnesium
sulphate and concentrated by evaporation. The crystals of N,N,6-trimethyl-2-
(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-acetamide obtained are triturated
with 500 ml of distilled water, stirred overnight, filtered off, washed again with
50 ml of distilled water and the residue is dried in a vacuum for 5 hours at
60°C. Yield: 17.94 g of light-brown crystals (45.7% of theoretical).
2).10.0 g (33.5 mmol) of 3-(4-methylbenzoyl)-2-bromopropyldimethylamide
and 7.25 g (67.0 mmol) of 6-amino-3-picoline are dissolved in 170 ml of 1,3-
dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone and stirred for 3 hours at 60°C. The reaction
mixture is cooled and diluted with 100 ml of dichloromethane. It is then
washed five times with 150 ml of distilled water. The organic phase is washed
twice with 150 ml of 2 N hydrochloric acid. The combined acid phases are
adjusted to pH 8 with 2 N sodium hydroxide solution. The mixture is extracted
twice with 150 ml of dichloromethane, the organic phases are dried with
MgSO 4 and concentrated by evaporation. The brown oil obtained is mixed with
50 ml of n-heptane and stirred for 30 min. The supernatant diluent is decanted off from the precipitated product which is then washed twice with 10
ml of n-heptane. The residue is evaporated down again, combined with 200
ml of distilled water and stirred for 30 min. The N,N,6-trimethyl-2-(4-
methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-acetamide is filtered off, washed with
50 ml of distilled water and dried. Yield: 2.38 g of beige crystals (23.1% of
theoretical.), melting point: 194-195°C.
3). 100 g (0.456 mol) of 3-(4-methylbenzoyl)propyldimethylamide are
dissolved in 400 ml of dichloromethane. 2 g (0.025 mol) of hydrogen bromide
are piped into the solution which is then refluxed. Then 86.1 g (0.539 mol) of
bromine is added dropwise within 45 min and the mixture is stirred for 30
min. It is then cooled to ambient temperature and washed with 600 ml of
distilled water. The aqueous phase is discarded. The organic phase is
evaporated down to about 10% (v/v) and then diluted with 300 ml of
acetonitrile. This solution is added dropwise within 45 min to a solution of
66.62 g (0.616 mol) of 6-amino-3-picoline in 150 ml of acetonitrile at 70°C
and stirred for 1.5 hours. Then 400 ml of toluene are added at 20-30°C and
the mixture is then extracted with 500 ml of 2 N hydrochloric acid. The
toluene phase is discarded, the aqueous phase is again combined with 400 ml
of toluene and adjusted to pH 4 with 20% sodium hydroxide solution. The
toluene phase is discarded, the aqueous phase is combined with 400 ml of
toluene and adjusted to pH 8.5 with 20% sodium hydroxide solution. The
toluene phase is separated off and evaporated down to 10% (v/v). The
residue is combined with MTBE and stirred for 2 hours at 5°C. The crystals of
N,N,6-trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-acetamide are
suction filtered, washed with MTBE and dried. Yield: 43 g of zolpidem
(30.7%).
17.94 g (94%) (54.9 mmol) of N,N,6-trimethyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo
[1,2-a]pyridine-3-acetamide are placed in 90 ml of methanol. A solution of
4.13 g (27.5 mmol) of (2R,3R)-(+)-tartaric acid and 125 ml of methanol are
added, followed by 28 ml of methyl-tert-butyl-ether (MTBE) within 30
seconds. The mixture is stirred for 15 hours at ambient temperature. The
light-brown suspension formed is stirred for another 1 hour at 5°C, filtered
off, the residue is washed with 50 ml of MTBE, and the crystals are dried for 5
hours in a vacuum at 50°C. Yield: 18.3 g crystals of N,N,6-trimethyl-2-(4-
methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-acetamide semitartrate (87.2% of
theoretical).
brand name
Ambien (Sanofi Aventis).
