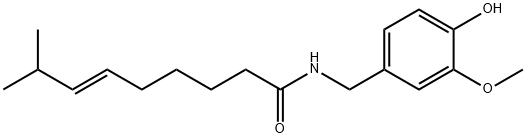
(Z)-CAPSAICIN
- CAS NO.:25775-90-0
- Empirical Formula: C18H27NO3
- Molecular Weight: 305.41
- MDL number: MFCD00209942
- EINECS: 636-760-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
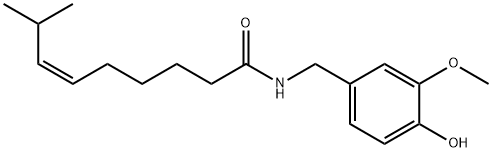
What is (Z)-CAPSAICIN?
Absorption
Zucapsaicin displays low systemic absorption and localizes at the area of application. In animal studies, systemic absorption is 0.075% .
Toxicity
Most common adverse effects involved application site reactions such as transient burning and warm sensation. Other adverse effects observed in clinical trials are eye irritation, arthralgia, aggravated osteoarthritis, burning sensation, headache, cough and sneezing. Oral LD50 in mouse is >87.5 mg/kg in male and <60 mg/kg in females. Oral LD50 in rats is >90 mg/kg in males and >60 mg/kg in females .
Description
Zucapsaicin is a topical analgesic that was approved in Canada in July 2010 for use in conjunction with oral COX-2 inhibitors or NSAIDs to relieve severe pain in adults with osteoarthritis of the knee. Zucapsaicin is the cis-isomer of the natural product capsaicin. Capsaicin is available without a prescription in creams, lotions, and patches for the treatment of neuropathic and musculoskeletal pain. Zucapsaicin is available as a 0.075% by weight cream. The advantages of zucapsaicin compared with capsaicin are reported to be a lesser degree of local irritation (stinging, burning, erythema) in patients and a greater degree of efficacy in preclinical animal models of pain. The analgesic action of zucapsaicin and capsaicin is mediated through the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channel.
Originator
E Merck AG (Germany)
The Uses of (Z)-CAPSAICIN
(Z)-CAPSAICIN is used as a tool in neurobiological research. Prototype vanilloid receptor agonist.
Indications
Indicated to be used in conjunction with oral COX-2 inhibitors or NSAIDs for the relief of severe pain in adult patients with osteoarthritis of the knee, not controlled with oral COX-2 inhibitors or NSAIDs alone, for a duration of no more than three months.
Background
Zucapsaicin, the cis-isomer of capsaicin, is a topical analgesic used to treat osteoarthritis of the knee and other neuropathic pain. It is a modulator of transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV-1), also known as the vanilloid or capsaicin receptor 1, that reduces pain and improves articular functions. Zucapsaicin has also been evaluated for the management of several conditions manifested by chronic nerve pain. These conditions include herpes simplex (HSV) infections, cluster headaches, migraine, and osteoarthritis of the knee. Zucapsaicin was approved by the Health Canada in 2010 as topical cream marketed under the brand name Zuacta but currently not FDA-approved.
Definition
ChEBI: Zucapsaicin is a member of phenols and a member of methoxybenzenes.
brand name
Civanex
Pharmacokinetics
Zucapsaicin mediates an antinociceptive action via acting as an agonist at TRPV1. TRPV1 play an important physiological role of transducing chemical, mechanical and thermal stimuli as well as pain transduction, and participate in pain modulation and perception. They are mainly distributed in C sensory nerve fibers as well as A? fibers to transmit sensory information involving inflammatory and neuropathic pain, and activation of these channels releasesomatostatin, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and other neuropeptides (neurokinin A, kassinin), leading to neurogenic inflammation . Zucapsaicin is also reported to affect the peptidergic afferent neurons via a desensitization mechanism to decrease the levels of dorsal root ganglia and sciatic calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P (SP) .
Clinical Use
Zucapsaicin, the cis-isomer of the natural product capsaicin, is a topical analgesic that was initially developed by Winston Pharmaceuticals and approved in Canada in July 2010 for the treatment of severe pain in adults with osteoarthritis of the knee. The advantages of zucapsaicin compared with naturally-occurring capsaicin are reported to be a lesser degree of local irritation (stinging, burning, erythema) in patients and a greater degree of efficacy in preclinical animal models of pain. The analgesic action of both zucapsaicin and capsaicin is mediated through the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channel, a ligand-gated ion channel expressed in the spinal cord, brain, and localized on neurons in sensory projections to the skin, muscles, joints, and gut.
Synthesis
The scale preparation of zucapsaicin likely parallels the original approach described by Gannett and co-workers involving the coupling of vanillylamine with (Z)-8-methylnon-6-enoyl chloride. 216 Orito and co-workers elaborated this original approach in an effort to prepare both capsaicin and zucapsaicin on gram-scale, and this route is described in the scheme.

Commercial 6-bromohexanoic acid (285) was activated as the Wittig salt prior to condensation with isobutylaldehyde in the presence of strong base to generate an 11:1 ratio of E/Z-olefinic acids favoring Z-isomer 286. Removal of the minor isomer was easily achieved by short-path distillation.217 Interestingly, the authors reported that facile olefin isomerization of 286 occurred upon exposure to nitric acid at elevated temperatures, converting 286 to the corresponding E-isomer. Recrystallization provided the product on multi-gram scale in 77% yield, representing a possible scale production method for capsaicin. For the preparation of zucapsaicin, acid 286 was converted the acid chloride via thionyl chloride followed by immediate condensation with commercially available vanillylamine (287). Two recrystallization steps were subsequently employed to produce gram-scale amounts of zucapsaicin (XXVI) in 66% yield overall for the two-step process.
Metabolism
In vitro studies demonstrates weak to moderate inhibitiory effects on various cytochrome P450 enzymes, although not clinically significant due to low systemic absorption.
Properties of (Z)-CAPSAICIN
| Melting point: | 70 °C |
| Boiling point: | 511.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.041±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 9.76±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
Safety information for (Z)-CAPSAICIN
Computed Descriptors for (Z)-CAPSAICIN
(Z)-CAPSAICIN manufacturer
BDR Pharmaceuticals International Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 25775-90-0 Zucapsaicin 98%View Details
25775-90-0 Zucapsaicin 98%View Details
25775-90-0 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1