Therapeutic Function
Hypnotic
Pharmacokinetics
Zolpidem exhibits a high selectivity for the α1 subunit. Its good bioavailability of 72% and rapid onset of action
of approximately 1.4 hours following oral absorption can be attributed to its weak base (pKa = 6.2) and high
lipophilicity (mlog P = 3.85). Its pharmacokinetic profile is characterized by rapid absorption from the
gastrointestinal tract and a short elimination half-life because of rapid oxidative metabolism to inactive
carboxylic acid metabolites. Zolpidem undergoes CYP3A4 (major), CYP2DG, and CYP2D6
hydroxylation of the aryl methyl groups, followed by further oxidation by aldehyde
dehydrogenase to the ionic carboxylic acids, which are readily eliminated in the urine.
Zolpidem
demonstrates linear (dose-proportional) kinetics in the dose range of 5 to 20 mg. Although protein binding was
90%, no drug accumulation was observed following nightly dosing with 20-mg zolpidem tartrate tablets for 2
weeks. Food can prolong the time to peak concentration from 1.4 to 2.2 hours without affecting the half-life.
These results suggest that for faster sleep onset, zolpidem should not be administered with or immediately after
a meal. In the elderly, the dose should be 5 mg, because the elimination half-life is increased by 50% (from ~2
to ~3 hours). No accumulation was observed in elderly subjects following nightly oral dosing of 10 mg for 1
week. In patients with hepatic insufficiency, the plasma concentration doubled with an increase in the
elimination half-life from approximately 2 to approximately 10 hours (range, 4–25 hours). Therefore, dosing
should be modified in patients with hepatic insufficiency. No dosage adjustment should be necessary in patients
with compromised renal function. Zolpidem is not hemodialyzable, but it does cross the placenta and into breast
milk. Because of its longer elimination half-life (when compared to zaleplon), it may be preferred when sleep
maintenance is a primary concern.
Clinical Use
Insomnia (short-term treatment)
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifampicin.
Antidepressants: increased sedative effects with
sertraline.
Antipsychotics: enhanced sedative effects.
Antivirals: concentration increased by ritonavir (risk
of extreme sedation and respiratory depression) -
avoid concomitant use.
Metabolism
Zolpidem tartrate is metabolised via several hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes, the main enzyme being CYP3A4 with the contribution of CYP1A2. All metabolites are pharmacologically inactive and are eliminated in the urine (56
%) and in the faeces (37
%).
Properties of Zolpidem tartrate
| Melting point: | 196 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in methylene chloride. |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 99294-93-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Zolpidem tartrate
Computed Descriptors for Zolpidem tartrate
Zolpidem tartrate manufacturer
New Products
Trans-methyl 4-aminocyclohexane- carboxylate HCl 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-Iodophenylacetic acid (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 3-Bromobenzaldehyde, 95% 2-Naphthol, 98% Cysteamine hydrochloride, 98% Copper(II) bromide, 98% 1-Chloro-2,4-difluorobenzene,98% Dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 95% L-Glycine methyl ester.HCl Fmoc-L-Tyr(tBu)-OH Calcium Alphaketoglutarate* H-Ser(t-Bu)-Ser(t-Bu)-Gly-OH Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Ser(Ψ(Me,Me)pro-OH Triphosgene 5-Cyanophthalide 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
![6-Methyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/88965-00-8.gif)
![Methyl 6-methyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-acetate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/258273-50-6.gif)
You may like
-
 99294-93-6 98%View Details
99294-93-6 98%View Details
99294-93-6 -
 Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 99%View Details
Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 99%View Details
99294-93-6 -
 99294-93-6 Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 99%View Details
99294-93-6 Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 99%View Details
99294-93-6 -
 Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 99294-93-6 99%View Details
Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 99294-93-6 99%View Details
99294-93-6 -
 Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 99294-93-6 98%View Details
Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 99294-93-6 98%View Details
99294-93-6 -
 Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 98%View Details
Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 98%View Details
99294-93-6 -
 99294-93-6 98%View Details
99294-93-6 98%View Details
99294-93-6 -
 99294-93-6 Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 98%View Details
99294-93-6 Zolpidem L-(+)-hemitartrate 98%View Details
99294-93-6
